
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 145-160.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.02.001
• 论著 · 基础研究 • 下一篇
邓青松1,2,3( ), 张长青1,2,3, 陶诗聪1,2(
), 张长青1,2,3, 陶诗聪1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-07
接受日期:2023-11-30
出版日期:2024-02-28
发布日期:2024-02-28
通讯作者:
陶诗聪,电子信箱:sctao@shsmu.edu.cn。作者简介:邓青松(1998—),男,硕士生;电子信箱:dqs1229@163.com。
基金资助:
DENG Qingsong1,2,3( ), ZHANG Changqing1,2,3, TAO Shicong1,2(
), ZHANG Changqing1,2,3, TAO Shicong1,2( )
)
Received:2023-08-07
Accepted:2023-11-30
Online:2024-02-28
Published:2024-02-28
Contact:
TAO Shicong, E-mail: sctao@shsmu.edu.cn.Supported by:摘要:
目的·利用生物信息学方法探索骨关节炎与烟酰胺代谢相关基因之间的关系,找到具有诊断价值和治疗潜力的关键基因。方法·以“Osteoarthritis”为检索词,在GEO数据库中获取GSE12021、GSE55235和GSE55457数据集,将GSE55457作为验证集。去除GSE12021和GSE55235数据集的批次效应后,得到标准化的合并数据集,将其作为训练集,并在训练集中筛选出差异表达基因(differentially expressed genes,DEGs)。在GeneCards数据库和MSigDB数据库中获取所有烟酰胺代谢相关基因(nicotinamide metabolism-related genes,NMRGs)。将DEGs与NMRGs取交集,得到烟酰胺代谢相关差异表达基因(nicotinamide metabolism-related differentially expressed genes,NMRDEGs)。对训练集进行基因集富集分析(gene set enrichment analysis,GSEA),对NMRDEGs进行基因本体(Gene Ontology,GO)、京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes,KEGG)分析。通过LASSO(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator)和支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)分析筛选出NMRDEGs关键基因,构建骨关节炎诊断模型,并用验证集GSE55457进行验证。通过单样本基因集富集分析(single sample gene set enrichment analysis,ssGSEA)分析免疫细胞的浸润类型。通过DGIdb数据库、ENCORI数据库和CHIPBase数据库对关键基因的mRNA进行相互作用网络和药物小分子预测。通过干扰小RNA(small interfering RNA,siRNA)敲降软骨细胞内NMRDEGs关键基因,用实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(real-time fluorogenic quantitative polymerase chain reaction,RT-qPCR)检测关键基因敲降对软骨形成相关基因表达的影响。结果·发现了NAMPT、TIPARP等7个NMRDEGs。GO和KEGG分析富集到核因子κB信号通路和正向调节白细胞介素-1介导的信号通路等。GSEA富集到缺氧诱导因子-1转录因子通路(Hif1 Tfpathway)和多配体蛋白聚糖1(syndecan 1)通路等信号通路。LASSO分析和SVM分析共同筛选得到NPAS2、TIPARP和NAMPT关键基因并构建了骨关节炎诊断模型,验证集检验提示诊断模型诊断效果具有高准确度。ssGSEA免疫浸润分析的结果显示,巨噬细胞等15种免疫细胞存在显著差异(均P<0.05)。找到了7个针对关键基因的潜在药物小分子,19种与关键基因相互作用且上游基因与下游基因数量之和大于10的miRNA,19种与关键基因结合且上游基因与下游基因数量之和大于7的转录因子,27个聚类数>19的RNA结合蛋白。RT-qPCR结果显示,关键基因敲降会降低软骨形成相关基因的表达。结论·NPAS2、TIPARP和NAMPT为烟酰胺代谢相关的关键基因,可据此构建骨关节炎诊断模型。
中图分类号:
邓青松, 张长青, 陶诗聪. 烟酰胺代谢相关基因与骨关节炎的关系探索[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 145-160.
DENG Qingsong, ZHANG Changqing, TAO Shicong. Exploration of the relationship between nicotinamide metabolism-related genes and osteoarthritis[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(2): 145-160.
| siRNA | Sense (5'→3') | Antisense (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| siNPAS2 | CAAAGGAAUUUCCAACUUAUGTT | CAUAAGUUGGAAAUUCCUUUGTT |
| siNAMPT | GCAGGACUUGCUCUAAUUAAATT | UUUAAUUAGAGCAAGUCCUGCTT |
| siTIPARP | CCAAGAGAACGGAAUUGAAAUTT | AUUUCAAUUCCGUUCUCUUGGTT |
表1 siRNA序列
Tab 1 Sequences for siRNA
| siRNA | Sense (5'→3') | Antisense (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| siNPAS2 | CAAAGGAAUUUCCAACUUAUGTT | CAUAAGUUGGAAAUUCCUUUGTT |
| siNAMPT | GCAGGACUUGCUCUAAUUAAATT | UUUAAUUAGAGCAAGUCCUGCTT |
| siTIPARP | CCAAGAGAACGGAAUUGAAAUTT | AUUUCAAUUCCGUUCUCUUGGTT |
| Primer | Forward primer (5'→3') | Reverse primer (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | CCTCTATGCCAACACAGT | AGCCACCAATCCACACAG |
| ACAN | TGGAGACAAGGATGAGTTTCC | GGCGAAGCAGTACACATCATA |
| SOX9 | AACACCTTGAGCCTTAAAACG | GATTTCATCTCCTTTGCTTGC |
表2 RT-qPCR引物序列
Tab 2 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Primer | Forward primer (5'→3') | Reverse primer (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | CCTCTATGCCAACACAGT | AGCCACCAATCCACACAG |
| ACAN | TGGAGACAAGGATGAGTTTCC | GGCGAAGCAGTACACATCATA |
| SOX9 | AACACCTTGAGCCTTAAAACG | GATTTCATCTCCTTTGCTTGC |
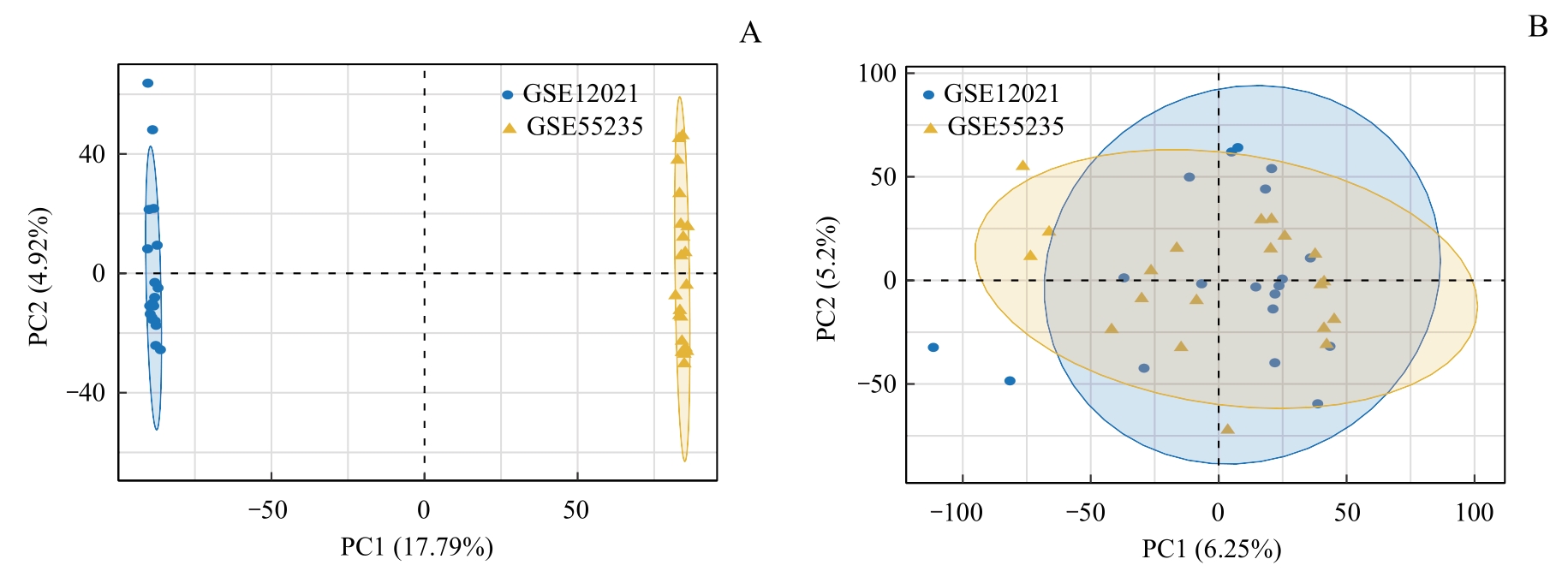
图1 去除批次效应和主成分分析Note: A. PCA plot of the merged datasets before batch effect removal. B. PCA plot of the merged dataset after batch effect removal.
