
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 1515-1526.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.11.011
• 论著 · 技术与方法 • 上一篇
朱玥1,2,3, 李晓琴1,2,3, 王文枭1,2,3, 周凌云1,2,3, 吴皓1,2,3, 陶永1,2,3( ), 杜婷婷1,2,3(
), 杜婷婷1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-13
接受日期:2025-04-25
出版日期:2025-11-28
发布日期:2025-12-03
通讯作者:
陶 永,副研究员,博士;电子信箱:taoyent@sjtu.edu.cn基金资助:
ZHU Yue1,2,3, LI Xiaoqin1,2,3, WANG Wenxiao1,2,3, ZHOU Lingyun1,2,3, WU Hao1,2,3, TAO Yong1,2,3( ), DU Tingting1,2,3(
), DU Tingting1,2,3( )
)
Received:2025-02-13
Accepted:2025-04-25
Online:2025-11-28
Published:2025-12-03
Contact:
TAO Yong, E-mail: taoyent@sjtu.edu.cnSupported by:摘要:
目的·建立一种稳定、高效的技术方法,用于分离并获得耳蜗血管纹中的周细胞,同时尽可能保留周细胞的原始理化性质。方法·取6日龄野生型C57BL/6J小鼠,于显微镜下解剖获取血管纹组织,改变酶的种类、酶解时间、机械解离时间等实验条件,并使用流式细胞技术比较酶解后的单细胞占比以及活细胞占比,以求达到酶解效果最佳、对细胞损伤最小的细胞解离方案。获得的单细胞悬液使用CD140b[即血小板衍生生长因子受体β(platelet derived growth factor receptor-β,PDGFR-β)]抗体和CD31抗体孵育,经流式细胞分选得到CD140b+CD31-和CD140b-细胞,利用实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(RT-qPCR)检测分选所得细胞的分子标志物,验证周细胞标志物[Pdgfrb、结蛋白(desmin,Desm)]的表达情况,并评估内皮细胞[标志物为血管性血友病因子(von Willebrand factor,Vwf)、葡萄糖转运蛋白1(glucose transporter 1,Glut1)]及黑色素样巨噬细胞[标志物为谷胱甘肽S-转移酶α4(glutathione S-transferase α4,Gsta4)、黏附G蛋白偶联受体E1(adhesion G protein-coupled receptor E1,Adgre1)]的污染情况,从而验证所得细胞类型和分离方法的有效性。结果·通过流式细胞分析发现:木瓜蛋白酶酶解血管纹组织对细胞损伤较大,细胞碎片率高;低温活性蛋白酶对血管纹组织分离效率不高;嗜热菌蛋白酶和细胞消化液Accutase联合使用酶解血管纹组织的酶解效果不稳定,且细胞碎片率也较高;而使用Accutase分离血管纹组织,可以较稳定地获得数量相对较多、细胞存活率相对高的单细胞悬液,故最终选用此酶解方法。通过Accutase酶解6日龄小鼠血管纹组织联合CD140b及CD31抗体分选,成功获得高纯度周细胞。RT-qPCR显示,CD140b+CD31-细胞特异性高表达周细胞标志物Pdgfrb、Desm,低表达内皮细胞标志物Vwf、Glut1,以及黑色素样巨噬细胞标志物Gsta4、Adgre1。结论·成功建立一种基于流式细胞术的稳定且有效分离血管纹周细胞的方法。
中图分类号:
朱玥, 李晓琴, 王文枭, 周凌云, 吴皓, 陶永, 杜婷婷. 高效耳蜗血管纹周细胞分选方法的建立[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(11): 1515-1526.
ZHU Yue, LI Xiaoqin, WANG Wenxiao, ZHOU Lingyun, WU Hao, TAO Yong, DU Tingting. An efficient isolation method for pericytes of the cochlear stria vascularis[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(11): 1515-1526.
