
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (10): 1287-1298.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.10.011
方馨悦1( ), 石岚1, 夏思易1, 王佳璇1, 吴英理2(
), 石岚1, 夏思易1, 王佳璇1, 吴英理2( ), 何珂骏3(
), 何珂骏3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-30
接受日期:2024-06-04
出版日期:2024-10-28
发布日期:2024-10-28
通讯作者:
吴英理,电子信箱:wuyingli@shsmu.edu.cn。作者简介:方馨悦(2000—),女,本科生;电子信箱:xinyue.fang@qq.com。
基金资助:
FANG Xinyue1( ), SHI Lan1, XIA Siyi1, WANG Jiaxuan1, WU Yingli2(
), SHI Lan1, XIA Siyi1, WANG Jiaxuan1, WU Yingli2( ), HE Kejun3(
), HE Kejun3( )
)
Received:2024-04-30
Accepted:2024-06-04
Online:2024-10-28
Published:2024-10-28
Contact:
WU Yingli, E-mail: wuyingli@shsmu.edu.cn.Supported by:摘要:
混合谱系白血病(mixed lineage leukemia,MLL)基因重排(MLL-rearranged,MLL-r)引起的急性白血病亚型侵袭性高且预后不良,缺少特异性治疗手段。MLL蛋白具有组蛋白甲基转移酶活性,在胚胎发育和正常造血中必不可少,可通过功能结构域与多种蛋白质相互作用,形成大分子复合体,并通过表观修饰调节下游靶基因的表达。MLL-r转录形成MLL融合蛋白(MLL fusion protein,MLL-FP),其中MLL蛋白的C端被融合伙伴蛋白所取代。现已发现超过100种融合伙伴蛋白。分子机制研究发现,Menin蛋白是MLL-FP致白血病必不可少的辅助因子,通过与MLL-N端特定区域相互作用形成关键致病复合体,导致特定靶基因的异常表达。这为Menin-MLL相互作用抑制剂的开发提供了理论依据。截至目前,多种小分子化合物被发现能抑制Menin-MLL相互作用,包括噻吩嘧啶类、哌啶类、嘧啶类和大环拟肽类。至少7种以此为原型开发的药物进入临床试验,部分已在安全性、耐受性和疗效方面取得乐观的初步数据。该文从MLL蛋白的结构功能、MLL-r导致白血病的机制出发,对Menin-MLL蛋白相互作用抑制剂在MLL-r白血病中应用的研究进展进行综述。
中图分类号:
方馨悦, 石岚, 夏思易, 王佳璇, 吴英理, 何珂骏. Menin-MLL蛋白相互作用及相关抑制剂在MLL基因重排白血病中应用的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(10): 1287-1298.
FANG Xinyue, SHI Lan, XIA Siyi, WANG Jiaxuan, WU Yingli, HE Kejun. Research progress in Menin-MLL interaction and its inhibitors in MLL-rearranged leukemia[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(10): 1287-1298.
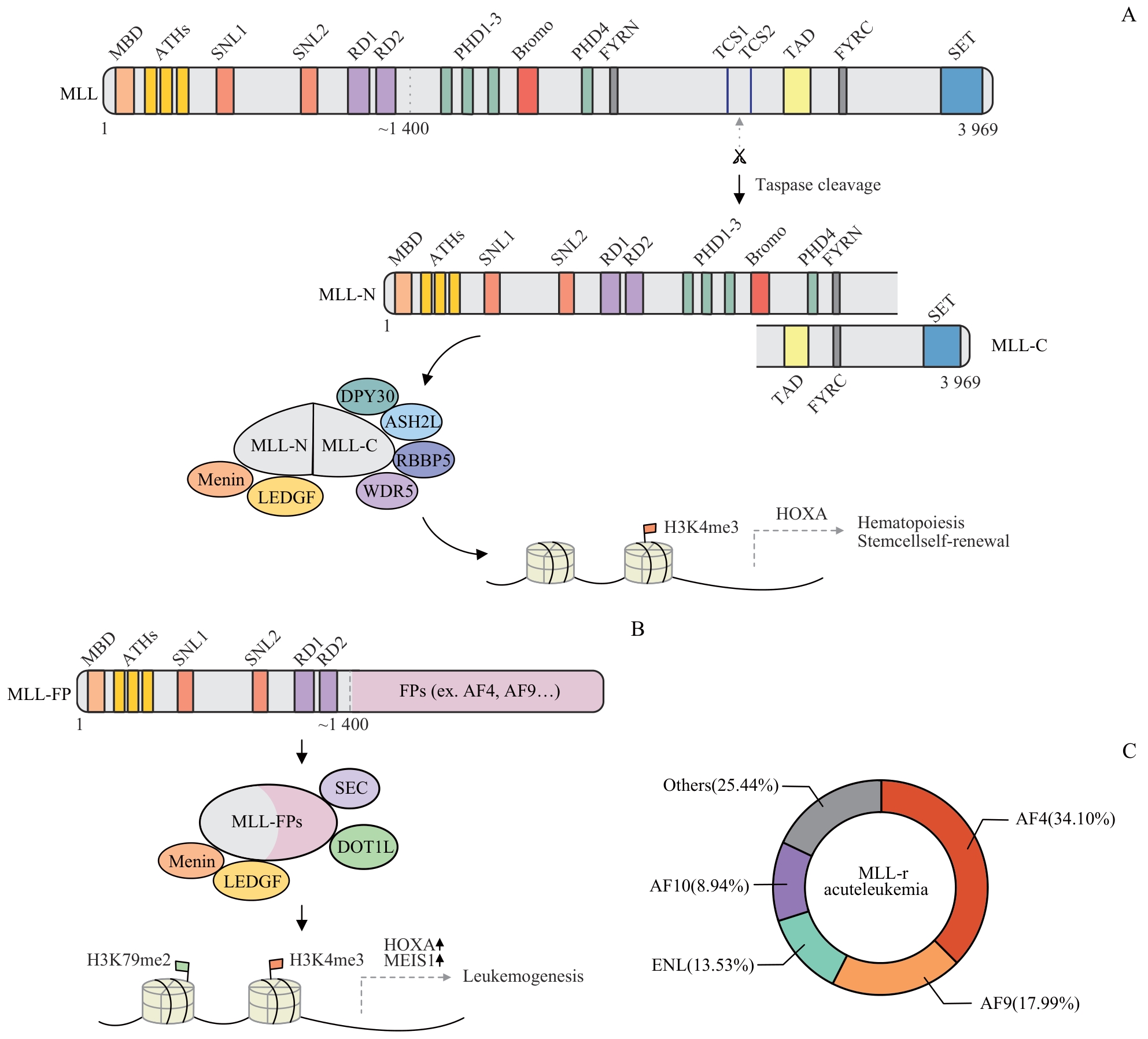
图1 MLL和MLL-FP的结构功能以及融合伙伴蛋白在MLL-r白血病中的比例Note: A. Functional domains of MLL protein, and structure and functions of MLL complex. The precursor MLL protein was cleaved by taspase 1, generating MLL-N and MLL-C, which then associated via FYRN and FYRC to be activated. B. Structure and leukemogenesis of MLL-FPs. Translocation occurred in the breakpoint cluster region. C. Proportions of fusion protein partners in MLL-r leukemia.
Fig 1 Structure and functions of MLL and MLL-FPs, as well as the proportion of fusion protein partners in MLL-r leukemia
| Drug | Reference | Phase | Designment | Status/ Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Revumenib (SNDX-5613) | NCT04065399 (AUGMENT-101) | Ⅰ | AML, ALL | n=94, discontinuation: 6.4% |
| Ⅱ | r/r AML with MLL-r, r/r ALL with MLL-r, r/r AML with mNPM1 | n=57, ORR=63.2%, CRc=43.9% (r/r AML with MLL-r and r/r ALL with MLL-r); n=13, ORR=46.2%, CRc=38.5% (pediatric r/r AML with MLL-r and r/r ALL with MLL-r) | ||
NCT05360160 (SAVE) | Ⅰ/Ⅱ | r/r AML with MLL-r/mNPM1/NUP98-r: ASTX727/venetoclax | n=9, ORR=100%, CRc=78% | |
NCT05326516 (AUGMENT-102) | Ⅰ | r/r AML, ALL with MLL-r/mNPM1/NUP98-r: Chemo Regimen 1, Chemo Regimen 2 | n=15, CRc=33% (Chemo Regimen 2) | |
NCT03013998 (BEAT-AML) | Ⅰ | AML with MLL-r/mNPM1, age≥60 years: venetoclax/azacitidine | n=13, CRc=100% | |
