
Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science) ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 312-322.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2022.03.008
• Basic research • Previous Articles Next Articles
XU Jingxuan( ), DU Shaoqian, CAO Yuan, WANG Hongxia(
), DU Shaoqian, CAO Yuan, WANG Hongxia( ), HUANG Weiyi(
), HUANG Weiyi( )
)
Received:2021-12-24
Online:2022-03-28
Published:2022-05-09
Contact:
WANG Hongxia,HUANG Weiyi
E-mail:zzxjx1996@163.com;whx365@126.com;huangweiyi1976@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
XU Jingxuan, DU Shaoqian, CAO Yuan, WANG Hongxia, HUANG Weiyi. MMP14 expression in pancreatic cancer and its correlation with characteristics of tumor immune microenvironment[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(3): 312-322.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://xuebao.shsmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2022.03.008
| Antibody | Source | Identifier | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-CD45 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 564585 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD3 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 566517 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD4 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 560909 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD8 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 612943 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-TCRγδ | BD Biosciences | Cat# 562511 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD19 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 612917 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD56 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 557919 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD16 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 748850 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD11b | BD Biosciences | Cat# 747357 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD14 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 566465 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD66b | BD Biosciences | Cat# 561645 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD11c | BD Biosciences | Cat# 612968 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD123 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 563072 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-HLA-DR | BD Biosciences | Cat# 561358 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD206 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 741860 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD45 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-19597 | mIHC |
| Anti-CD8 | Abcam | Cat# ab237709 | mIHC |
| Anti-CD14 | Abcam | Cat# ab133335 | mIHC |
| Anti-CD68 | Abcam | Cat# ab955 | mIHC |
| Anti-MMP14 | Abcam | Cat# ab51074 | mIHC |
Tab 1 Information of antibodies
| Antibody | Source | Identifier | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-CD45 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 564585 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD3 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 566517 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD4 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 560909 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD8 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 612943 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-TCRγδ | BD Biosciences | Cat# 562511 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD19 