| Gene | Forward (5′→3′) | Reverse (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Gapdh | AGCTTCGGCACATATTTCATCTG | CGTTCACTCCCATGACAAACA |
| Pdgfrb | ACCTGCAGAGACCTCAAAAGTAGGT | ACCACGGTGACCTCCTGCGA |
| Desm | AGCCAGCGCGTGTCCTCCTA | AGCGTCGGCCAGGGAGAAGT |
| Vwf | TGTTCATCAAATGGTGGGCAGC | ACAGACGCCATCTCCAGATTCA |
| Glut1 | GCTGTGCTTATGGGCTTCTC | AGAGGCCACAAGTCTGCATT |
| Gsta4 | GCTGCGGCTGGAGTGGAGTTTG | TGCCCAACTGAGCTGGTTGCC |
| Adgre1 | TGCATCTAGCAATGGACAGC | GCCTTCTGGATCCATTTGAA |
表1 RT-qPCR引物序列
Tab 1 Primer sequences used for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Forward (5′→3′) | Reverse (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Gapdh | AGCTTCGGCACATATTTCATCTG | CGTTCACTCCCATGACAAACA |
| Pdgfrb | ACCTGCAGAGACCTCAAAAGTAGGT | ACCACGGTGACCTCCTGCGA |
| Desm | AGCCAGCGCGTGTCCTCCTA | AGCGTCGGCCAGGGAGAAGT |
| Vwf | TGTTCATCAAATGGTGGGCAGC | ACAGACGCCATCTCCAGATTCA |
| Glut1 | GCTGTGCTTATGGGCTTCTC | AGAGGCCACAAGTCTGCATT |
| Gsta4 | GCTGCGGCTGGAGTGGAGTTTG | TGCCCAACTGAGCTGGTTGCC |
| Adgre1 | TGCATCTAGCAATGGACAGC | GCCTTCTGGATCCATTTGAA |
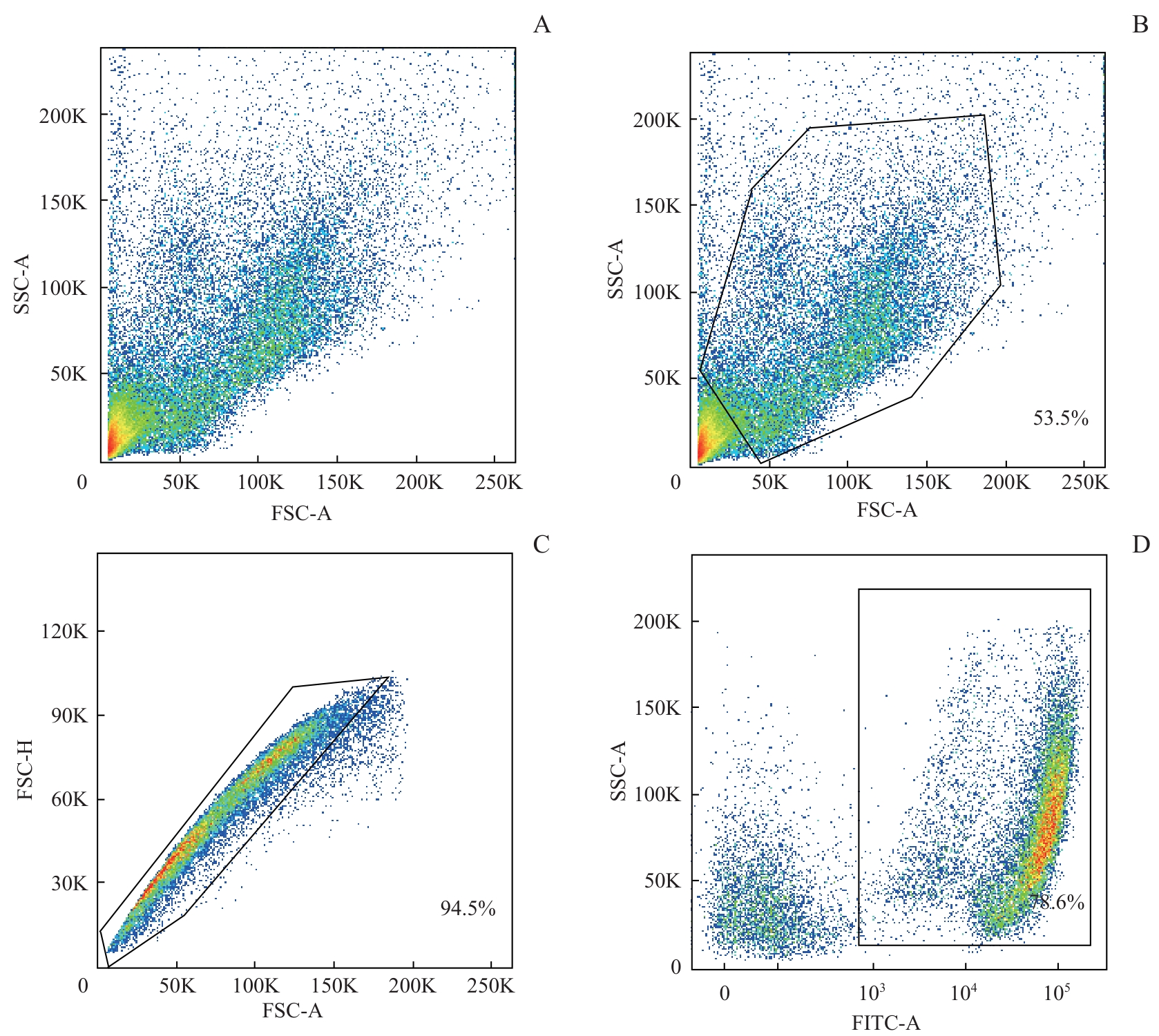
图1 木瓜蛋白酶酶解血管纹的流式细胞分析Note: The diagrams demonstrate the proportion of living single cells in the papain-dissociated suspension. The living and dead cell populations were distinctly separated. Samples were obtained from four mice (P6), with an enzyme concentration of 10 U/mL, and a mechanical dissociation time of 1 min. A. The total number of granules, including cells and fragments. B. The proportion of cells. C. The proportion of single cells. D. The proportion of living cells.
Fig 1 Flow cytometry analysis of stria vascularis digested by papain
| Enzyme type | Total number of granules/n | Proportion of cells/% | Proportion of single cells/% | Proportion of living cells/% | Digestion condition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme concentration/(U·mL-1) | Mechanical dissociation time/min | |||||