| ACTRN12621000439842 | Ⅰ/Ⅱ | MRD+ AML with MLL-r/mNPM1 | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT05886049 | Ⅰ | AML with MLL-r/mNPM1: 7+3 chemo | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT06222580 | Ⅰ | r/r AML with MLL-r/mNPM1 FLT3 co-mutation: gilteritinib | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT06226571 | Ⅰ | AML with MLL-r/mNPM1/NUP98-r: intensive chemotherapy | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT05761171 | Ⅱ | Pediatric r/r ALL, AML with MLL-r: fludarabine | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT06177067 | Ⅰ | Pediatric or young adult r/r AML with MLL-r/mNPM1/NUP98-r: venetoclax/azacitidine | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT05918913 | Expanded | r/r acute leukemia with genetic alterations associated with HOXA overexpression | Recruiting, unavailable | |
Ziftomenib (KO-539) | NCT04067336 (KOMET-001) | Ⅰ | r/r AML with MLL-r/mNPM1 | n=20, ORR=45%, CRc=40% |
| Ⅱ | r/r AML with mNPM1 | |||
NCT05735184 (KOMET-007) | Ⅰ | AMLwith MLL-r/mNPM1: venetoclax & azacitidin, venetoclax, 7+3 chemo | n=9, ORR=78%, CRc=67% (venetoclax & azacitidin); n=5, CRc=100% (7+3 chemo) | |
NCT06001788 (KOMET-008) | Ⅰ | r/r AML with MLL-r/mNPM1: FLAG-IDA, LD-AraC + gilteritinib (FLT3 co-mutation) | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT05848687 | Ⅰ/Ⅱ | Infant ALL | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT05738538 | Expanded | ALL with appropriate mutations, or AML with mNPM1 | Recruiting, unavailable | |
Icovamenib (BMF-219) | NCT05153330 (COVALENT-101) | Ⅰ | r/r AML, ALL, DLBCL, MM, CLL | n=5, CRc=40% (r/r AML) |
Emilumenib (DS-1594) | NCT04752163 | Ⅰ | r/r AML, ALL | Completed, unavailable |
| Ⅱ | r/r AML with MLL-r/mNPM1: venetoclax & azacitidine. r/r ALL with MLL-r: mini-HCVD | |||
| DSP-5336 | NCT04988555 | Ⅰ | r/r AML, ALL | n=6, CRc=33.3% |
| Ⅱ | r/r AML with MLLr, an r/r AML with mNPM1 | |||
| JNJ-75276617 | NCT04811560 | Ⅰ/Ⅱ | r/r AML, ALL with MLL-r/mNPM1 | n=41, CRc=29.2% |
| NCT05453903 | Ⅰ | AML with MLL-r/mNPM1: venetoclax, azacitidine or 7+3 chemo | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| BN-104 | NCT06052813 | Ⅰ/Ⅱ | r/r AML, ALL | Recruiting, unavailable |
表1 Menin-MLL抑制剂药物在血液肿瘤中的现行临床试验
Tab 1 Ongoing clinical trials of Menin-MLL inhibitory drugs in hematologic malignancies
| Drug | Reference | Phase | Designment | Status/ Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Revumenib (SNDX-5613) | NCT04065399 (AUGMENT-101) | Ⅰ | AML, ALL | n=94, discontinuation: 6.4% |
| Ⅱ | r/r AML with MLL-r, r/r ALL with MLL-r, r/r AML with mNPM1 | n=57, ORR=63.2%, CRc=43.9% (r/r AML with MLL-r and r/r ALL with MLL-r); n=13, ORR=46.2%, CRc=38.5% (pediatric r/r AML with MLL-r and r/r ALL with MLL-r) | ||
NCT05360160 (SAVE) | Ⅰ/Ⅱ | r/r AML with MLL-r/mNPM1/NUP98-r: ASTX727/venetoclax | n=9, ORR=100%, CRc=78% | |
NCT05326516 (AUGMENT-102) | Ⅰ | r/r AML, ALL with MLL-r/mNPM1/NUP98-r: Chemo Regimen 1, Chemo Regimen 2 | n=15, CRc=33% (Chemo Regimen 2) | |