Fig 1 Batch effect removal and PCA
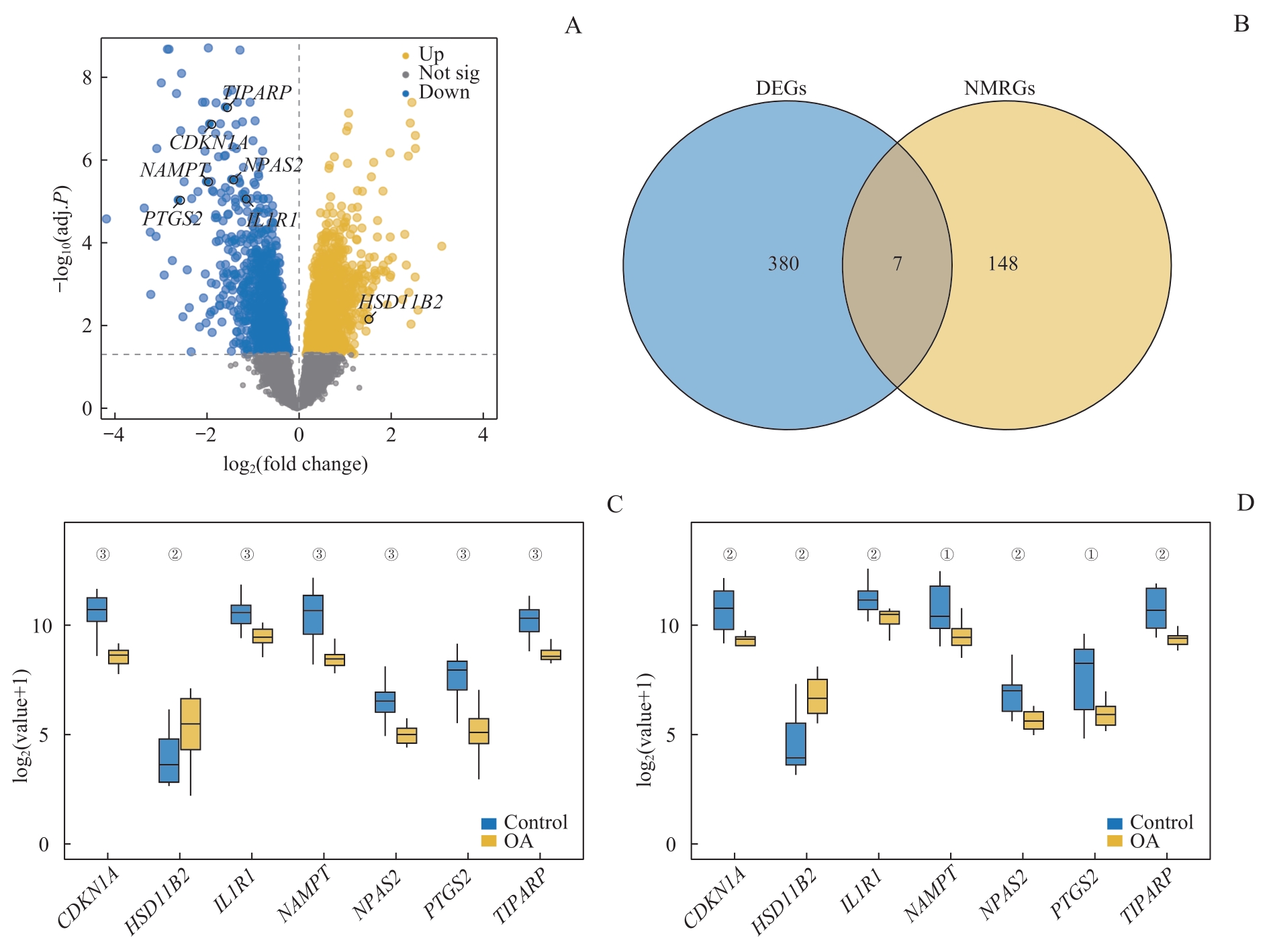
图2 DEGs分析Note: A. Volcano plot of DEGs analysis in the OA group and the control group in the training dataset. B. Venn diagram of DEGs and NMRGs in the training dataset. C. Group comparison chart of NMRDEGs in the training dataset. D. Group comparison chart of NMRDEGs in the validation set GSE55457. ①P<0.05, ②P<0.01, ③P=0.000, comparison between the control group and the OA group.
Fig 2 DEGs expression analysis
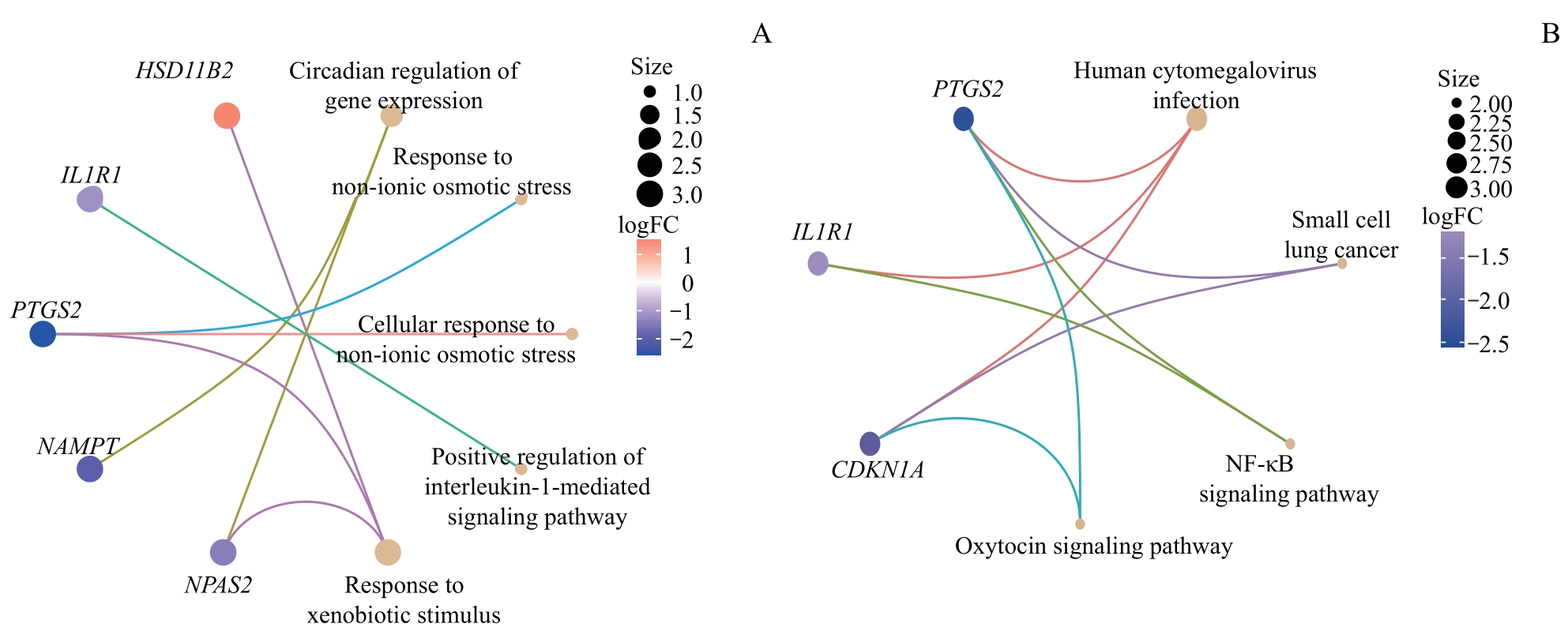
图3 NMRDEGs的GO和KEGG富集分析Note: A. The results of GO enrichment analysis combined with difference analysis results of NMRDEGs logFC network diagram display. B. The pathway KEGG enrichment analysis results of NMRDEGs combined with the difference analysis results of logFC network diagram display.