| Papain | 21 701 | 50.5 | 99.0 | 73.0 | 20 | 2 |
| 25 809 | 43.1 | 98.5 | 71.3 | 20 | 1 | |
| 37 429 | 53.5 | 94.5 | 78.6 | 10 | 1 | |
表2 不同条件下木瓜蛋白酶酶解效果
Tab 2 Digestion efficiency of papain under different conditions
| Enzyme type | Total number of granules/n | Proportion of cells/% | Proportion of single cells/% | Proportion of living cells/% | Digestion condition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme concentration/(U·mL-1) | Mechanical dissociation time/min | |||||
| Papain | 21 701 | 50.5 | 99.0 | 73.0 | 20 | 2 |
| 25 809 | 43.1 | 98.5 | 71.3 | 20 | 1 | |
| 37 429 | 53.5 | 94.5 | 78.6 | 10 | 1 | |
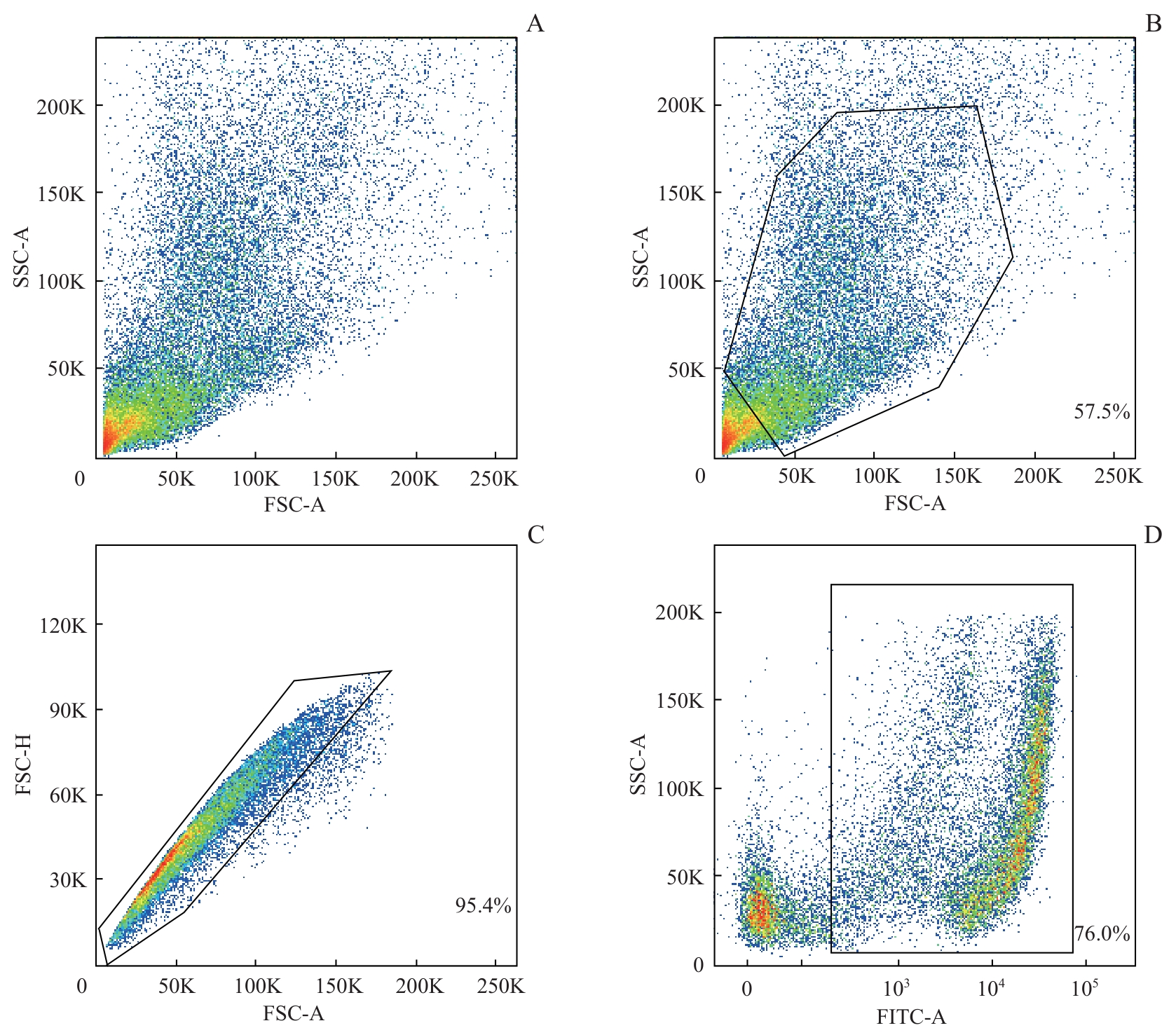
图2 CAP酶解血管纹的流式细胞分析Note: The diagrams demonstrate the proportion of living single cells in the CAP-dissociated suspension. The living and dead cell populations were distinctly separated. Samples were obtained from four mice (P6), with an enzyme concentration of 5 mg/mL, and a mechanical dissociation time of 1 min. A. The total number of granules, including cells and fragments. B. The proportion of cells. C. The proportion of single cells. D. The proportion of living cells.
Fig 2 Flow cytometry analysis of stria vascularis digested by CAP
| Enzyme type | Total number of granules/n | Proportion of cells/% | Proportion of single cells/% | Proportion of living cells/% | Digestion condition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme concentration/(mg·mL-1) | Mechanical dissociation time/min | |||||
| CAP | 26 696 | 31.6 | 94.5 | 58.3 | 10 | 2 |
| 22 715 | 42.8 | 96.5 | 69.1 | 5 | 2 | |
| 32 321 | 57.5 | 95.4 | 76.0 | 5 | 1 | |
表3 不同条件下CAP酶解效果
Tab 3 Digestion efficiency of CAP under different conditions
| Enzyme type | Total number of granules/n | Proportion of cells/% | Proportion of single cells/% | Proportion of living cells/% | Digestion condition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme concentration/(mg·mL-1) | Mechanical dissociation time/min | |||||
