
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (12): 1593-1600.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.12.013
• 综述 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-02-01
接受日期:2024-09-03
出版日期:2024-12-16
发布日期:2024-12-16
通讯作者:
刘梅芳
E-mail:2682445008@qq.com;lmf00719@163.com
作者简介:衣文婧(2002—),女,本科生;电子信箱:2682445008@qq.com。
基金资助:
YI Wenjing( ), FAN Yixuan, QIU Jiatai, FU Xiaoyan, LIU Meifang(
), FAN Yixuan, QIU Jiatai, FU Xiaoyan, LIU Meifang( )
)
Received:2024-02-01
Accepted:2024-09-03
Online:2024-12-16
Published:2024-12-16
Contact:
LIU Meifang
E-mail:2682445008@qq.com;lmf00719@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
炎症反应是机体应对感染或损伤等刺激时产生的系统性响应过程,与多种疾病的发生机制密切相关,并在疾病进展与转归过程中起着重要作用。正常情况下,炎症反应能够在机体受损不严重时做出响应并维持组织稳态;而在受到较严重的刺激时,失控的炎症反应往往会对机体造成严重危害。理想的炎症反应是在消除了炎症刺激后终止响应,因此有效调控炎症反应的程度和范围显得尤为重要。β-抑制蛋白1(β-arrestin 1,ARRB1)是一种多功能调节蛋白,在G蛋白偶联受体(G protein-coupled receptor,GPCR)和非GPCR介导的信号转导中发挥关键作用;同时,该蛋白还参与部分免疫细胞发育、分化等功能的调控。尽管ARRB1最初被认为是GPCR信号转导的终止子,可抑制炎症反应,但近年来的研究提示ARRB1在炎症反应中的作用较为复杂,具有抑制炎症和促进炎症的双重作用。基于此,该文回顾了近年来ARRB1与炎症反应的相关研究,详细阐述并讨论了ARRB1对信号通路转导和免疫细胞发育、分化功能的调控作用以及其调控炎症性疾病进展的作用机制,以期为炎症性疾病的临床精准治疗和药物效应靶点的筛选提供新思路。
中图分类号:
衣文婧, 范宜璇, 仇佳泰, 付晓燕, 刘梅芳. β-抑制蛋白1在炎症反应调控中作用的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(12): 1593-1600.