Fig 3 GO and KEGG enrichment analysis for NMRDEGs
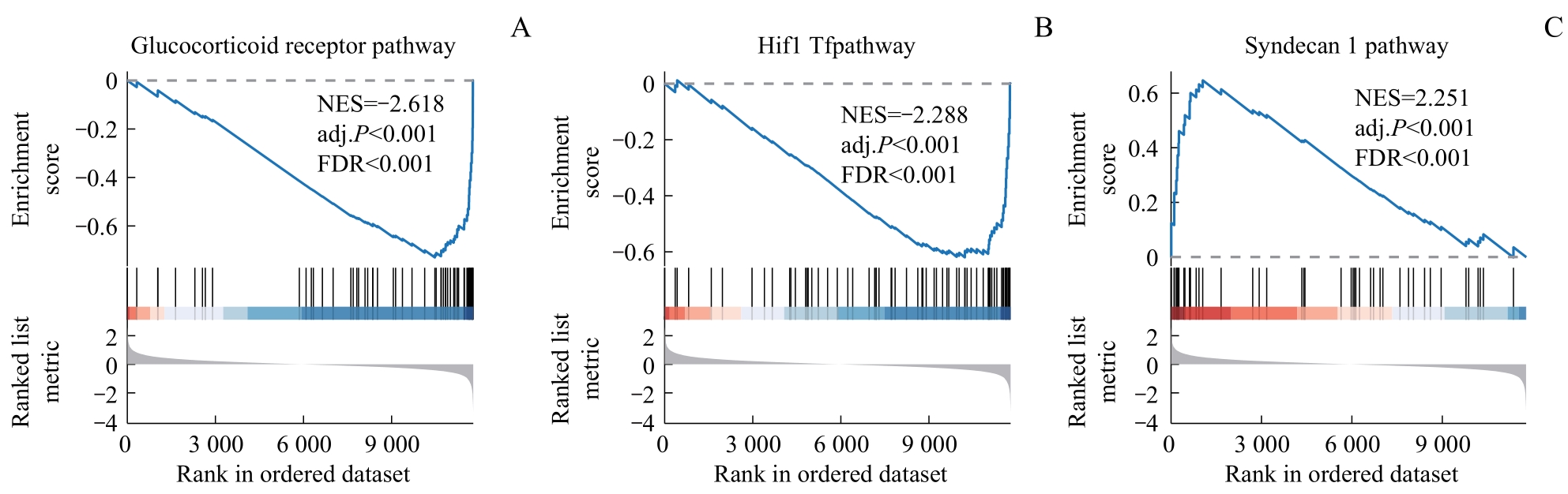
图4 训练集的GSEA分析Note: A. Glucocorticoid receptor pathway. B. Hif1 Tfpathway. C. Syndecan 1 pathway. NES—normalized enrichment score; FDR—false discovery rate.
Fig 4 GSEA for training dataset
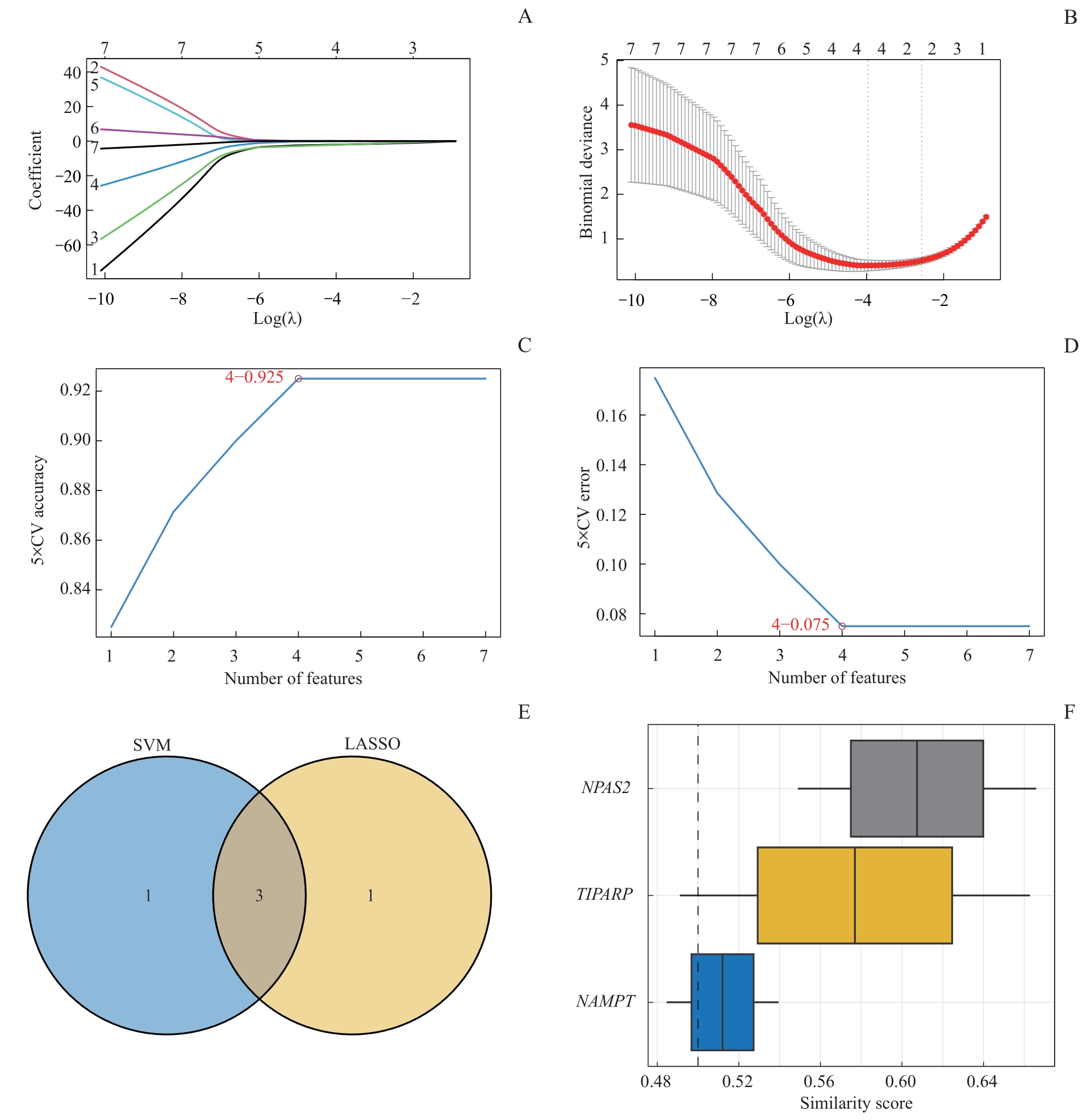
图5 LASSO模型与SVM模型的交集Note: A. LASSO regressor trajectories for NMRDEGs. B. LASSO regression diagnostic model diagram. C. The number of genes with the highest accuracy rate obtained by the SVM algorithm. D. The number of genes with the lowest error rate obtained by the SVM algorithm. E. Venn diagram of the intersection of SVM and LASSO models. F. Boxplot of functional similarity analysis of key genes.