| CAP | 26 696 | 31.6 | 94.5 | 58.3 | 10 | 2 |
| 22 715 | 42.8 | 96.5 | 69.1 | 5 | 2 | |
| 32 321 | 57.5 | 95.4 | 76.0 | 5 | 1 | |
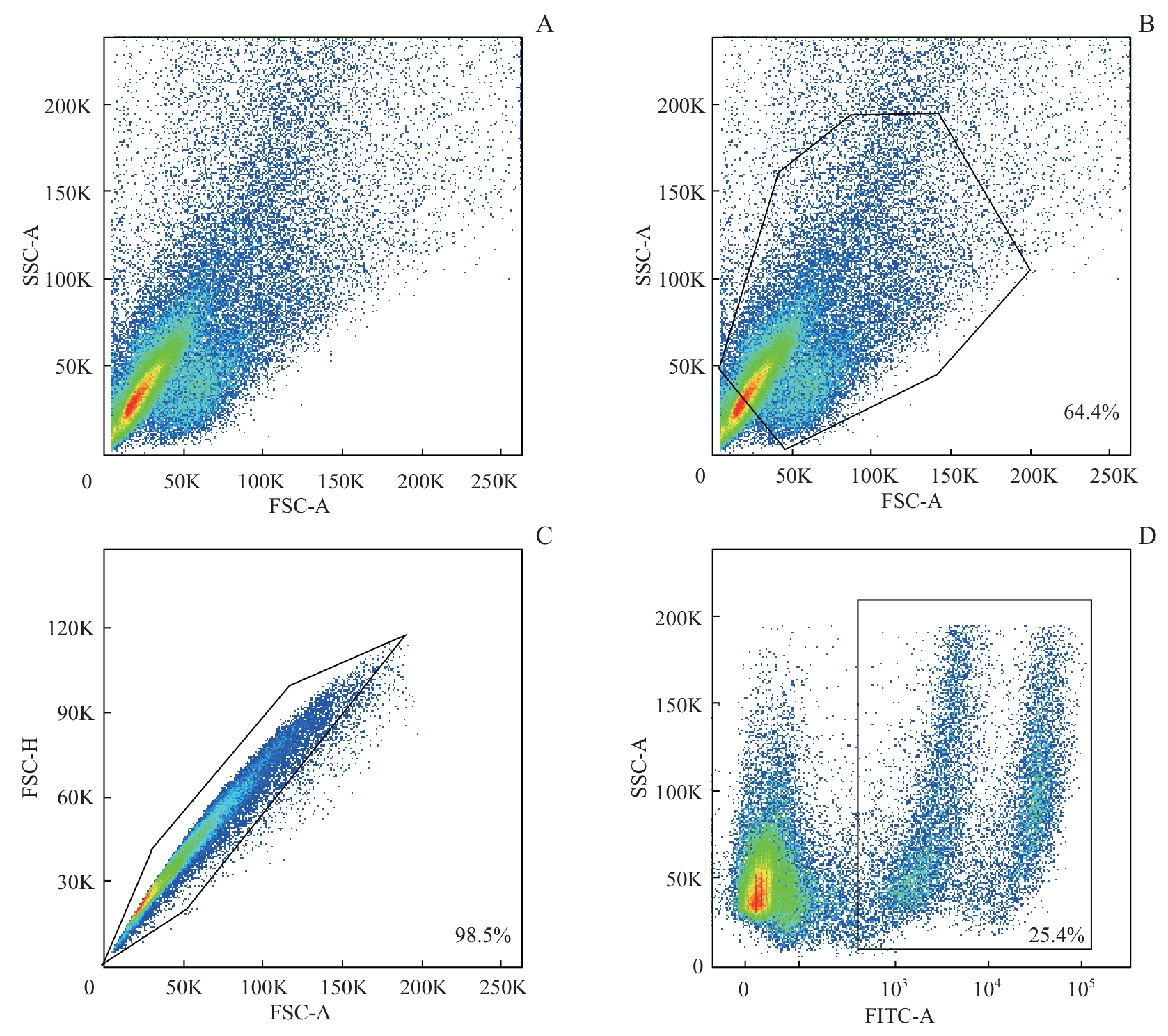
图3 嗜热菌蛋白酶和Accutase联合酶解血管纹的流式细胞分析Note: The diagrams demonstrate the proportion of living single cells in the thermolysin-and Accutase-dissociated suspension. The living and dead cell populations were distinctly separated. Samples were obtained from four mice (P6), under the conditions described in “1.3.4”. A. The total number of granules, including cells and fragments. B. The proportion of cells. C. The proportion of single cells. D. The proportion of living cells.
Fig 3 Flow cytometry analysis of stria vascularis digested by thermolysin and Accutase
| Enzyme type | Total number of granules/n | Proportion of cells/% | Proportion of single cells/% | Proportion of living cells/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermolysin and Accutase | 131 421 | 58.4 | 87.7 | 81.0 |
| 194 163 | 60.8 | 79.9 | 79.2 | |
| 105 934 | 64.4 | 98.5 | 25.4 |
表4 相同条件下3次嗜热菌蛋白酶和Accutase联合酶解效果
Tab 4 Digestion efficiency of thermolysin and Accutase in three replicates under the same condition
| Enzyme type | Total number of granules/n | Proportion of cells/% | Proportion of single cells/% | Proportion of living cells/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermolysin and Accutase | 131 421 | 58.4 | 87.7 | 81.0 |
| 194 163 | 60.8 | 79.9 | 79.2 | |
| 105 934 | 64.4 | 98.5 | 25.4 |
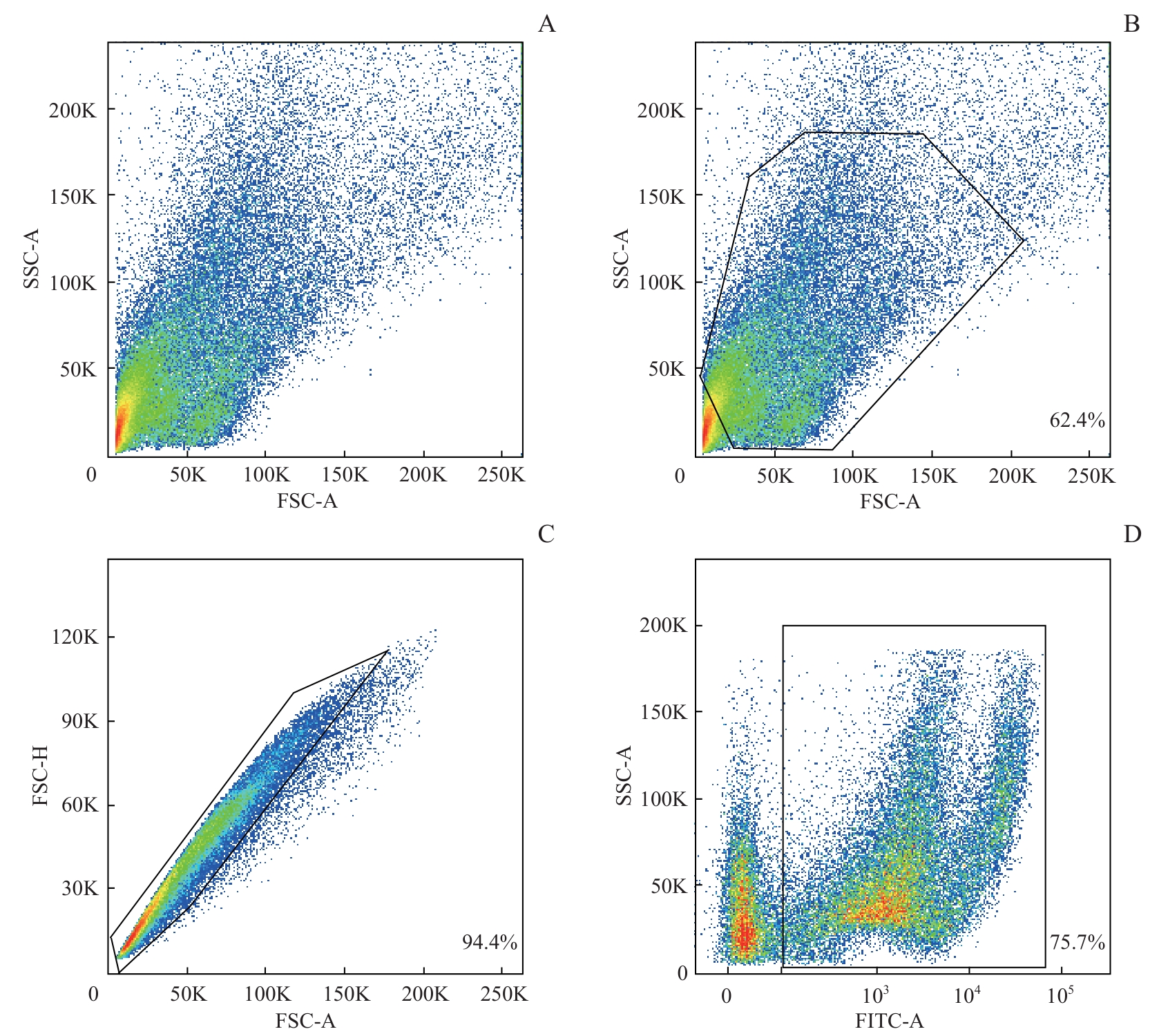
图4 Accutase酶解血管纹的流式细胞分析Note: The diagrams demonstrate the proportion of living single cells in the Accutase-dissociated suspension. The living and dead cell populations were distinctly separated. Samples were obtained from four mice (P6), with a digestion time of 3 min, and a mechanical dissociation time of 1 min. A. The total number of granules, including cells and fragments. B. The proportion of cells. C. The proportion of single cells. D. The proportion of living cells.
