
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (8): 1008-1016.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2023.08.008
• 论著 · 基础研究 •
收稿日期:2023-04-18
接受日期:2023-05-06
出版日期:2023-08-28
发布日期:2023-08-28
通讯作者:
曹清
E-mail:tsuyo300@163.com;caoqing@scmc.com.cn
作者简介:宋文汀(1997—),女,硕士生;电子信箱:tsuyo300@163.com。
SONG Wenting1( ), TAO Yue2, PAN Yi2, MO Xi2, CAO Qing1(
), TAO Yue2, PAN Yi2, MO Xi2, CAO Qing1( )
)
Received:2023-04-18
Accepted:2023-05-06
Online:2023-08-28
Published:2023-08-28
Contact:
CAO Qing
E-mail:tsuyo300@163.com;caoqing@scmc.com.cn
摘要:
目的·探讨沉默信息调节因子2(silent information regulator 2,SIRT2)通过组蛋白H4第8位赖氨酸(H4K8)去乳酸化修饰对早期感染后巨噬细胞免疫表型的调节作用及相应机制。方法·使用佛波醇-12-肉豆蔻酸酯-13-乙酸酯(phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate,PMA)诱导人单核细胞白血病THP-1细胞,使其分化为具有巨噬细胞特性的人血单核细胞株(PMA-primed THP-1,pTHP-1),再以脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide,LPS)刺激建立巨噬细胞感染模型。将未经LPS处理的巨噬细胞(pTHP-1)设为对照(CTRL)组,经过LPS处理的巨噬细胞设为感染(LPS)组。通过蛋白质印迹法(Western blotting)检测巨噬细胞中组蛋白乳酸化各位点修饰水平、组蛋白乙酰化各位点修饰水平及SIRT2蛋白水平;通过实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)方法检测2组间糖酵解限速酶乳酸脱氢酶A(lactate dehydrogenase A,LDHA)、肝脏磷酸果糖激酶(phosphofructokinase liver type,PKFL),糖酵解调剂因子低氧诱导因子1α(hypoxia inducible factor 1α,HIF-1α),以及Sirtuin家族基因和HDAC家族基因表达水平;通过Transwell方法检测巨噬细胞趋化能力;使用慢病毒包装及细胞感染方法建立SIRT2过表达细胞系;使用RNA测序技术(RNA sequencing,RNA-seq)与染色质免疫共沉淀测序技术(chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing,ChIP-seq)交互分析方法对组蛋白H4第8位赖氨酸乳酸化(lactylation of histone H4 lysine 8,H4K8la)特异性结合的基因进行差异性分析及通路富集分析。结果·相较于CTRL组,LPS组巨噬细胞糖酵解上调,组蛋白H4K8位点乳酸化水平显著增加(P<0.05),而组蛋白其余位点乙酰化水平未见显著变化。所有已知的具有去乳酸化修饰功能的酶中,仅SIRT2在LPS处理后出现显著降低(P<0.05),且SIRT2过表达可显著抑制巨噬细胞中组蛋白H4K8位点的乳酸化水平(P<0.05),但不影响组蛋白H4K8位点的乙酰化水平(P>0.05)。ChIP-seq与RNA-seq交互分析发现,组蛋白H4K8位点乳酸化修饰可调控巨噬细胞趋化相关基因,并且巨噬细胞的趋化能力在SIRT2过表达、H4K8la修饰水平下调后显著下降(P<0.05)。结论·SIRT2可通过去修饰组蛋白H4K8位点乳酸化改变趋化相关靶基因表达,从而降低巨噬细胞趋化能力。靶向SIRT2及H4K8la修饰将有助于控制巨噬细胞介导的炎症反应。
中图分类号:
宋文汀, 陶悦, 潘艺, 莫茜, 曹清. SIRT2通过组蛋白H4K8去乳酸化修饰调控巨噬细胞趋化功能[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(8): 1008-1016.
SONG Wenting, TAO Yue, PAN Yi, MO Xi, CAO Qing. SIRT2 regulates macrophage chemotaxis by de-modifying histone H4K8 lactylation[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(8): 1008-1016.