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 612917 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD56 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 557919 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD16 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 748850 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD11b | BD Biosciences | Cat# 747357 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD14 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 566465 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD66b | BD Biosciences | Cat# 561645 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD11c | BD Biosciences | Cat# 612968 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD123 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 563072 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-HLA-DR | BD Biosciences | Cat# 561358 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD206 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 741860 | Flow cytometry |
| Anti-CD45 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-19597 | mIHC |
| Anti-CD8 | Abcam | Cat# ab237709 | mIHC |
| Anti-CD14 | Abcam | Cat# ab133335 | mIHC |
| Anti-CD68 | Abcam | Cat# ab955 | mIHC |
| Anti-MMP14 | Abcam | Cat# ab51074 | mIHC |
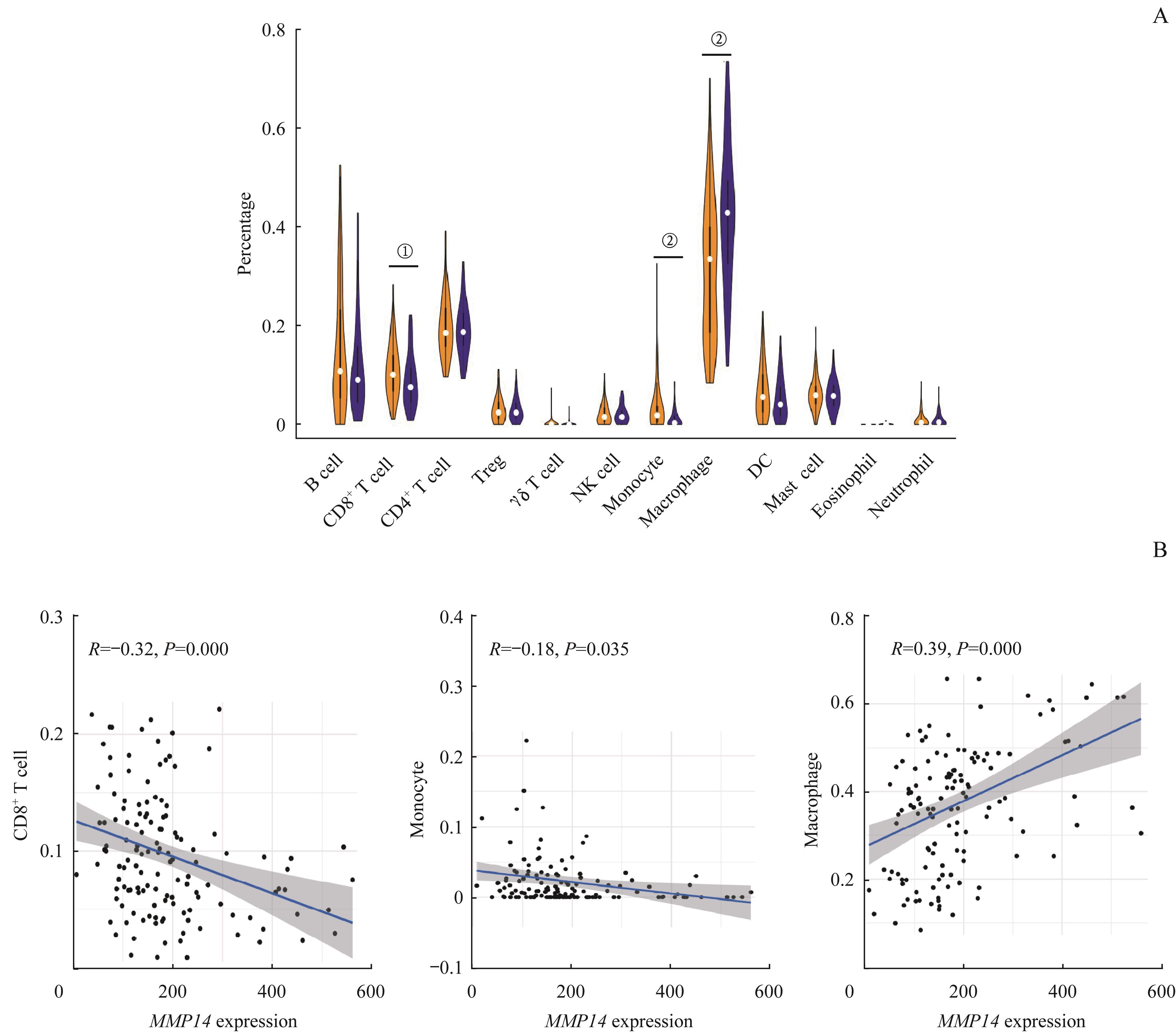
Fig 3 Distribution differences of tumor-infiltrating immune cells in the pancreatic cancer with different MMP14 expression levels and the correlation between the percentage of immune cell subsets and MMP14 expression in TCGA database
| 1 | ANSARI D, TINGSTEDT B, ANDERSSON B, et al. Pancreatic cancer: yesterday, today and tomorrow[J]. Future Oncol, 2016, 12(16): 1929-1946. |
| 2 | PISHVAIAN M J, BLAIS E M, BRODY J R, et al. Overall survival in patients with pancreatic cancer receiving matched therapies following molecular profiling: a retrospective analysis of the Know Your Tumor registry trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2020, 21(4): 508-518. |
| 3 | 王超, 宁克, 胡欢欢, 等. 胰腺癌肿瘤微环境的研究进展[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2020, 19(1): 109-112. |
| 4 | LI H B, YANG Z H, GUO Q Q. Immune checkpoint inhibition for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: limitations and prospects: a systematic review[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2021, 19(1): 117. |
| 5 | DANGAJ D, BRUAND M, GRIMM A J, et al. Cooperation between constitutive and inducible chemokines enables T cell engraftment and immune attack in solid tumors[J]. Cancer Cell, 2019, 35(6): 885-900.e10. |
| 6 | SHI B, CHU J F, HUANG T, et al. The scavenger receptor MARCO expressed by tumor-associated macrophages are highly associated with poor pancreatic cancer prognosis[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 771488. |
| 7 | AGER C R, BODA A, RAJAPAKSHE K, et al. High potency STING agonists engage unique myeloid pathways to reverse pancreatic cancer immune privilege[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2021, 9(8): e003246. |
| 8 | KAUR K, KO M W, CHEN F, et al. Defective NK cell expansion, cytotoxicity, and lack of ability to differentiate tumors from a pancreatic cancer patient in a long term follow-up: implication in the progression of cancer[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2021. DOI: 10.1007/s00262-021-03044-w. |
| 9 | GUO J, LIAO M F, HU X M, et al. Tumour-derived Reg3A educates dendritic cells to promote pancreatic cancer progression[J]. Mol Cells, 2021, 44(9): 647-657. |