Fig 4 Flow cytometry analysis of stria vascularis digested by Accutase
| Enzyme type | Total number of granules/n | Proportion of cells/% | Proportion of single cells/% | Proportion of living cells/% | Digestion condition | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digestion time/min | Mechanical dissociation time/min | Repeated time/n | |||||
| Accutase | 34 791 | 48.1 | 93.9 | 53.0 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| 48 120 | 67.9 | 94.0 | 73.9 | 5 | 1 | 4 | |
| 65 398 | 60.5 | 94.9 | 76.0 | 5 | 2 | 3 | |
表5 不同条件下Accutase酶解效果
Tab 5 Digestion efficiency of Accutase under different conditions
| Enzyme type | Total number of granules/n | Proportion of cells/% | Proportion of single cells/% | Proportion of living cells/% | Digestion condition | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digestion time/min | Mechanical dissociation time/min | Repeated time/n | |||||
| Accutase | 34 791 | 48.1 | 93.9 | 53.0 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| 48 120 | 67.9 | 94.0 | 73.9 | 5 | 1 | 4 | |
| 65 398 | 60.5 | 94.9 | 76.0 | 5 | 2 | 3 | |
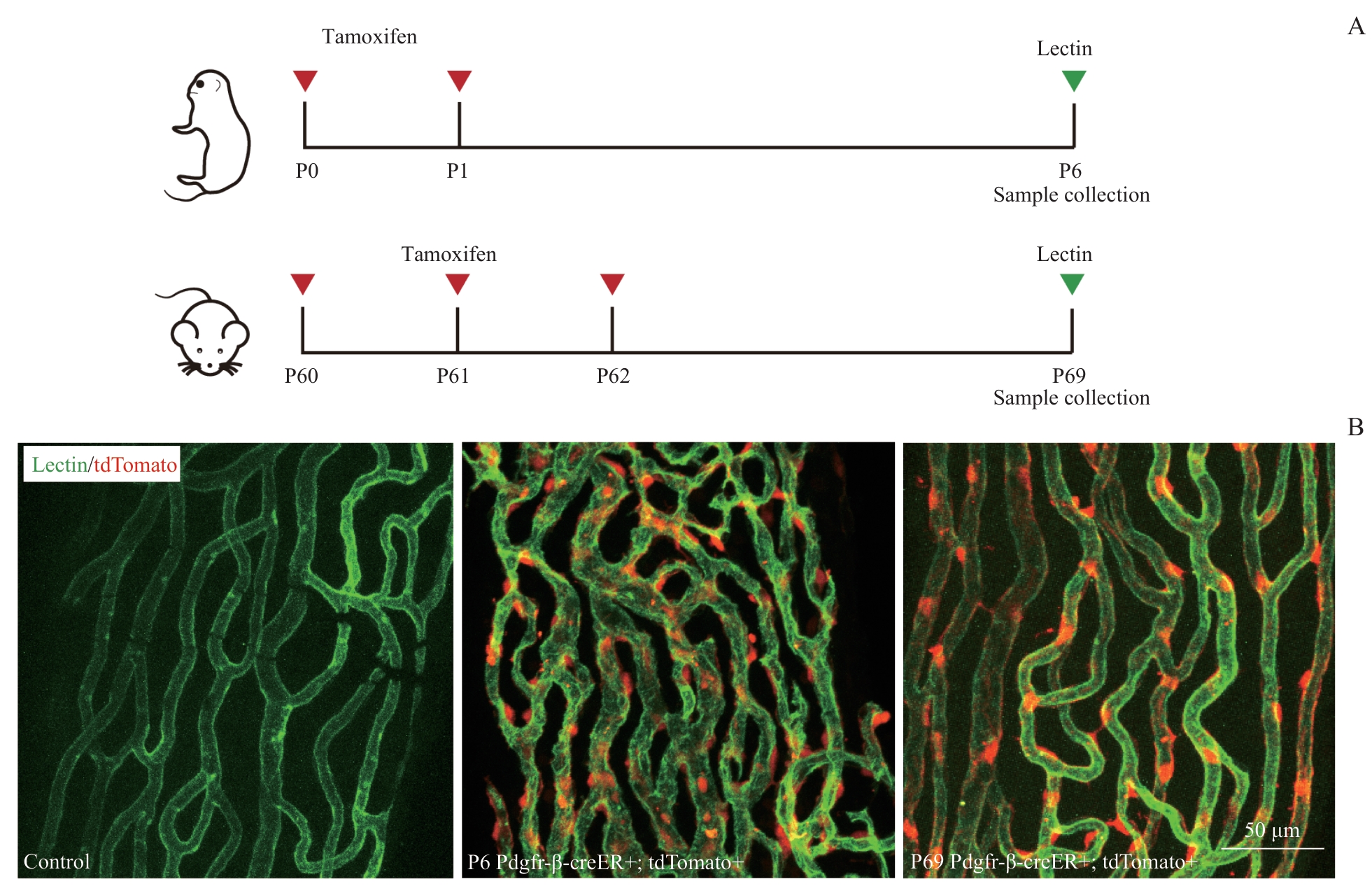
图5 他莫昔芬诱导Pdgfr-β-creER+;tdTomato+ 小鼠特异性标记周细胞Note: A. The timeline of tamoxifen injection and sample collection. B. Vessels were stained with lectin (green); after tamoxifen injection, pericytes in Pdgfr-β-creER+;tdTomato+ mice expressed tdTomato (red) (×400). This was validated in both P69 and P6 mice. Scale bar=50 μm.