| Gene | Forward primer (5´→3´) | Reverse primer (5´→3´) |
|---|---|---|
| HIF-1α | GAACGTCGAAAAGAAAAGTCTCG | CCTTATCAAGATGCGAACTCACA |
| PFKL | GTACCTGGCGCTGGTATCTG | CCTCTCACACATGAAGTTCTCC |
| LDHA | ATGGCAACTCTAAAFFATCAGC | CCAACCCCAACAACTGTAATCT |
| SIRT1 | AGGCCACGGATAGGTCCATA | GTGGAGGTATTGTTTCCGGC |
| SIRT2 | TGCGGAACTTATTCTCCCAGA | GAGAGCGAAAGTCGGGGAT |
| SIRT3 | TGCTCATCAACCGGGACTTG | TTGTCTGGTCCATCAAGCCTA |
| SIRT5 | CTCAAGATGCCAGCATCCCA | AGGAAGTGCCCACCACTAGA |
| HDAC1 | CATCGCTGTGAATTGGGCTG | ACCCTCTGGTGATACTTTAGCAG |
| HDAC2 | TCTGCTACTACTACGACGGTGA | TCATTTCTTCGGCAGTGGCT |
| HDAC3 | CATGACGGTGTCCTTCCACA | CAGAGTCAGCTCCACACTGG |
| GAPDH | TCTCCTCTGACTTCAACAGCGACA | CCCTGTTGCTGTAGCCAAATTCGT |
表1 RT-qPCR引物序列
Tab 1 Primer sequences for real-time qPCR
| Gene | Forward primer (5´→3´) | Reverse primer (5´→3´) |
|---|---|---|
| HIF-1α | GAACGTCGAAAAGAAAAGTCTCG | CCTTATCAAGATGCGAACTCACA |
| PFKL | GTACCTGGCGCTGGTATCTG | CCTCTCACACATGAAGTTCTCC |
| LDHA | ATGGCAACTCTAAAFFATCAGC | CCAACCCCAACAACTGTAATCT |
| SIRT1 | AGGCCACGGATAGGTCCATA | GTGGAGGTATTGTTTCCGGC |
| SIRT2 | TGCGGAACTTATTCTCCCAGA | GAGAGCGAAAGTCGGGGAT |
| SIRT3 | TGCTCATCAACCGGGACTTG | TTGTCTGGTCCATCAAGCCTA |
| SIRT5 | CTCAAGATGCCAGCATCCCA | AGGAAGTGCCCACCACTAGA |
| HDAC1 | CATCGCTGTGAATTGGGCTG | ACCCTCTGGTGATACTTTAGCAG |
| HDAC2 | TCTGCTACTACTACGACGGTGA | TCATTTCTTCGGCAGTGGCT |
| HDAC3 | CATGACGGTGTCCTTCCACA | CAGAGTCAGCTCCACACTGG |
| GAPDH | TCTCCTCTGACTTCAACAGCGACA | CCCTGTTGCTGTAGCCAAATTCGT |
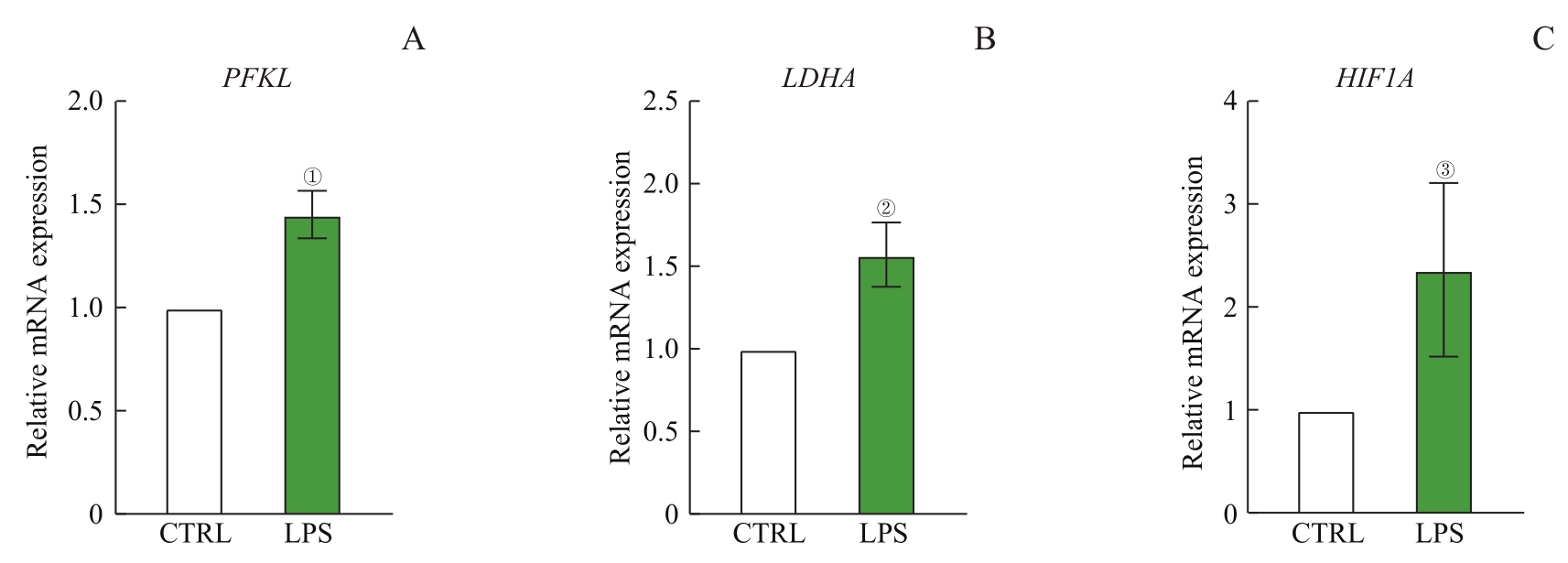
图1 RT-qPCR检测巨噬细胞糖酵解限速酶及糖酵解调节因子表达Note: ①P=0.027, ②P=0.015, ③P=0.049, compared with the CTRL group.