Fig 5 Intersection of LASSO and SVM models
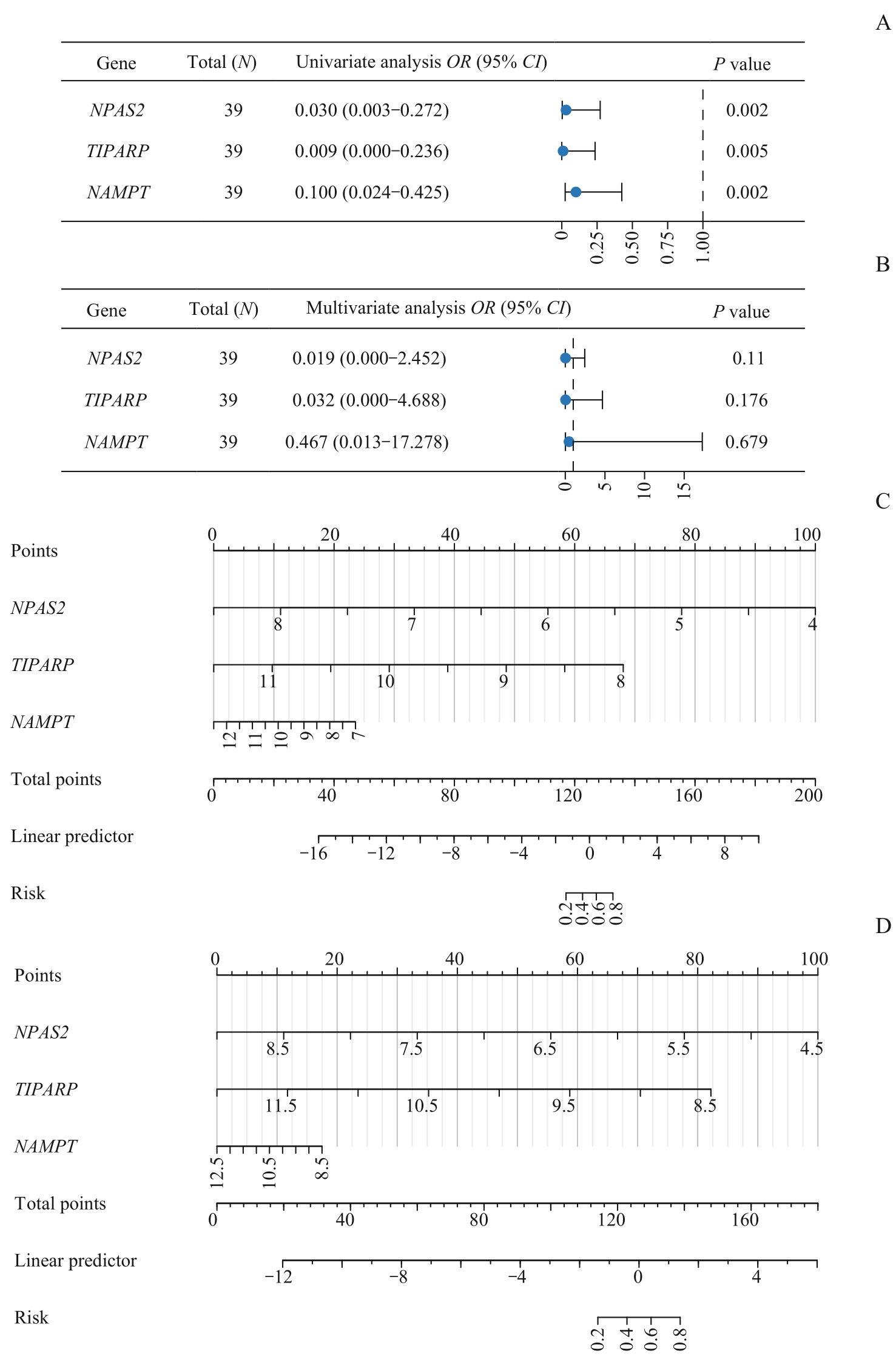
图6 OA的诊断模型构建Note: A. The key genes are included in the forest plot of the single factor Logistic regression model. B. The key genes are included in the forest plot of the multi-factor Logistic regression model. C. The nomogram of the key genes and Logistic predictive scoring model in the training dataset. D. The nomogram of the key genes and Logistic predictive value scoring model in the validation set GSE55457.
Fig 6 Diagnostic model of OA
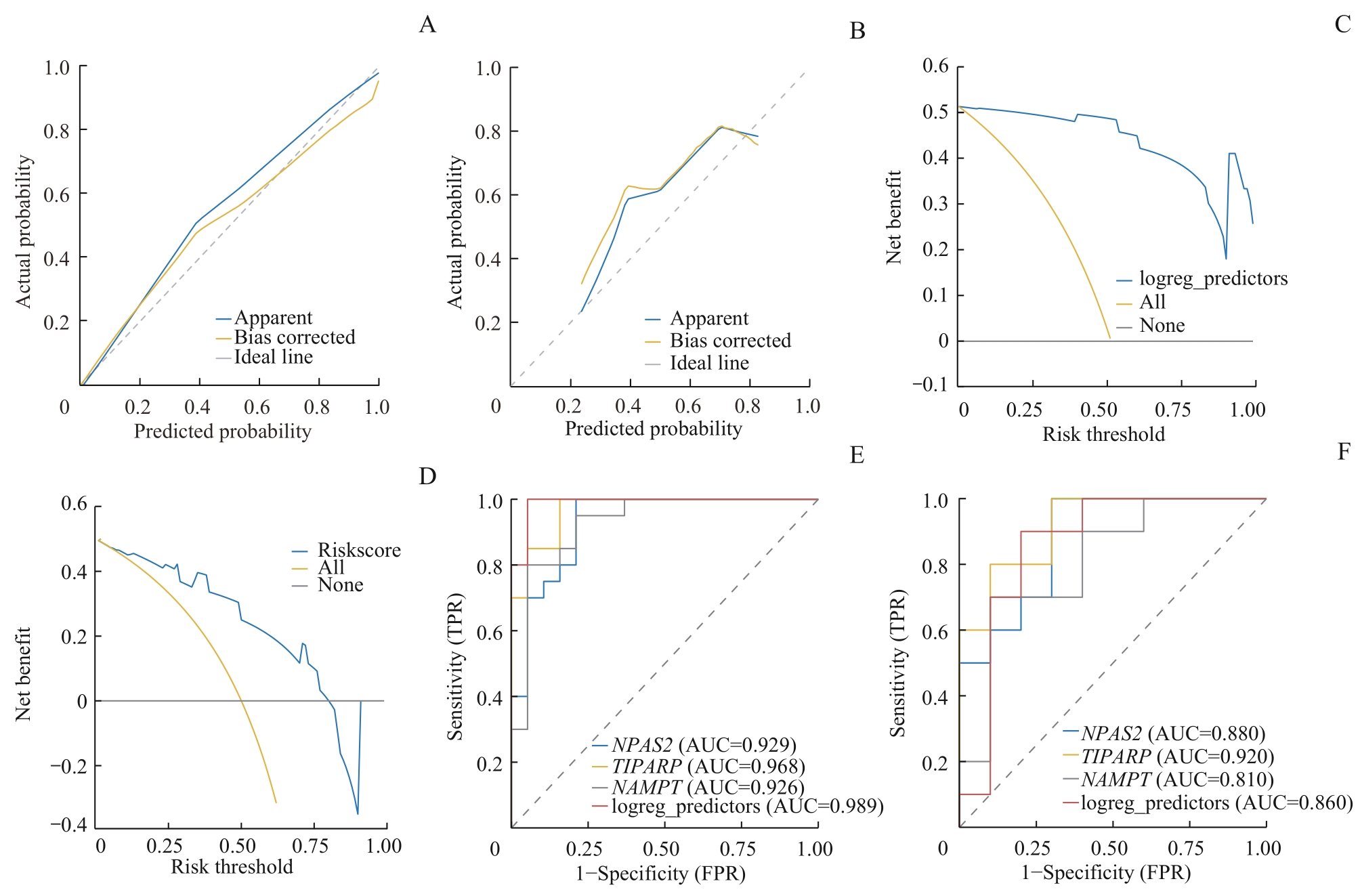
图7 OA诊断模型的验证分析Note: A. Calibration plot of the Logistic model in the training dataset. B. Calibration plot of the Logistic model in the validation set GSE55457. C. DCA plot of the Logistic model in the training dataset. D. DCA plot of the Logistic model in the validation set GSE55457. E. The ROC curve of the Logistic model in the training dataset. F. The ROC curve of the Logistic model in the validation set GSE55457. FPR—false positive rate.