NCT03013998 (BEAT-AML) | Ⅰ | AML with MLL-r/mNPM1, age≥60 years: venetoclax/azacitidine | n=13, CRc=100% | |
| ACTRN12621000439842 | Ⅰ/Ⅱ | MRD+ AML with MLL-r/mNPM1 | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT05886049 | Ⅰ | AML with MLL-r/mNPM1: 7+3 chemo | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT06222580 | Ⅰ | r/r AML with MLL-r/mNPM1 FLT3 co-mutation: gilteritinib | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT06226571 | Ⅰ | AML with MLL-r/mNPM1/NUP98-r: intensive chemotherapy | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT05761171 | Ⅱ | Pediatric r/r ALL, AML with MLL-r: fludarabine | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT06177067 | Ⅰ | Pediatric or young adult r/r AML with MLL-r/mNPM1/NUP98-r: venetoclax/azacitidine | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT05918913 | Expanded | r/r acute leukemia with genetic alterations associated with HOXA overexpression | Recruiting, unavailable | |
Ziftomenib (KO-539) | NCT04067336 (KOMET-001) | Ⅰ | r/r AML with MLL-r/mNPM1 | n=20, ORR=45%, CRc=40% |
| Ⅱ | r/r AML with mNPM1 | |||
NCT05735184 (KOMET-007) | Ⅰ | AMLwith MLL-r/mNPM1: venetoclax & azacitidin, venetoclax, 7+3 chemo | n=9, ORR=78%, CRc=67% (venetoclax & azacitidin); n=5, CRc=100% (7+3 chemo) | |
NCT06001788 (KOMET-008) | Ⅰ | r/r AML with MLL-r/mNPM1: FLAG-IDA, LD-AraC + gilteritinib (FLT3 co-mutation) | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT05848687 | Ⅰ/Ⅱ | Infant ALL | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| NCT05738538 | Expanded | ALL with appropriate mutations, or AML with mNPM1 | Recruiting, unavailable | |
Icovamenib (BMF-219) | NCT05153330 (COVALENT-101) | Ⅰ | r/r AML, ALL, DLBCL, MM, CLL | n=5, CRc=40% (r/r AML) |
Emilumenib (DS-1594) | NCT04752163 | Ⅰ | r/r AML, ALL | Completed, unavailable |
| Ⅱ | r/r AML with MLL-r/mNPM1: venetoclax & azacitidine. r/r ALL with MLL-r: mini-HCVD | |||
| DSP-5336 | NCT04988555 | Ⅰ | r/r AML, ALL | n=6, CRc=33.3% |
| Ⅱ | r/r AML with MLLr, an r/r AML with mNPM1 | |||
| JNJ-75276617 | NCT04811560 | Ⅰ/Ⅱ | r/r AML, ALL with MLL-r/mNPM1 | n=41, CRc=29.2% |
| NCT05453903 | Ⅰ | AML with MLL-r/mNPM1: venetoclax, azacitidine or 7+3 chemo | Recruiting, unavailable | |
| BN-104 | NCT06052813 | Ⅰ/Ⅱ | r/r AML, ALL | Recruiting, unavailable |
| 1 | FORGIONE M O, MCCLURE B J, EADIE L N, et al. KMT2A rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: unravelling the genomic complexity and heterogeneity of this high-risk disease[J]. Cancer Lett, 2020, 469: 410-418. |
| 2 | CHAER F E, KENG M, BALLEN K K. MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia[J]. Curr Hematol Malig Rep, 2020, 15(2): 83-89. |
| 3 | BRANDI M L, AGARWAL S K, PERRIER N D, et al. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1: latest insights[J]. Endocr Rev, 2021, 42(2): 133-170. |
| 4 | ARYAL S, ZHANG Y, WREN S, et al. Molecular regulators of HOXA9 in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. FEBS J, 2023, 290(2): 321-339. |