Fig 1 Expression of glycolytic rate-limiting enzyme and transcription factors in macrophages detected by RT-qPCR
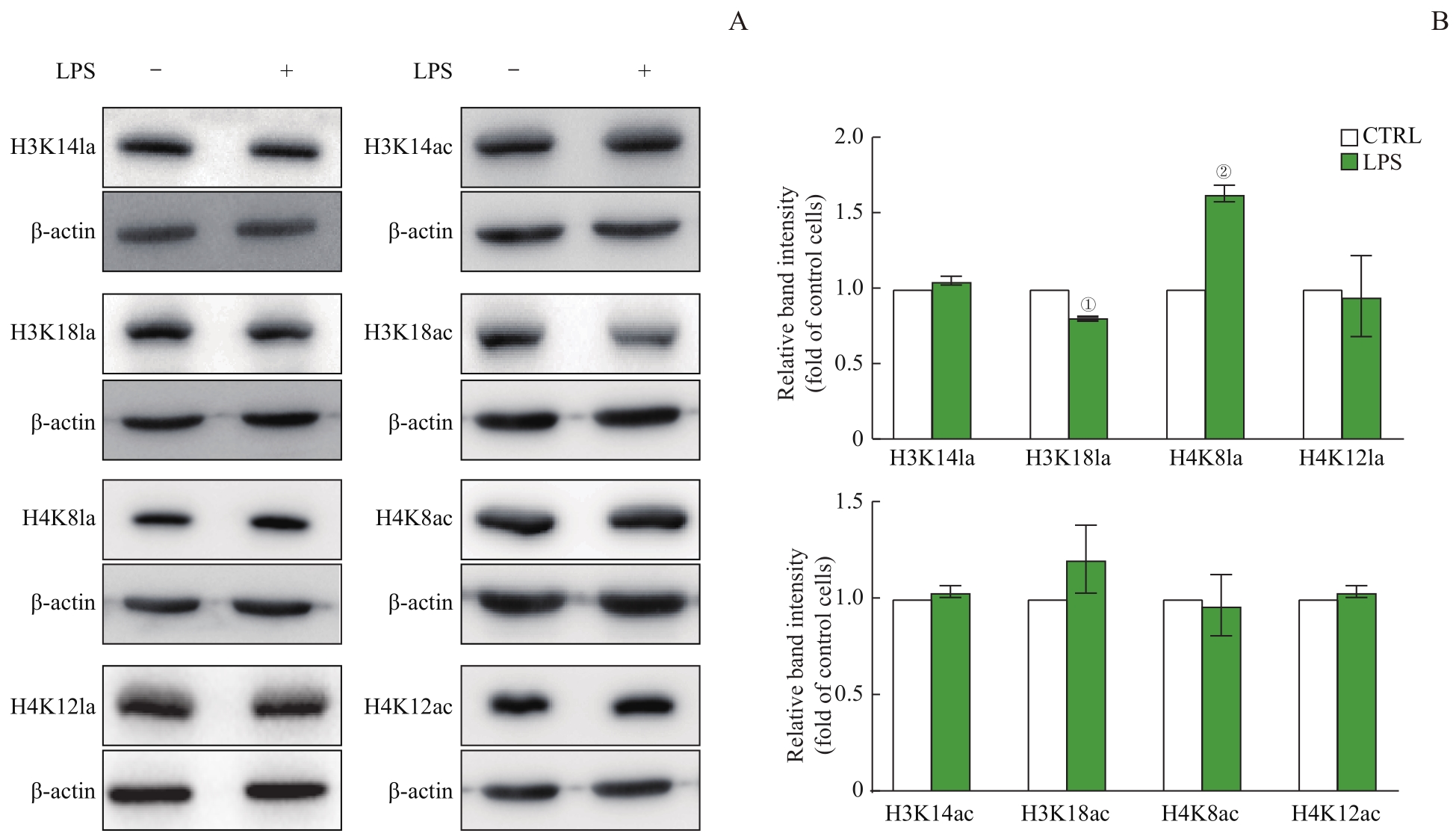
图2 蛋白质印迹法检测巨噬细胞组蛋白修饰水平Note: A. Detection of histone lactylation (left) and acetylation (right) levels by Western blotting. B. Expression of histone lactylation (above) and acetylation (below). ①P=0.000,②P=0.002, compared with the CTRL group.