Fig 7 Validation analysis of OA diagnostic model
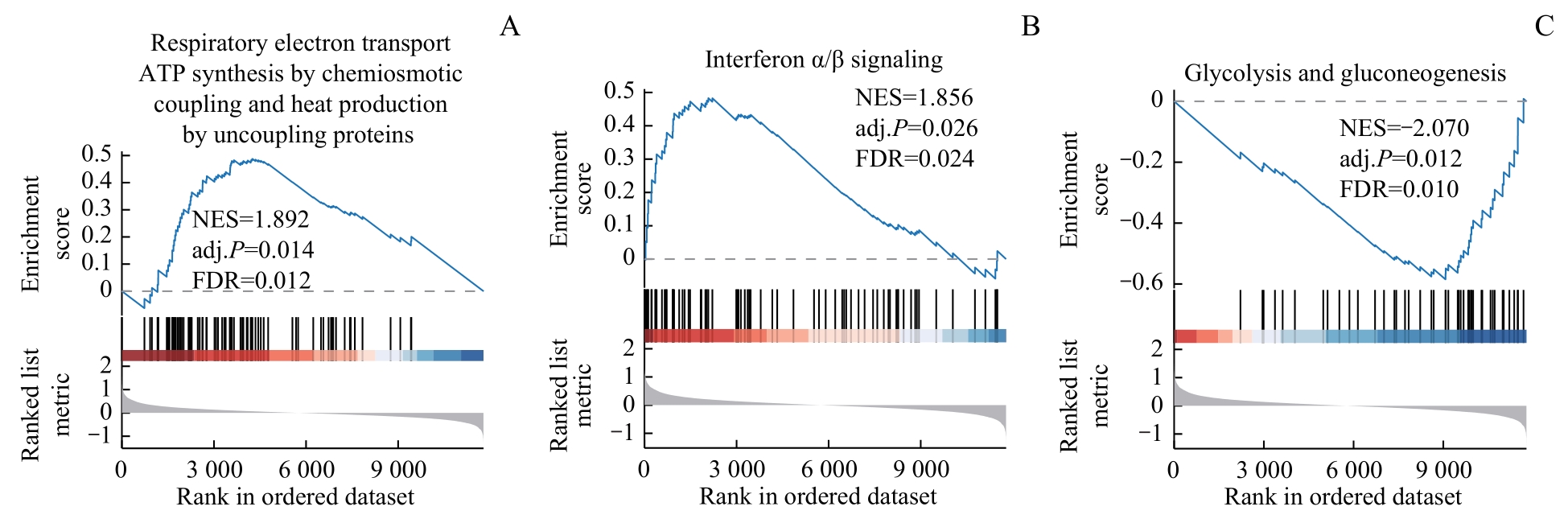
图8 基于高低风险分层的GSEANote: A. Respiratory electron transport ATP synthesis by chemiosmotic coupling and heat production by uncoupling proteins. B. Interferon α/β signaling. C. Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis.
Fig 8 GSEA based on high-low risk stratification
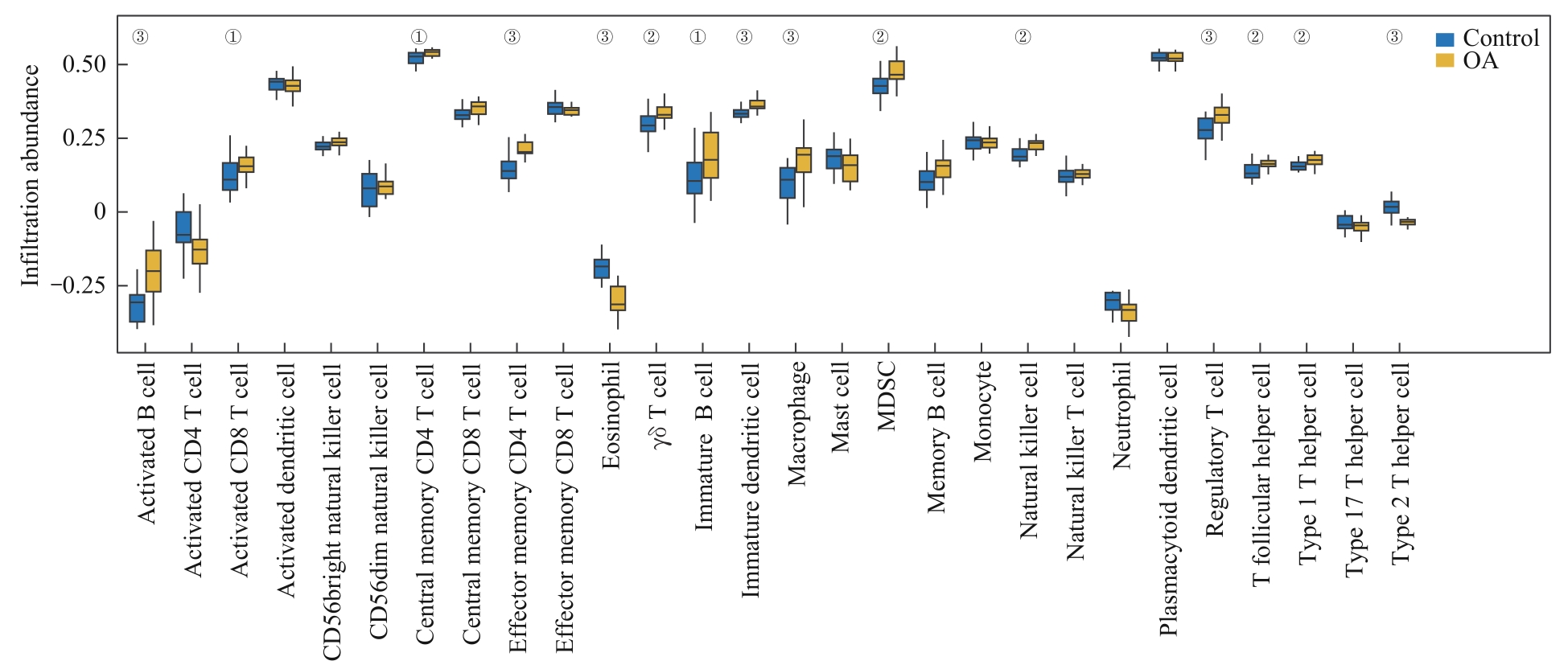
图9 训练集的ssGSEA算法免疫浸润分析Note: Group comparison chart showing the differences in immune infiltration between the OA group and the control group in the training dataset. ①P<0.05, ②P<0.01, ③P=0.000.