| 10 | OSTIOS-GARCIA L, VILLAMAYOR J, GARCIA-LORENZO E, et al. Understanding the immune response and the current landscape of immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2021, 27(40): 6775-6793. |
| 11 | MÄÄTTÄ M, SOINI Y, LIAKKA A, et al. Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-9, and membrane type 1-MMP in hepatocellular and pancreatic adenocarcinoma: implications for tumor progression and clinical prognosis[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2000, 6(7): 2726-2734. |
| 12 | DECOTRET L R, WADSWORTH B J, LI L V, et al. Receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha (PTPα) mediates MMP14 localization and facilitates triple-negative breast cancer cell invasion[J]. Mol Biol Cell, 2021, 32(7): 567-578. |
| 13 | YU J, HE Z, HE X W, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the expression and prognosis for MMPs in human colorectal cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 771099. |
| 14 | HILLEBRAND L E, WICKBERG S M, GOMEZ-AULI A, et al. MMP14 empowers tumor-initiating breast cancer cells under hypoxic nutrient-depleted conditions[J]. FASEB J, 2019, 33(3): 4124-4140. |
| 15 | ULASOV I V, MIJANOVIC O, SAVCHUK S, et al. TMZ regulates GBM stemness via MMP14-DLL4-Notch3 pathway[J]. Int J Cancer, 2020, 146(8): 2218-2228. |
| 16 | QIANG L, CAO H, CHEN J, et al. Pancreatic tumor cell metastasis is restricted by MT1-MMP binding protein MTCBP-1[J]. J Cell Biol, 2019, 218(1): 317-332. |
| 17 | 袁蒙, 阿卜杜海拜尔·萨杜拉, 任思谦, 等. 胰腺癌免疫微环境特点与相关免疫治疗策略[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2021, 101(12): 831-835. |
| 18 | OH D Y, KWEK S S, RAJU S S, et al. Intratumoral CD4+ T cells mediate anti-tumor cytotoxicity in human bladder cancer[J]. Cell, 2020, 181(7): 1612-1625.e13. |
| 19 | DI PILATO M, KFURI-RUBENS R, PRUESSMANN J N, et al. CXCR6 positions cytotoxic T cells to receive critical survival signals in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(17): 4512-4530.e22. |
| 20 | DALEY D, ZAMBIRINIS C P, SEIFERT L, et al. γδ T cells support pancreatic oncogenesis by restraining αβ T cell activation[J]. Cell, 2016, 166(6): 1485-1499.e15. |
| 21 | MILLER-OCUIN J L, LIANG X Y, BOONE B A, et al. DNA released from neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) activates pancreatic stellate cells and enhances pancreatic tumor growth[J]. Oncoimmunology, 2019, 8(9): e1605822. |
| 22 | POINCLOUX R, LIZÁRRAGA F, CHAVRIER P. Matrix invasion by tumour cells: a focus on MT1-MMP trafficking to invadopodia[J]. J Cell Sci, 2009, 122(Pt 17): 3015-3024. |
| 23 | SATHYAMOORTHY T, TEZERA L B, WALKER N F, et al. Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase regulates monocyte migration and collagen destruction in tuberculosis[J]. J Immunol, 2015, 195(3): 882-891. |
| 24 | LING B B, WATT K, BANERJEE S, et al. A novel immunotherapy targeting MMP-14 limits hypoxia, immune suppression and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer models[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(35): 58372-58385. |
| 25 | ANDREOU T, WILLIAMS J, BROWNLIE R J, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy targeting TGFβ enhances the efficacy of irradiation therapy in a preclinical glioblastoma model[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2021, 9(3): e001143. |
| 26 | FARHOOD B, NAJAFI M, MORTEZAEE K. CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in cancer immunotherapy: a review[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(6): 8509-8521. |
| 27 | XIA Q, JIA J, HU C P, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages promote PD-L1 expression in tumor cells by regulating PKM2 nuclear translocation in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Oncogene, 2022, 41(6): 865-877. |