| 5 | BAI H R, ZHANG S Q, LEI H, et al. Menin-MLL protein-protein interaction inhibitors: a patent review (2014-2021)[J]. Expert Opin Ther Pat, 2022, 32(5): 507-522. |
| 6 | SUGEEDHA J, GAUTAM J, TYAGI S. SET1/MLL family of proteins: functions beyond histone methylation[J]. Epigenetics, 2021, 16(5): 469-487. |
| 7 | LI X, SONG Y C. Structure, function and inhibition of critical protein-protein interactions involving mixed lineage leukemia 1 and its fusion oncoproteins[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2021, 14(1): 56. |
| 8 | MEYER C, LARGHERO P, LOPES B A, et al. The KMT2A/MLL consensus gene structure: a comprehensive update for research and diagnostic implications[J]. Leukemia, 2024, 38(6): 1403-1406. |
| 9 | ANTUNES E T B, OTTERSBACH K. The MLL/SET family and haematopoiesis[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech, 2020, 1863(8): 194579. |
| 10 | KHAN I, AMIN M A, EKLUND E A, et al. Regulation of HOX gene expression in AML[J]. Blood Cancer J, 2024, 14(1): 42. |
| 11 | JAMBHEKAR A, DHALL A, SHI Y. Roles and regulation of histone methylation in animal development[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2019, 20(10): 625-641. |
| 12 | YANG L, JIN M L, JEONG K W. Histone H3K4 methyltransferases as targets for drug-resistant cancers[J]. Biology, 2021, 10(7): 581. |
| 13 | COWELL I G, AUSTIN C A. DNA fragility at the KMT2A/MLL locus: insights from old and new technologies[J]. Open Biol, 2023, 13(1): 220232. |
| 14 | JUUL-DAM K L, SHUKLA N N, COOPER T M, et al. Therapeutic targeting in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia with aberrant HOX/MEIS1 expression[J]. Eur J Med Genet, 2023, 66(12): 104869. |
| 15 | MEYER C, LARGHERO P, ALMEIDA LOPES B, et al. The KMT2A recombinome of acute leukemias in 2023[J]. Leukemia, 2023, 37(5): 988-1005. |
| 16 | TAKAHASHI S, YOKOYAMA A. The molecular functions of common and atypical MLL fusion protein complexes[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech, 2020, 1863(7): 194548. |
| 17 | FUJINAGA K, HUANG F, PETERLIN B M. P-TEFb: the master regulator of transcription elongation[J]. Mol Cell, 2023, 83(3): 393-403. |
| 18 | YUAN Y N, DU L, TAN R L, et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluations of DOT1L peptide mimetics targeting the protein-protein interactions between DOT1L and MLL-AF9/MLL-ENL[J]. J Med Chem, 2022, 65(11): 7770-7785. |
| 19 | SO C W, LIN M, AYTON P M, et al. Dimerization contributes to oncogenic activation of MLL chimeras in acute leukemias[J]. Cancer Cell, 2003, 4(2): 99-110. |
| 20 | KUNDU A, KOWARZ E, MARSCHALEK R. The role of reciprocal fusions in MLL-r acute leukemia: studying the chromosomal translocation t(6;11)[J]. Oncogene, 2021, 40(40): 5902-5912. |
| 21 | CHEN B R, DESHPANDE A, BARBOSA K, et al. A JAK/STAT-mediated inflammatory signaling cascade drives oncogenesis in AF10-rearranged AML[J]. Blood, 2021, 137(24): 3403-3415. |