Fig 9 Training dataset immune infiltration analysis by ssGSEA algorithm
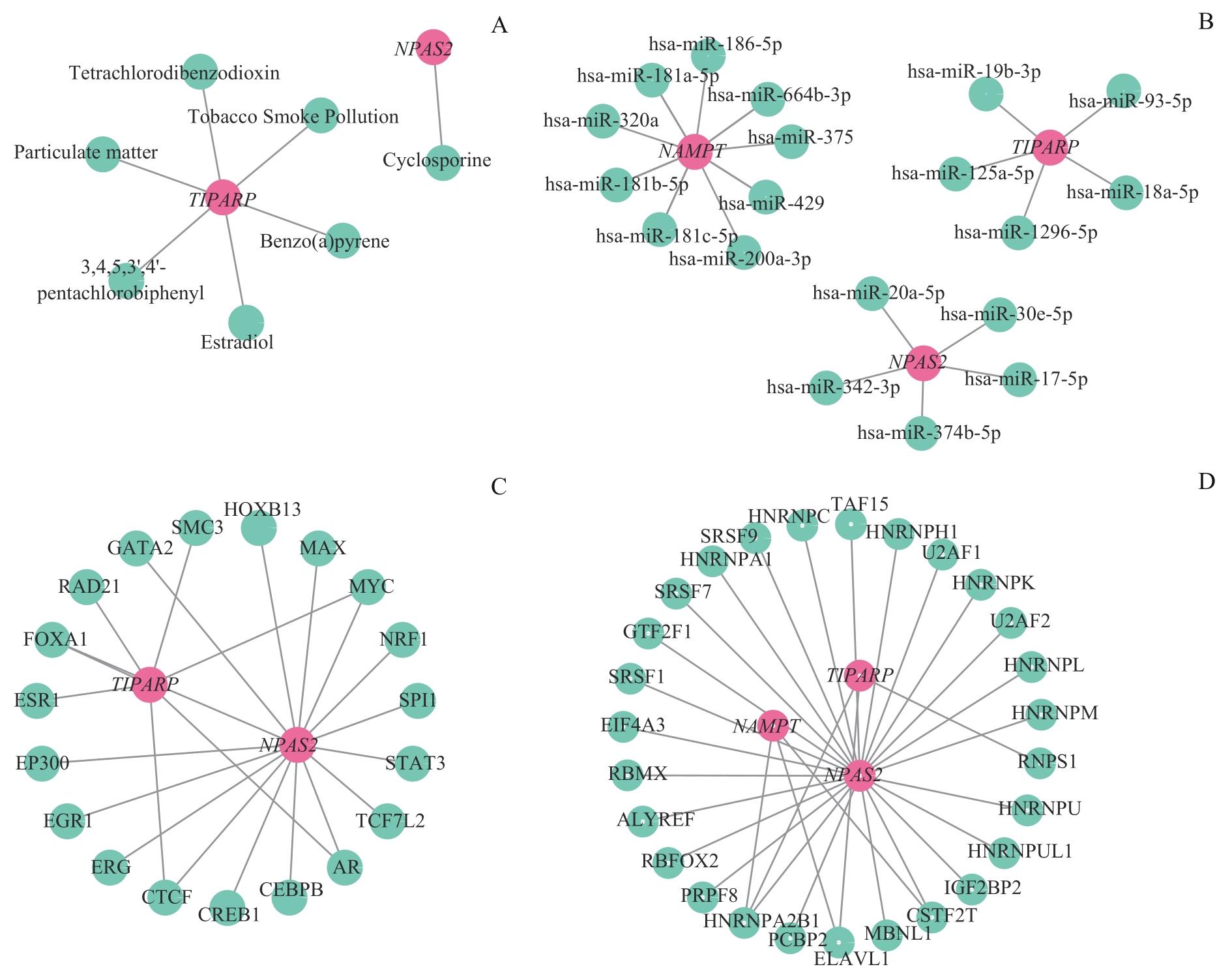
图10 mRNA相互作用网络与药物预测Note: A. mRNA-drug interaction network between key genes and small molecules. B. mRNA-miRNA interaction network of key genes and miRNA. C. mRNA-TF interaction network of key genes and transcription factors. D. The mRNA-RBP interaction network of key genes and RBP.
Fig 10 mRNA interactome network and drug prediction
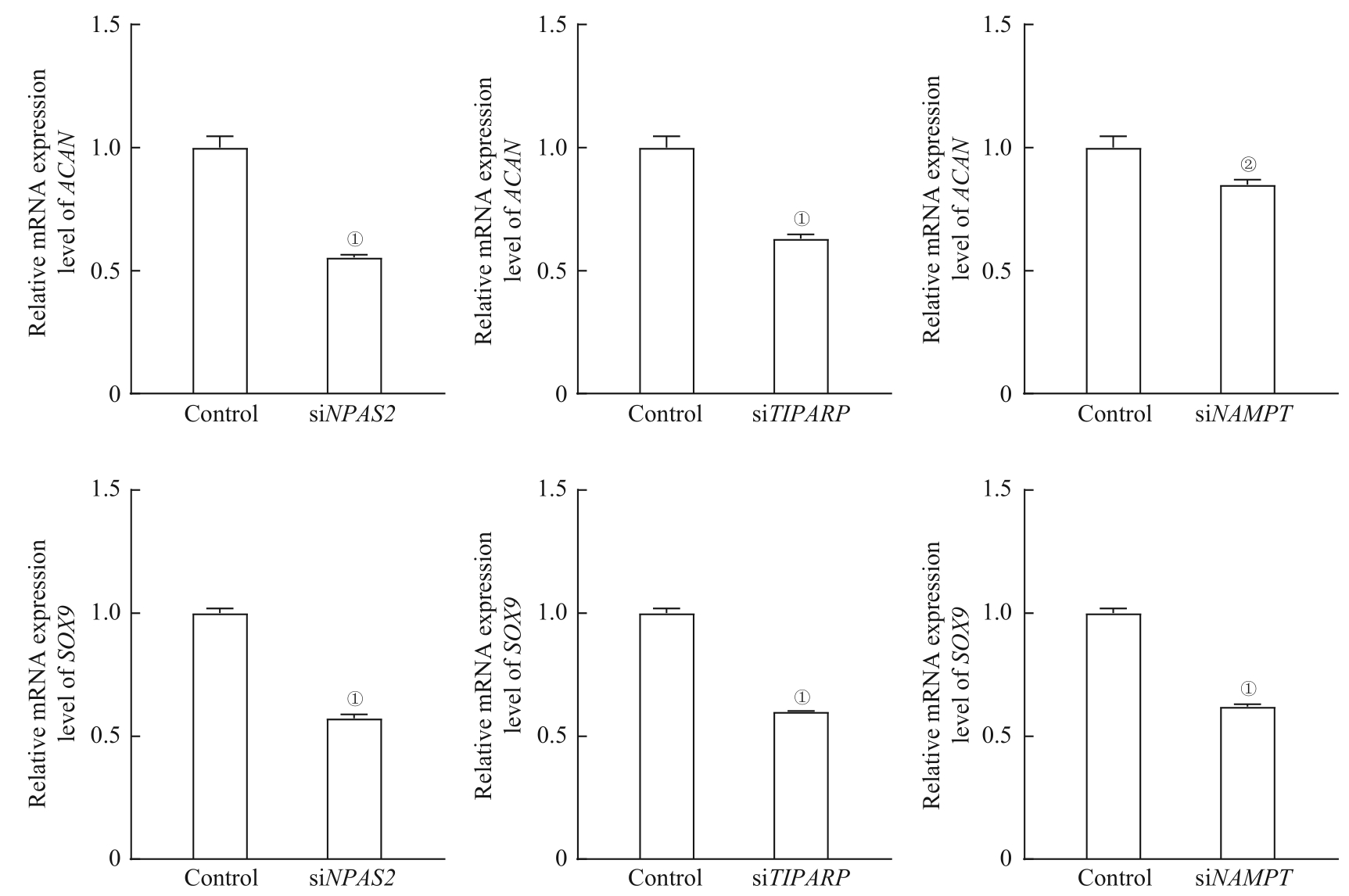
图11 关键基因敲降后软骨形成相关基因 ACAN 和 SOX9 的mRNA表达水平Note: ①P=0.000, ②P<0.01, compared with the control group.