| 28 | HALBROOK C J, PONTIOUS C, KOVALENKO I, et al. Macrophage-released pyrimidines inhibit gemcitabine therapy in pancreatic cancer[J]. Cell Metab, 2019, 29(6): 1390-1399.e6. |
| 29 | CAO D J, SONG Q Q, LI J Q, et al. Opportunities and challenges in targeted therapy and immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer[J]. Expert Rev Mol Med, 2021, 23: e21. |
| [1] | Jianru WANG, Guangcao PENG, Mingjun ZHU. Screening potential hub genes associated with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice based on GEO database and bioinformatics analysis [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2022, 42(1): 51-62. |
| [2] | Jing-wei LI, Li-wen WANG, Ling-xi JIANG, Qian ZHAN, Hao CHEN, Bai-yong SHEN. Review of immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment of pancreatic cancer [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2021, 41(8): 1103-1108. |
| [3] | Lu-di YANG, Gao-ming WANG, Ren-hao HU, Xiao-hua JIANG, Ran CUI. Identification of core genes in pancreatic cancer progression by bioinformatics analysis [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2021, 41(5): 571-578. |
| [4] | XU Kang-li1, MA Ya-ni2, WANG Xiao-jin3, MIAO Yan-yan1, HAN Da1#, TAN Wei-hong1#. Using aptamer of sgc8 for diagnosis of acute leukemia [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2020, 40(9): 1157-1167. |
| [5] | GAO Jing-ze, WU Xia. CXCL9 mRNA in ovarian tumor tissue and its relations with prognosis and characteristics of immune microenvironment [J]. , 2020, 40(4): 457-. |
| [6] | ZHANG Wei-ran1, 2, LIN Xue-feng3, LI Xin2, ZHANG Hao2, WANG Meng2, SUN Wei2, HAN Xing-peng2, SUN Da-qiang1, 4. Transcriptional identification of potential biomarkers of lung adenocarcinoma [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2020, 40(12): 1598-1606. |
| [7] | LIANG Yu, JIANG Ming-jie, TIAN Ling. Advances in prostaglandin E2 reprogramming pancreatic cancer microenvironment [J]. , 2019, 39(8): 923-. |
| [8] | ZHANG Peng1, CHANG Zheng-yan2, YANG Lei1, XUE Song1, LIAN Feng1. Bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed genes in ischemic cardiomyopathy [J]. , 2019, 39(7): 698-. |
| [9] | WANG Yun-han1, CHI Ya-nan1, YANG Guan-heng2, FAN Shu-yue1, MA Ji1, XUE Yan1, 2, ZENG Fan-yi1, 2. Biological characteristics and gene profile analysis of two kinds of mofetal liver stromal cells [J]. , 2019, 39(11): 1226-. |
| [10] | ZHANG Xiao-cui, FU Rong, ZHAO Ben-peng. Condition optimization of the flow cytometry MoFlo Astrios EQ on single-cell sorting in 96-well plate [J]. , 2018, 38(7): 845-. |
| [11] | TIAN Ye, LIU Ao, DONG Rui, QI Xing, YI Jing, YANG Jie. Flow cytometry detection of cellular redox status with genetically encoded fluorescent probe [J]. , 2018, 38(1): 10-. |
| [12] | LUAN Xiao-rui, LI Wei-ping . Relationship between subtypes of T follicular helper cells and unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion [J]. , 2017, 37(10): 1346-. |
| [13] | LI Xiao-ping, ZHANG Xiao-wei, GUO Wei-jian, et al. Expression of CD44 of patients with pancreatic cancer and its clinical significance [J]. , 2015, 35(9): 1354-. |
| [14] | FU Rong, ZHAO Ben-peng, YANG Jie, et al. Feasibility on treating indigestible cell lines by trypsin-EDTA solution for detection of cell apoptosis [J]. , 2015, 35(9): 1422-. |
| [15] | HU Bin, SONG Shao-li. Progresses of treatment of pancreatic cancer [J]. , 2015, 35(3): 445-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||