Fig 5 Tamoxifen-induced specific labeling of pericytes in PDGFR-β-creER+; tdTomato+ mice
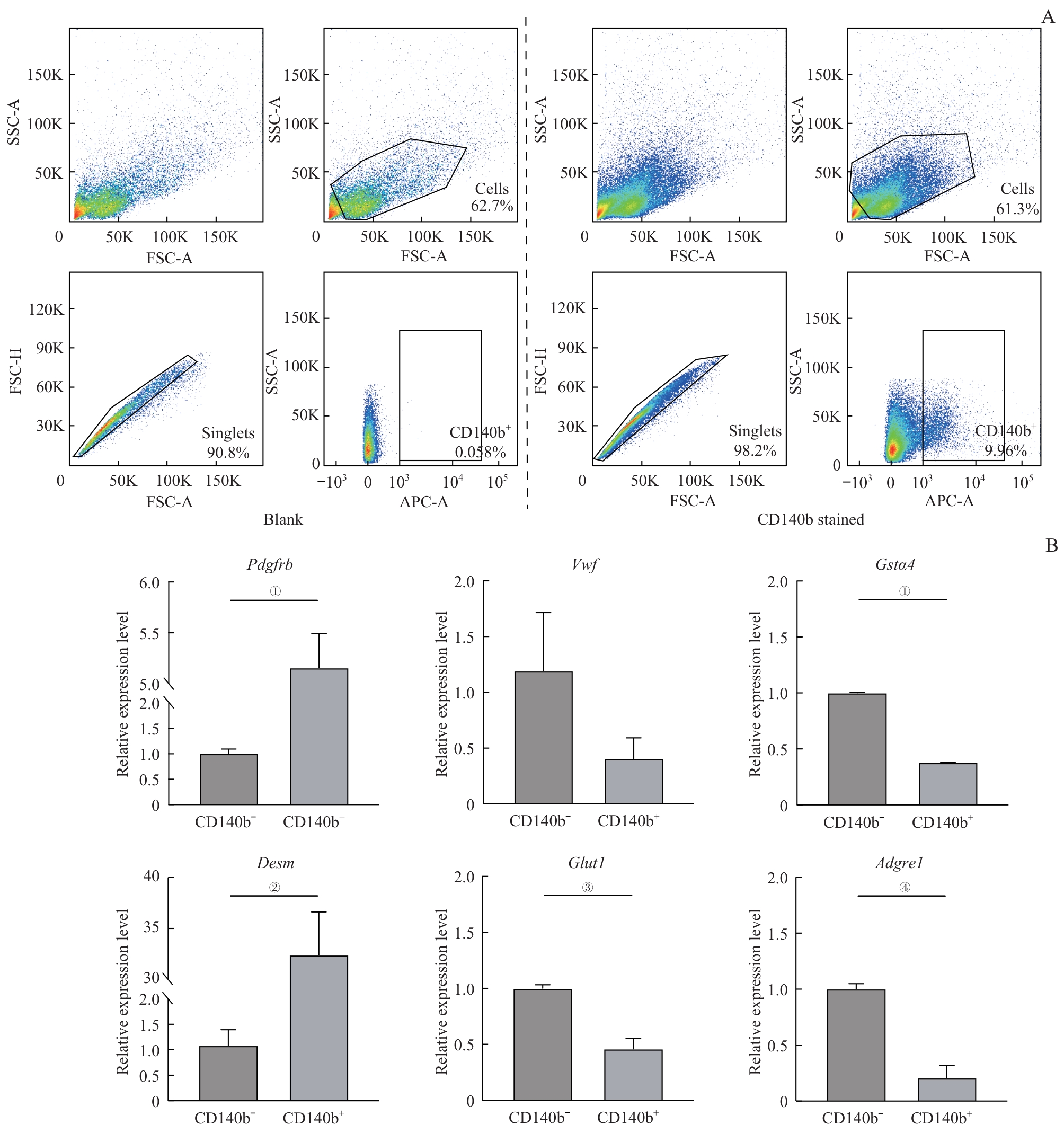
图6 CD140b标记周细胞流式分选及验证Note: A. The blank group was not stained with the CD140b antibody (left). After staining with the CD140b antibody (right), both positive and negative cells were collected. B. RNA was extracted from the collected cells of eight mice (P6). mRNA levels were detected by RT-qPCR. ①P<0.001, ②P=0.002, ③P=0.005, ④P=0.003.