| 22 | VERSCHUUR A V D, KOK A S M, MORSINK F H M, et al. Diagnostic utility of menin immunohistochemistry in patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 syndrome[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2023, 47(7): 785-791. |
| 23 | BIANCANIELLO C, D'ARGENIO A, GIORDANO D, et al. Investigating the effects of amino acid variations in human menin[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(5): 1747. |
| 24 | LEI H, ZHANG S Q, FAN S, et al. Recent progress of small molecule menin-MLL interaction inhibitors as therapeutic agents for acute leukemia[J]. J Med Chem, 2021, 64(21): 15519-15533. |
| 25 | KÜHN M W M, GANSER A. The menin story in acute myeloid leukaemia: the road to success[J]. Br J Haematol, 2024. DOI: 10. 1111/bjh.19508. |
| 26 | ISSA G C, RAVANDI F, DINARDO C D, et al. Therapeutic implications of menin inhibition in acute leukemias[J]. Leukemia, 2021, 35(9): 2482-2495. |
| 27 | THOMAS X. Small molecule menin inhibitors: novel therapeutic agents targeting acute myeloid leukemia with KMT2A rearrangement or NPM1 mutation[J]. Oncol Ther, 2024, 12(1): 57-72. |
| 28 | GREMBECKA J, HE S H, SHI A B, et al. Menin-MLL inhibitors reverse oncogenic activity of MLL fusion proteins in leukemia[J]. Nat Chem Biol, 2012, 8(3): 277-284. |
| 29 | KÜHN M W, SONG E, FENG Z H, et al. Targeting chromatin regulators inhibits leukemogenic gene expression in NPM1 mutant leukemia[J]. Cancer Discov, 2016, 6(10): 1166-1181. |
| 30 | RASOULI M, BLAIR H, TROESTER S, et al. The MLL-menin interaction is a therapeutic vulnerability in NUP98-rearranged AML[J]. Hemasphere, 2023, 7(8): e935. |
| 31 | SHI A B, MURAI M J, HE S H, et al. Structural insights into inhibition of the bivalent menin-MLL interaction by small molecules in leukemia[J]. Blood, 2012, 120(23): 4461-4469. |
| 32 | BORKIN D, HE S H, MIAO H Z, et al. Pharmacologic inhibition of the Menin-MLL interaction blocks progression of MLL leukemia in vivo[J]. Cancer Cell, 2015, 27(4): 589-602. |
| 33 | BORKIN D, POLLOCK J, KEMPINSKA K, et al. Property focused structure-based optimization of small molecule inhibitors of the protein-protein interaction between menin and mixed lineage leukemia (MLL)[J]. J Med Chem, 2016, 59(3): 892-913. |
| 34 | BORKIN D, KLOSSOWSKI S, POLLOCK J, et al. Complexity of blocking bivalent protein-protein interactions: development of a highly potent inhibitor of the menin-mixed-lineage leukemia interaction[J]. J Med Chem, 2018, 61(11): 4832-4850. |
| 35 | BRZEZINKA K, NEVEDOMSKAYA E, LESCHE R, et al. Characterization of the menin-MLL interaction as therapeutic cancer target[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(1): 201. |
| 36 | KLOSSOWSKI S, MIAO H Z, KEMPINSKA K, et al. Menin inhibitor MI-3454 induces remission in MLL1-rearranged and NPM1-mutated models of leukemia[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130(2): 981-997. |