YI Wenjing, FAN Yixuan, QIU Jiatai, FU Xiaoyan, LIU Meifang. Research progress in the role of β-arrestin 1 in the regulation of inflammatory response[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(12): 1593-1600.
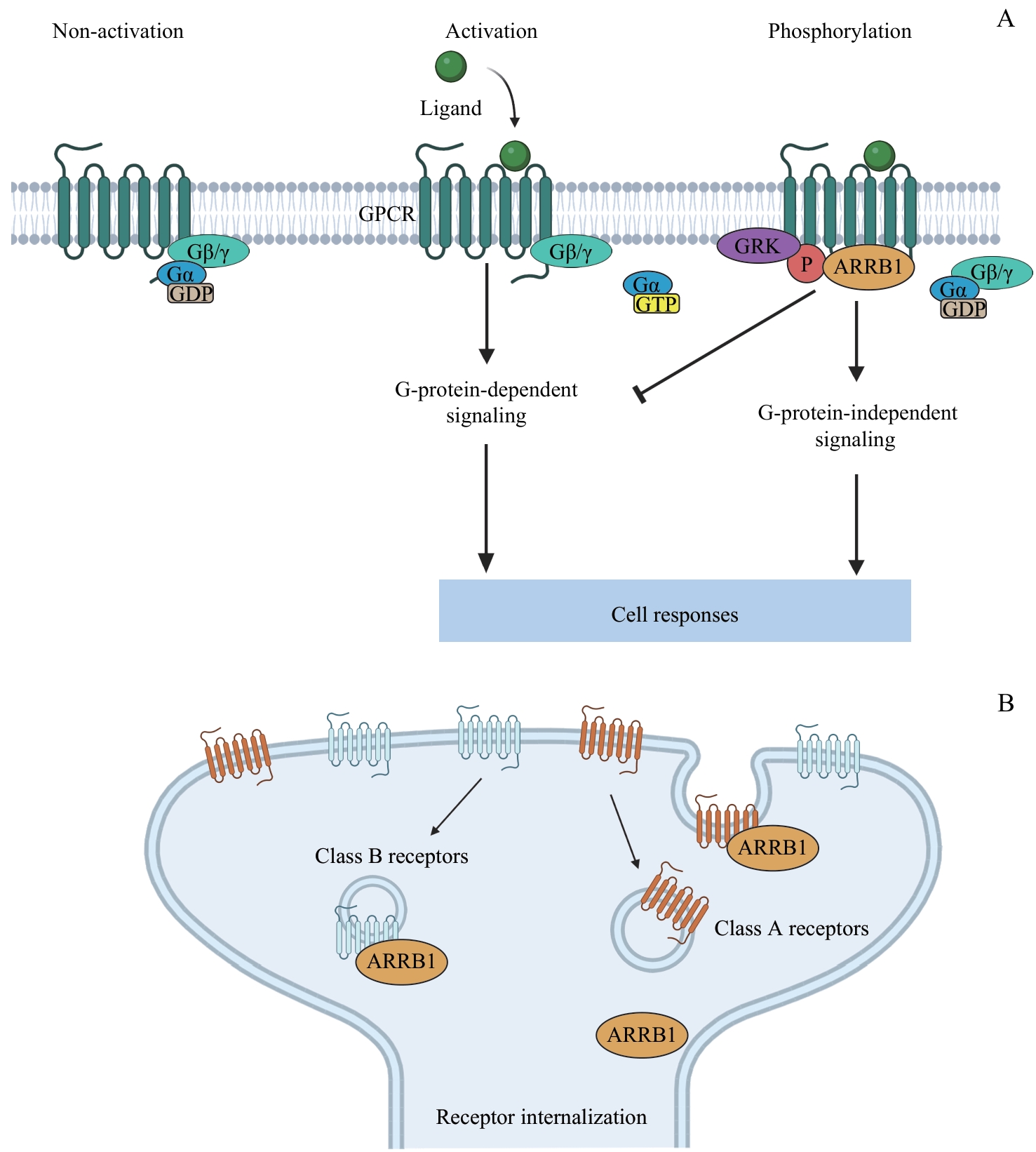
图1 ARRB1调控细胞内信号转导的相关机制示意图Note: A. ARRB1 is involved in GPCR desensitization and activation of G-protein-independent signaling pathways. B. ARRB1 is involved in receptor internalization.
Fig 1 Schematic diagram of the mechanism by which ARRBl regulates intracellular signal transduction
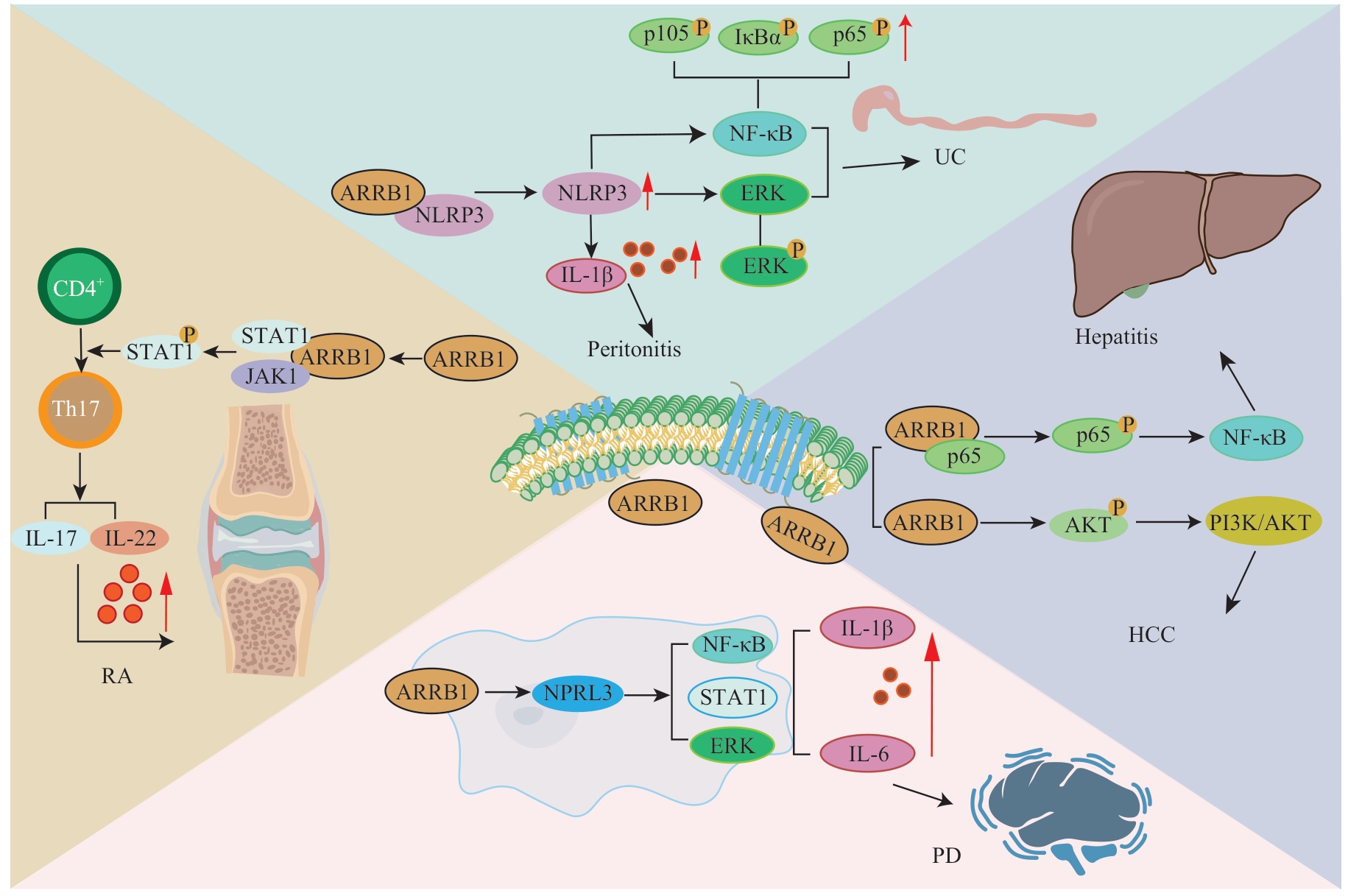
图3 ARRB1促进炎症反应的机制总结图示Note: IκBα—inhibitor-κ binding protein α; HCC—hepatocellular carcinoma; PD—Parkinson's disease; RA—rheumatoid arthritis.