Fig 11 The relative mRNA expression of ACAN and SOX9 after knocking down key genes
| 1 | HUNTER D J, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis[J]. Lancet, 2019, 393(10182): 1745-1759. |
| 2 | YAO Q, WU X H, TAO C, et al. Osteoarthritis: pathogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targets[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 56. |
| 3 | REVOLLO J R, GRIMM A A, IMAI S. The NAD biosynthesis pathway mediated by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase regulates Sir2 activity in mammalian cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2004, 279(49): 50754-50763. |
| 4 | TRAVELLI C, COLOMBO G, MOLA S, et al. NAMPT: A pleiotropic modulator of monocytes and macrophages[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2018, 135: 25-36. |
| 5 | GARTEN A, SCHUSTER S, PENKE M, et al. Physiological and pathophysiological roles of NAMPT and NAD metabolism[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2015, 11(9): 535-546. |
| 6 | JOHNSON S, IMAI S. NAD+ biosynthesis, aging, and disease[J]. F1000Res, 2018, 7: 132. |
| 7 | YANG S, RYU J H, OH H, et al. NAMPT (visfatin), a direct target of hypoxia-inducible factor-2α, is an essential catabolic regulator of osteoarthritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2015, 74(3): 595-602. |
| 8 | PRESLE N, POTTIE P, DUMOND H, et al. Differential distribution of adipokines between serum and synovial fluid in patients with osteoarthritis. Contribution of joint tissues to their articular production[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2006, 14(7): 690-695. |
| 9 | DAVIS S, MELTZER P S. GEOquery: a bridge between the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and BioConductor[J]. Bioinformatics, 2007, 23(14):1846-1847. |
| 10 | HUBER R, HUMMERT C, GAUSMANN U, et al. Identification of intra-group, inter-individual, and gene-specific variances in mRNA expression profiles in the rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2008, 10(4): R98. |
| 11 | WOETZEL D, HUBER R, KUPFER P, et al. Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2014, 16(2): R84. |
| 12 | STELZER G, ROSEN N, PLASCHKES I, et al. The GeneCards suite: from gene data mining to disease genome sequence analyses[J]. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics, 2016, 54: 1.30.1-1.30.33. |
| 13 | LIBERZON A, BIRGER C, THORVALDSDÓTTIR H, et al. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection[J]. Cell Syst, 2015, 1(6): 417-425. |
| 14 | LEEK J T, JOHNSON W E, PARKER H S, et al. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments[J]. Bioinformatics, 2012, 28(6): 882-883. |
| 15 | RITCHIE M E, PHIPSON B, WU D, et al. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015, 43(7): e47. |
| 16 | YU G, WANG L G, HAN Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters[J]. OMICS, 2012, 16(5): 284-287. |
| 17 | LIBERZON A, SUBRAMANIAN A, PINCHBACK R, et al. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0[J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27(12): 1739-1740. |
| 18 | YANG L, QU Q, HAO Z, et al. Powerful identification of large quantitative trait loci using genome-wide R/glmnet-based regression[J]. J Hered, 2022, 113(4): 472-478. |
| 19 | NARALA S, LI S Q, KLIMAS N K, et al. Application of least absolute shrinkage and selection operator logistic regression for the histopathological comparison of chondrodermatitis nodularis helicis and hyperplastic actinic keratosis[J]. J Cutan Pathol, 2021, 48(6): 739-744. |
| 20 | PARK S Y. Nomogram: an analogue tool to deliver digital knowledge[J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2018, 155(4): 1793. |
| 21 | SUN L, PANG Y, WANG X, et al. Ablation of gut microbiota alleviates obesity-induced hepatic steatosis and glucose intolerance by modulating bile acid metabolism in hamsters[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2019, 9(4): 702-710. |
| 22 | XIAO B, LIU L, LI A, et al. Identification and verification of immune-related gene prognostic signature based on ssGSEA for osteosarcoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 607622. |
| 23 | FRESHOUR S L, KIWALA S, COTTO K C, et al. Integration of the Drug-Gene Interaction Database (DGIdb 4.0) with open crowdsource efforts[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 49(D1): D1144-D1151. |
| 24 | LI J H, LIU S, ZHOU H, et al. starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2014, 42(D1): D92-D97. |
| 25 | ZHOU K R, LIU S, SUN W J, et al. ChIPBase v2.0: decoding transcriptional regulatory networks of non-coding RNAs and protein-coding genes from ChIP-seq data[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(D1): D43-D50. |
| 26 | NAVAS L E, CARNERO A. NAD+ metabolism, stemness, the immune response, and cancer[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6(1): 2. |
| 27 | WANG Q H, LI Y, DOU D Y, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide-elicited NAMPT signaling activation aggravated adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats by affecting peripheral immune cells differentiation[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 98: 107856. |
| 28 | NOWELL M, EVANS L, WILLIAMS A. PBEF/NAMPT/visfatin: a promising drug target for treating rheumatoid arthritis?[J]. Future Med Chem, 2012, 4(6): 751-769. |
| 29 | DIOUM E M, RUTTER J, TUCKERMAN J R, et al. NPAS2: a gas-responsive transcription factor[J]. Science, 2002, 298(5602): 2385-2387. |
| 30 | BECKER-KRAIL D D, PAREKH P K, KETCHESIN K D, et al. Circadian transcription factor NPAS2 and the NAD+-dependent deacetylase SIRT1 interact in the mouse nucleus accumbens and regulate reward[J]. Eur J Neurosci, 2022, 55(3): 675-693. |
| 31 | ZHANG L, CAO J, DONG L, et al. TiPARP forms nuclear condensates to degrade HIF-1α and suppress tumorigenesis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020, 117(24): 13447-13456. |
| 32 | SWAHN H, OLMER M, LOTZ M K. RNA-binding proteins that are highly expressed and enriched in healthy cartilage but suppressed in osteoarthritis[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2023, 11: 1208315. |
| 33 | WYATT L A, NWOSU L N, WILSON D, et al. Molecular expression patterns in the synovium and their association with advanced symptomatic knee osteoarthritis[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2019, 27(4): 667-675. |
| 34 | YANG S, KIM J, RYU J H, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α is a catabolic regulator of osteoarthritic cartilage destruction[J]. Nat Med, 2010, 16(6): 687-693. |
| 35 | QIN Y Y, LI M, FENG X, et al. Combined NADPH and the NOX inhibitor apocynin provides greater anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects in a mouse model of stroke[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2017, 104: 333-345. |
| 36 | CORYELL P R, DIEKMAN B O, LOESER R F. Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of cellular senescence in osteoarthritis[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2021, 17(1): 47-57. |
| 37 | SAVVIDOU O, MILONAKI M, GOUMENOS S, et al. Glucocorticoid signaling and osteoarthritis[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2019, 480: 153-166. |
| 38 | SACTA M A, THARMALINGAM B, COPPO M, et al. Gene-specific mechanisms direct glucocorticoid-receptor-driven repression of inflammatory response genes in macrophages[J]. Elife, 2018, 7: e34864. |
| 39 | MIHAILIDOU C, PANAGIOTOU C, KIARIS H, et al. Crosstalk between C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) and glucocorticoid receptor in lung cancer[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2016, 436: 211-223. |