| 37 | ERBA H P, FATHI A T, ISSA G C, et al. Update on a phase 1/2 first-in-human study of the menin-KMT2A (MLL) inhibitor ziftomenib (KO-539) in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Blood, 2022, 140(Supplement 1): 153-156. |
| 38 | HE S H, SENTER T J, POLLOCK J, et al. High-affinity small-molecule inhibitors of the menin-mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) interaction closely mimic a natural protein-protein interaction[J]. J Med Chem, 2014, 57(4): 1543-1556. |
| 39 | XU S L, AGUILAR A, XU T F, et al. Design of the first-in-class, highly potent irreversible inhibitor targeting the menin-MLL protein-protein interaction[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2018, 57(6): 1601-1605. |
| 40 | AGUILAR A, ZHENG K, XU T F, et al. Structure-based discovery of M-89 as a highly potent inhibitor of the menin-mixed lineage leukemia (menin-MLL) protein-protein interaction[J]. J Med Chem, 2019, 62(13): 6015-6034. |
| 41 | XU S L, AGUILAR A, HUANG L Y, et al. Discovery of M-808 as a highly potent, covalent, small-molecule inhibitor of the menin-MLL interaction with strong in vivo antitumor activity[J]. J Med Chem, 2020, 63(9): 4997-5010. |
| 42 | ZHANG M, AGUILAR A, XU S L, et al. Discovery of M-1121 as an orally active covalent inhibitor of menin-MLL interaction capable of achieving complete and long-lasting tumor regression[J]. J Med Chem, 2021, 64(14): 10333-10349. |
| 43 | KRIVTSOV A V, EVANS K, GADREY J Y, et al. A menin-MLL inhibitor induces specific chromatin changes and eradicates disease in models of MLL-rearranged leukemia[J]. Cancer Cell, 2019, 36(6): 660-673.e11. |
| 44 | ISSA G C, ALDOSS I, DIPERSIO J, et al. The menin inhibitor revumenib in KMT2A-rearranged or NPM1-mutant leukaemia[J]. Nature, 2023, 615(7954): 920-924. |
| 45 | FORTUNA P, LINHARES B M, PUROHIT T, et al. Covalent and noncovalent constraints yield a figure eight-like conformation of a peptide inhibiting the menin-MLL interaction[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2020, 207: 112748. |
| 46 | ZHOU H B, LIU L, HUANG J, et al. Structure-based design of high-affinity macrocyclic peptidomimetics to block the menin-mixed lineage leukemia 1 (MLL1) protein-protein interaction[J]. J Med Chem, 2013, 56(3): 1113-1123. |
| 47 | MCGEEHAN J. A first-in-class Menin-MLL1 antagonist for the treatment of MLL-r and NPM1 mutant leukemias[C]//Proceedings of the 111th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR). Philadelphia (PA): AACR, 2020: Abstract DDT01-01. |
| 48 | ALDOSS I, ISSA G C, THIRMAN M, et al. Revumenib monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory KMT2Ar acute leukemia: topline efficacy and safety results from the pivotal augment-101 phase 2 study[J]. Blood, 2023, 142(Supplement 2): LBA-5-LBA-5. |
| 49 | ZWAAN C M, SHUKLA N, KARRAS N, et al. Pivotal phase 2 results of AUGMENT-101 for revumenib in KMT2Ar acute leukemia: pediatric experience[C]//2024 American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology (ASPHO). Seattle, Washington: ASPHO, 2024: Abstract 2002. |