Fig 6 Flow cytometric sorting based on the CD140b marker and verification of pericytes
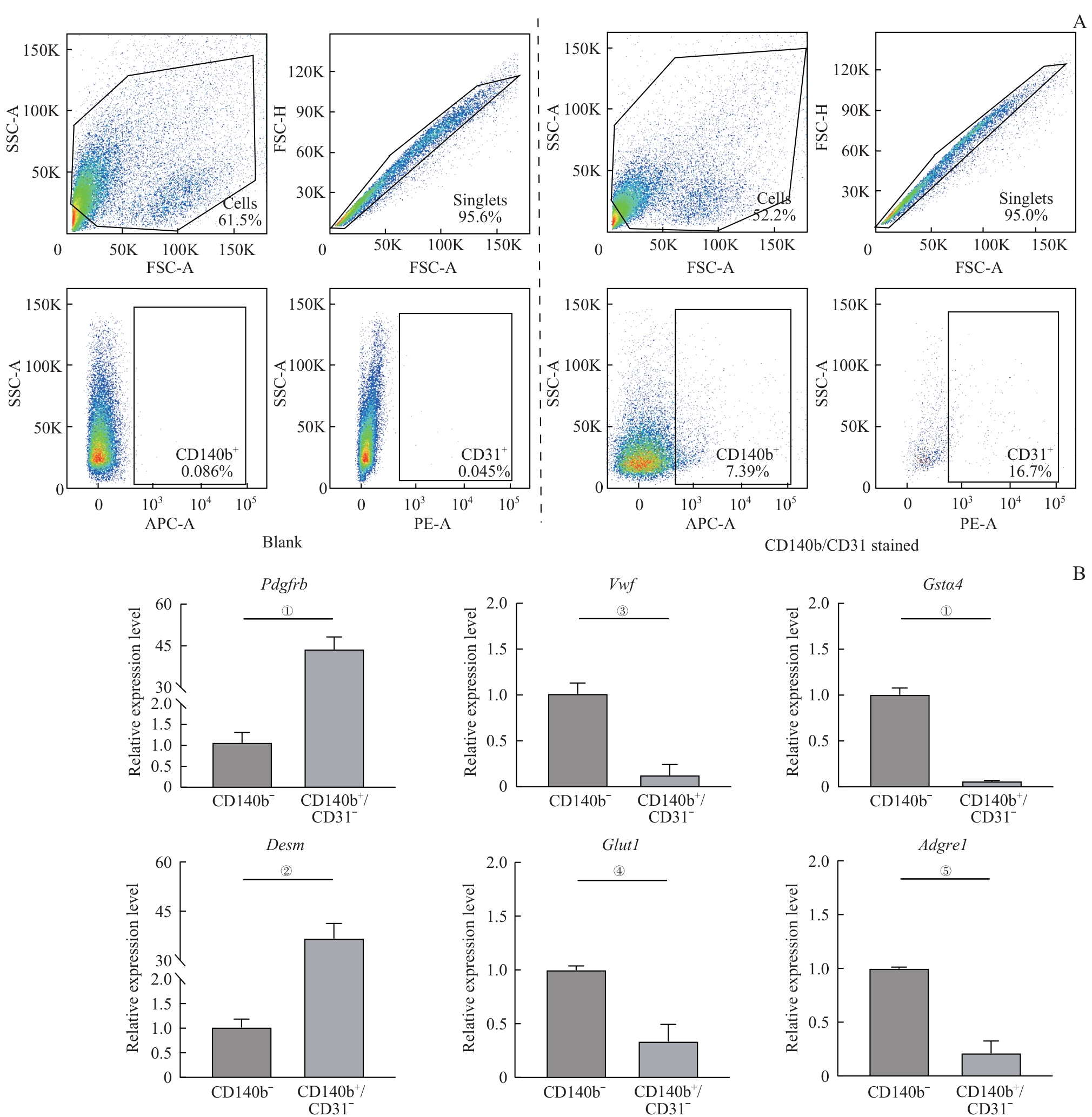
图7 CD140b/CD31双选得到周细胞及其纯度验证Note: A. The blank group was stained with neither antibodies (left). After staining with the CD140b antibody and CD31 antibody (right), both the CD140b+/CD31- cells and CD140b- cells were collected. The data indicated that the dissociation effect was relatively stable, with a subset of CD140b+ cells exhibiting CD31+. B. RNA was extracted from the collected cells of eight mice (P6). mRNA levels were detected by RT-qPCR. Due to the very low expression levels of Vwf and Adgre1 in the CD140b+/CD31- cells, these markers were undetectable in some replicates. For quantification, undetectable transcripts were assigned a CT value of 38. ①P<0.001, ②P=0.001, ③P=0.006, ④P=0.015, ⑤P=0.002.
Fig 7 Flow cytometric sorting based on CD140b and CD31 markers and verification of pericytes
| [1] | LI M M, ABOU TAYOUN A, DISTEFANO M, et al. Clinical evaluation and etiologic diagnosis of hearing loss: a clinical practice resource of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG)[J]. Genet Med, 2022, 24(7): 1392-1406. |
| [2] | YU W T, ZONG S M, DU P Y, et al. Role of the stria vascularis in the pathogenesis of sensorineural hearing loss: a narrative review[J]. Front Neurosci, 2021, 15: 774585. |
| [3] | LANG H N, NOBLE K V, BARTH J L, et al. The stria vascularis in mice and humans is an early site of age-related cochlear degeneration, macrophage dysfunction, and inflammation[J]. J Neurosci, 2023, 43(27): 5057-5075. |
| [4] | HIBINO H, NIN F, TSUZUKI C, et al. How is the highly positive endocochlear potential formed? The specific architecture of the stria vascularis and the roles of the ion-transport apparatus[J]. Pflugers Arch, 2010, 459(4): 521-533. |
| [5] | ZHANG Y P, NENG L L, SHARMA K, et al. Pericytes control vascular stability and auditory spiral ganglion neuron survival[J]. eLife, 2023, 12: e83486. |
| [6] | SHI X R. Pathophysiology of the cochlear intrastrial fluid-blood barrier (review)[J]. Hear Res, 2016, 338: 52-63. |
| [7] | ARMULIK A, GENOVÉ G, BETSHOLTZ C. Pericytes: developmental, physiological, and pathological perspectives, problems, and promises[J]. Dev Cell, 2011, 21(2): 193-215. |
| [8] | SHI X R. Cochlear pericyte responses to acoustic trauma and the involvement of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor[J]. Am J Pathol, 2009, 174(5): 1692-1704. |
| [9] | SHI T F, ZHOU Z, JIANG W J, et al. Hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress exacerbates mitochondrial apoptosis damage to cochlear stria vascularis pericytes via the ROS-mediated Bcl-2/CytC/AIF pathway[J]. Redox Rep, 2024, 29(1): 2382943. |
| [10] | GU J Y, TONG L, LIN X, et al. The disruption and hyperpermeability of blood-labyrinth barrier mediates cisplatin-induced ototoxicity[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2022, 354: 56-64. |
| [11] | NENG L L, ZHANG W J, HASSAN A, et al. Isolation and culture of endothelial cells, pericytes and perivascular resident macrophage-like melanocytes from the young mouse ear[J]. Nat Protoc, 2013, 8(4): 709-720. |
| [12] | KORRAPATI S, TAUKULIS I, OLSZEWSKI R, et al. Single cell and single nucleus RNA-seq reveal cellular heterogeneity and homeostatic regulatory networks in adult mouse stria vascularis[J]. Front Mol Neurosci, 2019, 12: 316. |
| [13] | THULASIRAM M R, OGIER J M, DABDOUB A. Hearing function, degeneration, and disease: spotlight on the stria vascularis[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 841708. |
| [14] | GU S J, OLSZEWSKI R, TAUKULIS I, et al. Characterization of rare spindle and root cell transcriptional profiles in the stria vascularis of the adult mouse cochlea[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 18100. |
| [15] | ZHOU L Y, JIN C X, WANG W X, et al. Differential regulation of hair cell actin cytoskeleton mediated by SRF and MRTFB[J]. eLife, 2023, 12: e90155. |
| [16] | HERTZANO R, GWILLIAM K, ROSE K, et al. Cell type-specific expression analysis of the inner ear: a technical report[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021, 131(Suppl 5): S1-S16. |