| 40 | DIBATTISTA J A, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, ANTAKLY T, et al. Reduced expression of glucocorticoid receptor levels in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Role in the suppression of metalloprotease synthesis[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 1993, 76(5): 1128-1134. |
| 41 | PELLETIER J P, DIBATTISTA J A, RANGER P, et al. Modulation of the expression of glucocorticoid receptors in synovial fibroblasts and chondrocytes by prostaglandins and NSAIDs[J]. Am J Ther, 1996, 3(2): 115-119. |
| 42 | ZHANG F J, LUO W, LEI G H. Role of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in osteoarthritis[J]. Joint Bone Spine, 2015, 82(3): 144-147. |
| 43 | HU S L, ZHANG C W, NI L B, et al. Stabilization of HIF-1α alleviates osteoarthritis via enhancing mitophagy[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(6): 481. |
| 44 | OKADA K, MORI D, MAKII Y, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 α maintains mouse articular cartilage through suppression of NF-κB signaling[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 5425. |
| 45 | BOUAZIZ W, SIGAUX J, MODROWSKI D, et al. Interaction of HIF1α and β-catenin inhibits matrix metalloproteinase 13 expression and prevents cartilage damage in mice[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2016, 113(19): 5453-5458. |
| 46 | ZHANG H, WANG L, CUI J, et al. Maintaining hypoxia environment of subchondral bone alleviates osteoarthritis progression[J]. Sci Adv, 2023, 9(14): eabo7868. |
| 47 | ZHANG X A, KONG H. Mechanism of HIFs in osteoarthritis[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1168799. |
| 48 | PATTERSON A M, CARTWRIGHT A, DAVID G, et al. Differential expression of syndecans and glypicans in chronically inflamed synovium[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2008, 67(5): 592-601. |
| 49 | KAUFMAN J, CARIC D, VUKOJEVIC K. Expression pattern of Syndecan-1 and HSP-70 in hip tissue of patients with osteoarthritis[J]. J Orthop, 2019, 17: 134-138. |
| 50 | SALMINEN-MANKONEN H, SÄÄMÄNEN A M, JALKANEN M, et al. Syndecan-1 expression is upregulated in degenerating articular cartilage in a transgenic mouse model for osteoarthritis[J]. Scand J Rheumatol, 2005, 34(6): 469-474. |
| 51 | ZHANG Y Q, YANG Y, WANG C Z, et al. Identification of diagnostic biomarkers of osteoarthritis based on multi-chip integrated analysis and machine learning[J]. DNA Cell Biol, 2020, 39(12): 2245-2256. |
| 52 | HAN Y, WU J, GONG Z, et al. Identification and development of a novel 5-gene diagnostic model based on immune infiltration analysis of osteoarthritis[J]. J Transl Med, 2021, 19(1): 522. |
| 53 | JAIME P, GARCÍA-GUERRERO N, ESTELLA R, et al. CD56+/CD16- natural killer cells expressing the inflammatory protease granzyme A are enriched in synovial fluid from patients with osteoarthritis[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2017, 25(10): 1708-1718. |
| 54 | WANG H, ZENG Y, ZHANG M, et al. CD56brightCD16- natural killer cells are shifted toward an IFN-γ-promoting phenotype with reduced regulatory capacity in osteoarthritis[J]. Hum Immunol, 2019, 80(10): 871-877. |
| 55 | MORADI B, SCHNATZER P, HAGMANN S, et al. CD4+ CD25⁺/highCD127low/⁻ regulatory T cells are enriched in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis joints: analysis of frequency and phenotype in synovial membrane, synovial fluid and peripheral blood[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2014, 16(2): R97. |
| 56 | LI Y S, LUO W, ZHU S A, et al. T cells in osteoarthritis: alterations and beyond[J]. Front Immunol, 2017, 8: 356. |
| 57 | CHEN K, KOLLS J K. T cell-mediated host immune defenses in the lung[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2013, 31: 605-633. |
| 58 | REN W K, LIU G, CHEN S, et al. Melatonin signaling in T cells: functions and applications[J]. J Pineal Res, 2017, 62(3): e12394. |
| 59 | ZHANG L, LI Y G, LI Y H, et al. Increased frequencies of Th22 cells as well as Th17 cells in the peripheral blood of patients with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(4): e31000. |
| 60 | DOLHAIN R J E M, van der HEIDEN A N, TER HAAR N T, et al. Shift toward T lymphocytes with a T helper 1 cytokine-secretion profile in the joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1996, 39(12): 1961-1969. |
| 61 | NEES T A, ZHANG J A, PLATZER H, et al. Infiltration profile of regulatory T cells in osteoarthritis-related pain and disability[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 10(9): 2111. |
| 62 | KELLY P A, BURCKART G J, VENKATARAMANAN R. Tacrolimus: a new immunosuppressive agent[J]. Am J Health Syst Pharm, 1995, 52(14): 1521-1535. |
| 63 | KITAHARA K, KAWAI S. Cyclosporine and tacrolimus for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2007, 19(3): 238-245. |
| 64 | BAGRI N K. Cyclosporine for systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis: current stand and future directions[J]. Indian J Pediatr, 2019, 86(7): 576-577. |
| 65 | MANEIX L, BEAUCHEF G, SERVENT A, et al. 17β-oestradiol up-regulates the expression of a functional UDP-glucose dehydrogenase in articular chondrocytes: comparison with effects of cytokines and growth factors[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2008, 47(3): 281-288. |
| 66 | CLAASSEN H, SCHÜNKE M, KURZ B. Estradiol protects cultured articular chondrocytes from oxygen-radical-induced damage[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2005, 319(3): 439-445. |
| 67 | PANG H W, CHEN S H, KLYNE D M, et al. Low back pain and osteoarthritis pain: a perspective of estrogen[J]. Bone Res, 2023, 11(1): 42. |
| [1] | 黄昕, 刘家辉, 叶敬文, 钱文莉, 许万星, 王琳. 基于机器学习的小细胞肺癌代谢分子诊断模型的建立和临床应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(8): 1009-1016. |
| [2] | 魏祥, 魏凌飞, 徐纯峰, 高玉洁, 聂萍, 于德栋. 负载牛磺熊去氧胆酸的光交联明胶水凝胶支架在兔膝关节软骨缺损修复中的效能[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(7): 829-837. |
| [3] | 陈蓉, 张锰, 朱荻绮, 郭颖, 沈捷. 基于抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体的列线图模型对川崎病患儿并发冠状动脉病变风险的预测作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(4): 459-467. |
| [4] | 刘楚萱, 左佳鑫, 熊屏. 基于超声评分参数及临床指标的列线图鉴别原发性干燥综合征与IgG4相关唾液腺炎[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(3): 373-380. |
| [5] | 敦译霆, 赵婧, 冯成领, 李行健, 崔迪, 韩邦旻. 机器人辅助腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术后患者尿失禁的在线风险计算器和列线图预测模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1361-1371. |
| [6] | 陆佳萍, 刘醒, 张林杉, 赵琳, 张敏, 李小英, 刘玥隽. 腹部脂肪面积与2型糖尿病患者胰岛β细胞第一时相分泌功能的关系[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(1): 42-50. |
| [7] | 魏云鑫, 蒋绪顺, 蔡梦瑶, 温睿智, 杜晓刚. COMP与糖尿病肾病自噬相关性分析及其功能验证[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(7): 847-858. |
| [8] | 王鑫, 王晓霞, 李彦庆, 郑永鑫, 乌杰, 任猛, 贾向东, 许天祥. 香叶基香叶基焦磷酸合成酶在肺鳞状细胞癌中的表达及临床意义[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(3): 312-324. |
| [9] | 洪洋, 王洁, 张霞芬, 赵丹, 程敏. 智能可穿戴设备BPMpathway在全膝关节置换术后患者居家康复中的应用效果[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(3): 342-349. |
| [10] | 杨婧偊, 陈留宝, 王康太, 杨兴智, 于海涛. 基于实验室指标的系统性红斑狼疮鉴别诊断列线图的构建及评估[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 204-211. |
| [11] | 俞思薇, 徐梓淇, 陶梦玉, 范广建. 脂肪酸代谢紊乱通过上调ZNF143促进胰腺癌进展的机制研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(10): 1255-1265. |
| [12] | 杜少倩, 陶梦玉, 曹源, 王红霞, 胡孝渠, 范广建, 臧丽娟. CXCL9在乳腺癌中的表达及其与肿瘤免疫浸润特征的相关性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 860-872. |
| [13] | 李清林, 王文波, 刘伟. 肌腱去应力退化机制的生物信息学分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 560-570. |
| [14] | 薛淋淋, 李秉翰, 常丽仙, 李卫昆, 刘春云, 刘立. 丙型病毒性肝炎肝硬化失代偿期患者发生细菌感染的列线图预测模型构建及评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 52-60. |
| [15] | 韩夏夏, 蒋扬, 顾霜霜, 戴黛, 沈南. 系统性红斑狼疮患者免疫细胞代谢通路转录组分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(9): 1197-1207. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||