| 50 | PERNER F, STEIN E M, WENGE D V, et al. MEN1 mutations mediate clinical resistance to menin inhibition[J]. Nature, 2023, 615(7954): 913-919. |
| 51 | MAURO G. Early data with revumenib combo show 100% ORR in relapsed/refractory AML[EB/OL]. (2023-12-09)[2024-04-30]. https://www.cancernetwork.com/view/early-data-with-revumenib-combo-show-100-orr-in-relapsed-refractory-aml. |
| 52 | Syndax. Syndax Investor Meeting & American Society of Hematology Meeting[EB/OL]. (2023-12-11)[2024-04-30]. https://ir.syndax.com/static-files/aaa432c9-146c-4f4c-9a43-11321505a6b5. |
| 53 | ERBA H, WANG E, ISSA G, et al. AML-475 activity, tolerability, and resistance profile of the menin inhibitor ziftomenib in adults with relapsed/refractory NPM1-mutated AML[J]. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk, 2023, 23: S304-S305. |
| 54 | RAUSCH J, DZAMA M M, DOLGIKH N, et al. Menin inhibitor ziftomenib (KO-539) synergizes with drugs targeting chromatin regulation or apoptosis and sensitizes acute myeloid leukemia with MLL rearrangement or NPM1 mutation to venetoclax[J]. Haematologica, 2023, 108(10): 2837-2843. |
| 55 | Kura Oncology. Developing precision medicines for the treatment of cancer[EB/OL]. (2024-01-30) [2024-04-30]. https://ir.kuraoncology.com/static-files/29767eca-422c-42a3-9d84-0c6d9c2a a96d. |
| 56 | SOMANATH P, LU D, LAW B, et al. Preclinical activity of irreversible Menin inhibitor, BMF-219, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2022, 40(16_suppl): 7541. |
| 57 | RAVANDI-KASHANI F, KISHTAGARI A, CARRAWAY H, et al. P587: COVALENT-101: a phase 1 study of BMF-219, a novel oral irreversible menin inhibitor, in patients with relapsed/refractory acute leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and multiple myeloma[J]. Hemasphere, 2022, 6: 486-487. |
| 58 | MOMIN A A, RUGHWANI T, TANATAWEETHUM N, et al. Abstract 3314: molecular profiling of covalent menin inhibitor, BMF-219, in KRAS-mutated solid tumors[J]. Cancer Res, 2024, 84(6_ Supplement): 3314. |
| 59 | SOMANATH P, MOURYA S, LI W Q, et al. 113-LB: oral menin inhibitor, BMF-219, displays a significant and durable reduction in HbA1c in a type 2 diabetes mellitus rat model[J]. Diabetes, 2022, 71(Supplement_1): 113-LB. |
| 60 | LANCET J, RAVANDI F, MONTESINOS P, et al. Covalent menin inhibitor BMF-219 in patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) acute leukemia (AL): preliminary phase 1 data from the COVALENT-101 study[J]. Blood, 2023, 142(Supplement 1): 2916. |
| 61 | NUMATA M, HAGINOYA N, SHIROISHI M, et al. A novel Menin-MLL1 inhibitor, DS-1594a, prevents the progression of acute leukemia with rearranged MLL1 or mutated NPM1[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2023, 23(1): 36. |
| 62 | CIAURRO V, KONOPLEVA M Y, DAVER N, et al. Synergistic growth inhibition of NPM1 mutant AML PDX by combined therapy with BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax (ABT-199) and menin inhibitor DS-1594b in vivo[J]. Blood, 2023, 142(Supplement 1): 4169. |