Fig 3 Summary diagram of the mechanism of ARRB1 promoting inflammatory response
| 1 | CHEN S Z, HUANG M Y, ZHANG L M, et al. Inflammatory response signature score model for predicting immunotherapy response and pan-cancer prognosis[J]. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2024, 23: 369-383. |
| 2 | AGIRMAN G, YU K B, HSIAO E Y. Signaling inflammation across the gut-brain axis[J]. Science, 2021, 374(6571): 1087-1092. |
| 3 | SCHROEDER H T, DE LEMOS MULLER C H, HECK T G, et al. Heat shock response during the resolution of inflammation and its progressive suppression in chronic-degenerative inflammatory diseases[J]. Cell Stress Chaperones, 2024, 29(1): 116-142. |
| 4 | FURMAN D, CAMPISI J, VERDIN E, et al. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span[J]. Nat Med, 2019, 25(12): 1822-1832. |
| 5 | YING W, FU W X, LEE Y S, et al. The role of macrophages in obesity-associated islet inflammation and β-cell abnormalities[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2020, 16(2): 81-90. |
| 6 | LI D J, TONG J, LI Y H, et al. Melatonin safeguards against fatty liver by antagonizing TRAFs-mediated ASK1 deubiquitination and stabilization in a β-arrestin-1 dependent manner[J]. J Pineal Res, 2019, 67(4): e12611. |
| 7 | DAWED A Y, MARI A, BROWN A, et al. Pharmacogenomics of GLP-1 receptor agonists: a genome-wide analysis of observational data and large randomised controlled trials[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2023, 11(1): 33-41. |
| 8 | DEWIRE S M, AHN S, LEFKOWITZ R J, et al. β-arrestins and cell signaling[J]. Annu Rev Physiol, 2007, 69: 483-510. |
| 9 | LOVGREN A K, KOVACS J J, XIE T, et al. β-arrestin deficiency protects against pulmonary fibrosis in mice and prevents fibroblast invasion of extracellular matrix[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2011, 3(74): 74ra23. |
| 10 | CHOI Y J, KIM J E, LEE S J, et al. Promotion of the inflammatory response in mid colon of complement component 3 knockout mice[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 1700. |
| 11 | 张泉, 张梅. β-arrestin1在炎-癌转化中的研究进展[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2022, 30(15): 2864-2867. |
| ZHANG Q, ZHANG M. Research progress of β-arrestin1 in inflammation-induced carcinogenesis[J]. Journal of Modern Oncology, 2022, 30(15): 2864-2867. | |
| 12 | MAFI A, KIM S K, GODDARD WA 3rd. The mechanism for ligand activation of the GPCR-G protein complex[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2022, 119(18): e2110085119. |
| 13 | LEFKOWITZ R J, SHENOY S K. Transduction of receptor signals by β-arrestins[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5721): 512-517. |
| 14 | KO M J, CHIANG T, MUKADAM A A, et al. β-arrestin-dependent ERK signaling reduces anxiety-like and conditioned fear-related behaviors in mice[J]. Sci Signal, 2021, 14(694): eaba0245. |
| 15 | ZHANG Z, ZHONG X H, XIAO Y P, et al. MicroRNA-296 inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and enhances apoptosis by targeting ARRB1-mediated AKT activation[J]. Oncol Rep, 2019, 41(1): 619-629. |
| 16 | LI J, WEI B, GUO A, et al. Deficiency of β-arrestin1 ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis with impaired TH17 cell differentiation[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2013, 110(18): 7395-7400. |
| 17 | XU X, LEI Y M, CHEN L J, et al. Phosphorylation of NF-κBp65 drives inflammation-mediated hepatocellular carcinogenesis and is a novel therapeutic target[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 40(1): 253. |