| [17] | JEAN P, WONG JUN TAI F, SINGH-ESTIVALET A, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic profiling of the mouse cochlea: an atlas for targeted therapies[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2023, 120(26): e2221744120. |
| [18] | DA SILVA MEIRELLES L, MALTA T M, DE DEUS WAGATSUMA V M, et al. Cultured human adipose tissue pericytes and mesenchymal stromal cells display a very similar gene expression profile[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2015, 24(23): 2822-2840. |
| [19] | HOU Z Q, WANG X H, CAI J, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor subunit B signaling promotes pericyte migration in response to loud sound in the cochlear stria vascularis[J]. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol, 2018, 19(4): 363-379. |
| [20] | SHI X, HAN W, YAMAMOTO H, et al. The cochlear pericytes[J]. Microcirculation, 2008, 15(6): 515-529. |
| [21] | SHI X R. Resident macrophages in the cochlear blood-labyrinth barrier and their renewal via migration of bone-marrow-derived cells[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2010, 342(1): 21-30. |
| [22] | BURNS J C, KELLY M C, HOA M, et al. Single-cell RNA-Seq resolves cellular complexity in sensory organs from the neonatal inner ear[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6: 8557. |
| [23] | JAN T A, ELTAWIL Y, LING A H, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of inner ear sensory and non-sensory cells revealed by single-cell transcriptomics[J]. Cell Rep, 2021, 36(2): 109358. |
| [24] | ROBERTSON R T, LEVINE S T, HAYNES S M, et al. Use of labeled tomato lectin for imaging vasculature structures[J]. Histochem Cell Biol, 2015, 143(2): 225-234. |
| [25] | HOU Z Q, NENG L L, ZHANG J H, et al. Acoustic trauma causes cochlear pericyte-to-myofibroblast-like cell transformation and vascular degeneration, and transplantation of new pericytes prevents vascular atrophy[J]. Am J Pathol, 2020, 190(9): 1943-1959. |
| [26] | SHIN S A, LYU A R, JEONG S H, et al. Acoustic trauma modulates cochlear blood flow and vasoactive factors in a rodent model of noise-induced hearing loss[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(21): 5316. |
| [27] | ANFUSO C D, COSENTINO A, AGAFONOVA A, et al. Pericytes of stria vascularis are targets of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: new insights into the molecular mechanisms involved in blood-labyrinth barrier breakdown[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(24): 15790. |
| [28] | DUFEK B, MEEHAN D T, DELIMONT D, et al. Pericyte abnormalities precede strial capillary basement membrane thickening in Alport mice[J]. Hear Res, 2020, 390: 107935. |
| [1] | 成亚琼, 杜一唯, 刘思迪, 经典, 吴皓. 基于多尺度分辨率的耳蜗神经纤维三维成像[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(11): 1421-1431. |
| [2] | 周卫军, 刘思迪, 蔡瑞捷, 刘宏超, 王美建, 吴皓, 刘辉辉, 汪照炎. 星形胶质细胞在噪声损伤后小鼠耳蜗核突触修复中的作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(4): 454-461. |
| [3] | 杨璐, 黄美萍, 周嵌, 李进, 李蕴, 黄治物. 蜗神经发育不良先天性耳聋儿童人工耳蜗植入干预的听觉及言语能力长效评估研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 890-897. |
| [4] | 顾文汐, 贾欢, 吴皓. 人工耳蜗植入术后CT影像学评估的临床价值及进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(12): 1463-1469. |
| [5] | 许静轩, 杜少倩, 曹源, 王红霞, 黄伟翼. MMP14在胰腺癌中的表达及其与肿瘤免疫微环境特征的相关性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(3): 312-322. |
| [6] | 周佳蕾, 盛海斌, 王皓煜, 鲁岩, 王方方, 吴皓, 华云峰. 三维电镜在脑干耳蜗核神经元形态学研究中的应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(2): 142-149. |
| [7] | 徐康力1,马亚妮2,王筱金3,苗彦彦1,韩 达1#,谭蔚泓1#. 核酸适配体sgc8在急性白血病诊断中的应用研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(9): 1157-1167. |
| [8] | 王沄汉1,迟亚男1,杨冠恒2,范书玥1,马 姬1,薛 燕1, 2,曾凡一1, 2. 2类小鼠胎肝基质细胞的生物学特征及表达谱分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 39(11): 1226-. |
| [9] | 田烨,刘奥,董瑞,祁星,易静,杨洁. 流式细胞术在检测细胞氧化还原状态荧光蛋白探针中的应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2018, 38(1): 10-. |
| [10] | 栾晓蕊,李卫平 . 滤泡性辅助 T 细胞亚型与原因不明复发性流产的关系研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2017, 37(10): 1346-. |
| [11] | 符蓉,赵犇鹏,杨洁,等. 采用EDTA-胰酶处理难消化细胞株在凋亡检测分析中的可行性[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2015, 35(9): 1422-. |
| [12] | 阮莉莉,杜俊君,林 艳,等. CD64指数在新生儿脓毒症早期诊断中的意义[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2014, 34(10): 1503-. |
| [13] | 王 丽, 刘家应, 夏 敏, 等. 儿童急性白血病Th1和Th2细胞因子的临床研究[J]. , 2011, 31(11): 1657-. |
| [14] | 钟 华, 韩宝惠. 小鼠肺部肿瘤集聚髓源性抑制细胞实验研究[J]. , 2010, 30(9): 1176-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||