| 63 | EGUCHI K, SHIMIZU T, KATO D, et al. Preclinical evaluation of a novel orally bioavailable menin-MLL interaction inhibitor, DSP-5336, for the treatment of acute leukemia patients with MLL-rearrangement or NPM1 mutation[J]. Blood, 2021, 138(Supplement 1): 3339. |
| 64 | DAVER N, ZEIDNER J F, YUDA J, et al. Phase 1/2 first-in-human study of the menin-MLL inhibitor DSP-5336 in patients with relapsed or refractory acute leukemia[J]. Blood, 2023, 142(Supplement 1): 2911. |
| 65 | KWON M C, QUEROLLE O, DAI X D, et al. Pharmacological characterization of JNJ-75276617, a menin-KMT2A inhibitor, as targeted treatment for KMT2A-altered and NPM1-mutant acute leukemia[J]. Blood, 2022, 140(Supplement 1): 5928-5929. |
| 66 | JABBOUR E, SEARLE E, ABDUL-HAY M, et al. A first-in-human phase 1 study of the menin-KMT2A (MLL1) inhibitor JNJ-75276617 in adult patients with relapsed/refractory acute leukemia harboring KMT2A or NPM1 alterations[J]. Blood, 2023, 142(Supplement 1): 57. |
| 67 | LIBBRECHT C, XIE H M, KINGSLEY M C, et al. Menin is necessary for long term maintenance of meningioma-1 driven leukemia[J]. Leukemia, 2021, 35(5): 1405-1417. |
| [1] | 禹恺, 帅哲玮, 黄洪军, 罗艳. 小胶质细胞在中枢神经系统炎症性疾病中的作用和机制研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(5): 630-638. |
| [2] | 罗文, 吕明君, 张珍, 张雪, 姚志荣. 自噬在皮肤黑色素瘤中的双重效应及耐药中的作用研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 233-240. |
| [3] | 唐珺倩, 李本尚. 儿童高危细胞遗传学B系急性淋巴细胞白血病治疗新进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1390-1399. |
| [4] | 张勇, 李伟宏, 程志鹏, 王斌, 王思珩, 王毓斌. 受体相互作用蛋白激酶1调节癌症进展和免疫反应的研究现状[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(6): 788-794. |
| [5] | 徐文晖, 杨畅, 李瑞卿, 卞京, 李夏伊, 郑磊贞. 干扰素调节因子3促结直肠癌细胞增殖与侵袭相关探索[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(3): 301-311. |
| [6] | 丁艳玲, 李杰, 袁军, 李燕. 慢性淋巴细胞白血病靶向治疗的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 264-270. |
| [7] | 唐思洁, 糜坚青. 抗体药物偶联物在血液肿瘤中的临床应用研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(12): 1607-1614. |
| [8] | 周婉桢, 滕银成. 非经典Wnt通路在卵巢癌中的作用与潜在治疗意义研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(8): 1056-1063. |
| [9] | 梅艳青, 韩雨洁, 翁文筠, 张蕾, 唐玉杰. 靶向抑制CDK12/13在高级别胶质瘤中的体外治疗效果和作用分子机制探究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 545-559. |
| [10] | 徐瀛濂, 田静, 张翔, 赵顺英. 气道上皮细胞在哮喘发病机制中的作用研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 619-623. |
| [11] | 魏兰懿, 薛晓川, 陈君君, 杨全军, 王梦月, 韩永龙. 骨肉瘤免疫微环境中肿瘤相关巨噬细胞及其靶向治疗的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 624-630. |
| [12] | 刘铁鑫, 林俊卿, 郑宪友. 靶向亚细胞结构治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(2): 230-236. |
| [13] | 秦雅含, 张珂, 张梦雨, 沈洁, 彭美玉. MDSC靶向免疫治疗胰腺癌的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(10): 1317-1323. |
| [14] | 韩永琪, 韩达, 閤谦, 姬丁坤, 谭蔚泓. 核酸适体药物偶联物——肿瘤精准治疗新风向[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(9): 1176-1181. |
| [15] | 李若楠, 陈小科, 许元元, 谭强. ⅠB~ⅢA期非小细胞肺癌患者术后辅助靶向治疗研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(11): 1612-1619. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||