| 18 | RANJAN R, GUPTA P, SHUKLA A K. GPCR signaling: β-arrestins kiss and remember[J]. Curr Biol, 2016, 26(7): R285-R288. |
| 19 | OAKLEY R H, LAPORTE S A, HOLT J A, et al. Differential affinities of visual arrestin, β arrestin1, and β arrestin2 for G protein-coupled receptors delineate two major classes of receptors[J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275(22): 17201-17210. |
| 20 | CHEN K, ZHANG C H, LIN S L, et al. Tail engagement of arrestin at the glucagon receptor[J]. Nature, 2023, 620(7975): 904-910. |
| 21 | SUN L N, SU Y H, JIAO A J, et al. T cells in health and disease[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 235. |
| 22 | 陈燕华, 蒋光洁, 郭维, 等. Arrb1基因敲除对小鼠T淋巴细胞发育的影响[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报, 2018, 40(3): 373-380. |
| CHEN Y H, JIANG G J, GUO W, et al. Effects of Arrb1 knockout on the development of mice T lymphocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Cell Biology, 2018, 40(3): 373-380. | |
| 23 | GUREVICH V V, GUREVICH E V. Arrestin makes T cells stop and become active[J]. EMBO J, 2014, 33(6): 531-533. |
| 24 | BJØRGO E, TASKÉN K. Novel mechanism of signaling by CD28[J]. Immunol Lett, 2010, 129(1): 1-6. |
| 25 | ABRAHAMSEN H, BAILLIE G, NGAI J, et al. TCR- and CD28-mediated recruitment of phosphodiesterase 4 to lipid rafts potentiates TCR signaling[J]. J Immunol, 2004, 173(8): 4847-4858. |
| 26 | SHI Y F, FENG Y, KANG J H, et al. Critical regulation of CD4+ T cell survival and autoimmunity by β-arrestin 1[J]. Nat Immunol, 2007, 8(8): 817-824. |
| 27 | GÓMEZ-MELERO S, GARCÍA-MACEIRA F I, GARCÍA-MACEIRA T, et al. Amino terminal recognition by a CCR6 chemokine receptor antibody blocks CCL20 signaling and IL-17 expression via β-arrestin[J]. BMC Biotechnol, 2021, 21(1): 41. |
| 28 | KUMAR R, THEISS A L, VENUPRASAD K. RORγt protein modifications and IL-17-mediated inflammation[J]. Trends Immunol, 2021, 42(11): 1037-1050. |
| 29 | CAO Y P, HE W, LI X P, et al. Rosiglitazone protects against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting multiple endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2022, 2022: 6098592. |
| 30 | LEI Y M, WAN S Z, LIU H L, et al. ARRB1 suppresses the activation of hepatic macrophages via modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2021, 7(1): 223. |
| 31 | WU B S, ZHOU Q, HE Z Q, et al. Protective effect of the Abelmoschus manihot flower extract on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021: 7422792. |
| 32 | KANG S, NARAZAKI M, METWALLY H, et al. Historical overview of the interleukin-6 family cytokine[J]. J Exp Med, 2020, 217(5): e20190347. |
| 33 | FANG Y Q, JIANG Q L, LI S S, et al. Opposing functions of β-arrestin 1 and 2 in Parkinson's disease via microglia inflammation and Nprl3[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2021, 28(6): 1822-1836. |
| 34 | ZHANG Q, XU N, HU X, et al. Anti-colitic effects of Physalin B on dextran sodium sulfate-induced BALB/c mice by suppressing multiple inflammatory signaling pathways[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 259: 112956. |
| 35 | MAO K, CHEN S, WANG Y, et al. β-arrestin1 is critical for the full activation of NLRP3 and NLRC4 inflammasomes[J]. J Immunol, 2015, 194(4): 1867-1873. |
| 36 | YANG Y D, GUO Y W, TAN S W, et al. β-arrestin1 enhances hepatocellular carcinogenesis through inflammation-mediated Akt signalling[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6: 7369. |
| 37 | ZHANG Z C, XU X L, TIAN W F, et al. ARRB1 inhibits non-alcoholic steatohepatitis progression by promoting GDF15 maturation[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 72(5): 976-989. |
| 38 | ZHUANG L N, HU W X, XIN S M, et al. β-arrestin-1 protein represses adipogenesis and inflammatory responses through its interaction with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ)[J]. J Biol Chem, 2011, 286(32): 28403-28413. |
| 39 | TAO L, LIN X Y, TAN S W, et al. β-arrestin1 alleviates acute pancreatitis via repression of NF-κBp65 activation[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 34(1): 284-292. |
| 40 | WITHEROW D S, GARRISON T R, MILLER W E, et al. β-arrestin inhibits NF-κB activity by means of its interaction with the NF-κB inhibitor IκBα[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2004, 101(23): 8603-8607. |
| 41 | ZHENG F, XIAO F, YUAN Q H, et al. Penehyclidine hydrochloride decreases pulmonary microvascular endothelial inflammatory injury through a β-arrestin-1-dependent mechanism[J]. Inflammation, 2018, 41(5): 1610-1620. |
| 42 | FAN H K, LUTTRELL L M, TEMPEL G E, et al. β-arrestins 1 and 2 differentially regulate LPS-induced signaling and pro-inflammatory gene expression[J]. Mol Immunol, 2007, 44(12): 3092-3099. |
| 43 | WANG M W, YANG Z, CHEN X, et al. Activation of PTH1R alleviates epididymitis and orchitis through Gq and β-arrestin-1 pathways[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2021, 118(45): e2107363118. |
| 44 | SHU Y, WANG Y, LV W Q, et al. ARRB1-promoted NOTCH1 degradation is suppressed by oncomiR miR-223 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia[J]. Cancer Res, 2020, 80(5): 988-998. |
| [1] | 王莹, 平立风, 刘彤彤, 刘珊珊, 刘磊. 甲基莲心碱调节SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路对糖尿病肾病的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 183-195. |
| [2] | 王卫, 王红丽, 阿力比亚提·艾尼, 衣力亚尔·肉苏, 阿依努尔, 杨亮. 血管抑制蛋白2在三阴性乳腺癌中的功能及其调控可变剪接机制[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(12): 1526-1535. |
| [3] | 洪磊, 郭传亮, 蔡勤, 李婉睿, 曾溢滔, 薛燕, 曾凡一. 双同源盒诱导小鼠胚胎干细胞向胚外内胚层分化的机制研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(11): 1359-1369. |
| [4] | 施泽纶, 王青, 何雯, 傅唯佳, 王颖雯, 韩晓, 张晓波. 纳米塑料诱导肺泡Ⅱ型上皮细胞DNA损伤加重重症哮喘[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(11): 1391-1405. |
| [5] | 宣臻全, 陈轩祎, 姚志荣. 神经免疫紊乱在特应性皮炎中的作用研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(8): 1049-1055. |
| [6] | 王青, 韩晓, 张晓波. 表观遗传修饰调控肺炎免疫应答的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 931-938. |
| [7] | 李清林, 王文波, 刘伟. 肌腱去应力退化机制的生物信息学分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 560-570. |
| [8] | 潘泓, 廖颖娜, 盖严支, 钱立恒, 聂惠贞. 分选链接蛋白1在胰腺导管腺癌中的表达及其促进胰腺导管腺癌进展的机制研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(3): 278-292. |
| [9] | 吴以加, 房燕, 沈菲洋, 黄蕊, 沈键锋, 范先群. FBXO38通过PI3K-Akt信号通路调控眼部黑色素瘤增殖[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(12): 1470-1479. |
| [10] | 谢小雷, 江佩欣, 张敬鸿, 莫骏健, 吴可凡, 曾康逸. 视网膜母细胞瘤结合锌指蛋白1调控肥胖和肿瘤信号通路研究综述[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 114-119. |
| [11] | 杨文倩, 陈迟琪, 赵路, 曹力元, 夏一秋, 卢智刚, 郑俊克. 免疫抑制性受体LILRB2促进新型冠状病毒刺突蛋白介导的炎症过程[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(9): 1188-1196. |
| [12] | 褚云开, 廖春华, 邓华云, 黄雷. 黏蛋白1与肿瘤相关蛋白的调控网络研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(8): 1024-1033. |
| [13] | 林家俞, 秦洁洁, 蒋玲曦. 肿瘤微环境中免疫细胞的代谢研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(8): 1122-1130. |
| [14] | 戴芹, 王伟铭. IgA肾病细胞模型中的炎症表达及丙戊酸钠的抗炎作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(6): 751-757. |
| [15] | 张桓瑜, 江旖婷, 朱晓晨, 何智妍, 周薇, 宋忠臣. 牙龈素提取物对小鼠脑神经炎症的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(5): 570-577. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||