Fig 2 Histone modification levels in macrophages detected by Western blotting

图3 LPS处理后巨噬细胞Sirtuin家族和 HDAC 家族的RNA表达水平Note: A. Expression of Sirtuin family mRNA. B. Expression of HDAC family mRNA. C. Detection of SIRT2 protein by Western blotting. ①P=0.010, compared with the CTRL group.
Fig 3 RNA expression levels of Sirtuin family and HDAC family of macrophages after LPS treatment

图4 Western blotting检测巨噬细胞SIRT2和H4K8la水平Note: A. Detection of SIRT2 protein by Western blotting. B. Detection of H4K8la by Western blotting. ①P=0.001.
Fig 4 The levels of SIRT2 and H4K8la in macrophages detected by Western blotting

图5 测序结果概述Note: A. Genomic distribution of H4k8la signal peaks. B. Volcano plot of differential genes after LPS stimulation. MERTK—MER proto-oncogene, tyrosine kinase; APBB1IP—amyloid beta precursor protein binding family B member 1 interacting protein; SLC7A8—solute carrier family 7 member 8; LRP1—LDL receptor related protein 1; ADAMTS8—ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 8; RAB7B—RAB7B, member RAS oncogene family; MSR1—macrophage scavenger receptor 1; SPNS2—SPNS lysolipid transporter 2, sphingosine-1-phosphate; CHST13—carbohydrate sulfotransferase 13; PRAG1—PEAK1 related, kinase-activating pseudokinase 1; SHANK3—SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains 3; DHRS3—dehydrogenase/reductase 3; SPP1—secreted phosphoprotein 1; LGI2—leucine rich repeat LGI family member 2; LOXL4—lysyl oxidase like 4; TAC4—tachykinin precursor 4; P2RY12—purinergic receptor P2Y12; TRAF1—TNF receptor associated factor 1; CACNA1E—calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 E; PARM1—prostate androgen-regulated mucin-like protein 1; EBI3—Epstein-Barr virus induced 3; ABTB2—ankyrin repeat and BTB domain containing 2; CCL5—C-C motif chemokine ligand 5; PERP—p53 apoptosis effector related to PMP22; IL1B—interleukin 1 beta; CKB—creatine kinase B; RFTN1—raftlin, lipid raft linker 1; TNFAIP2—TNF alpha induced protein 2; MT2A—metallothionein 2A; ECE1—endothelin converting enzyme 1; CHST2—carbohydrate sulfotransferase 2; GIMAP8—GTPase, IMAP family member 8; TNF—tumor necrosis factor; SLAMF7—SLAM family member 7; NRP2—neuropilin 2; SERPINE2—serpin family E member 2; KCNQ4—potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily Q member 4; ADA—adenosine deaminase; SOCS3—suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; DLL4—delta like canonical Notch ligand 4; HIVEP2—HIVEP zinc finger 2; TFPI2—tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2; PIM2—Pim-2 proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase; KCNN2—potassium calcium-activated channel subfamily N member 2; DTX4—deltex E3 ubiquitin ligase 4; TFPI2—tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2; PTGS2—prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2; MCOLN2—mucolipin TRP cation channel 2; EVA1A—eva-1 homolog A, regulator of programmed cell death; RIN3—Ras and Rab interactor 3; SLC7A2—solute carrier family 7 member 2; TNFAIP6—TNF alpha induced protein 6; IGFBP5—insulin like growth factor binding protein 5; SERPINB7—serpin family B member 7; IDO1—indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1; SERPINA9—serpin family A member 9; CCL1—C-C motif chemokine ligand 1; CCR7—C-C motif chemokine receptor 7; CSF2—colony stimulating factor 2; LAMP3—lysosomal associated membrane protein 3.
Fig 5 Overview of sequencing results
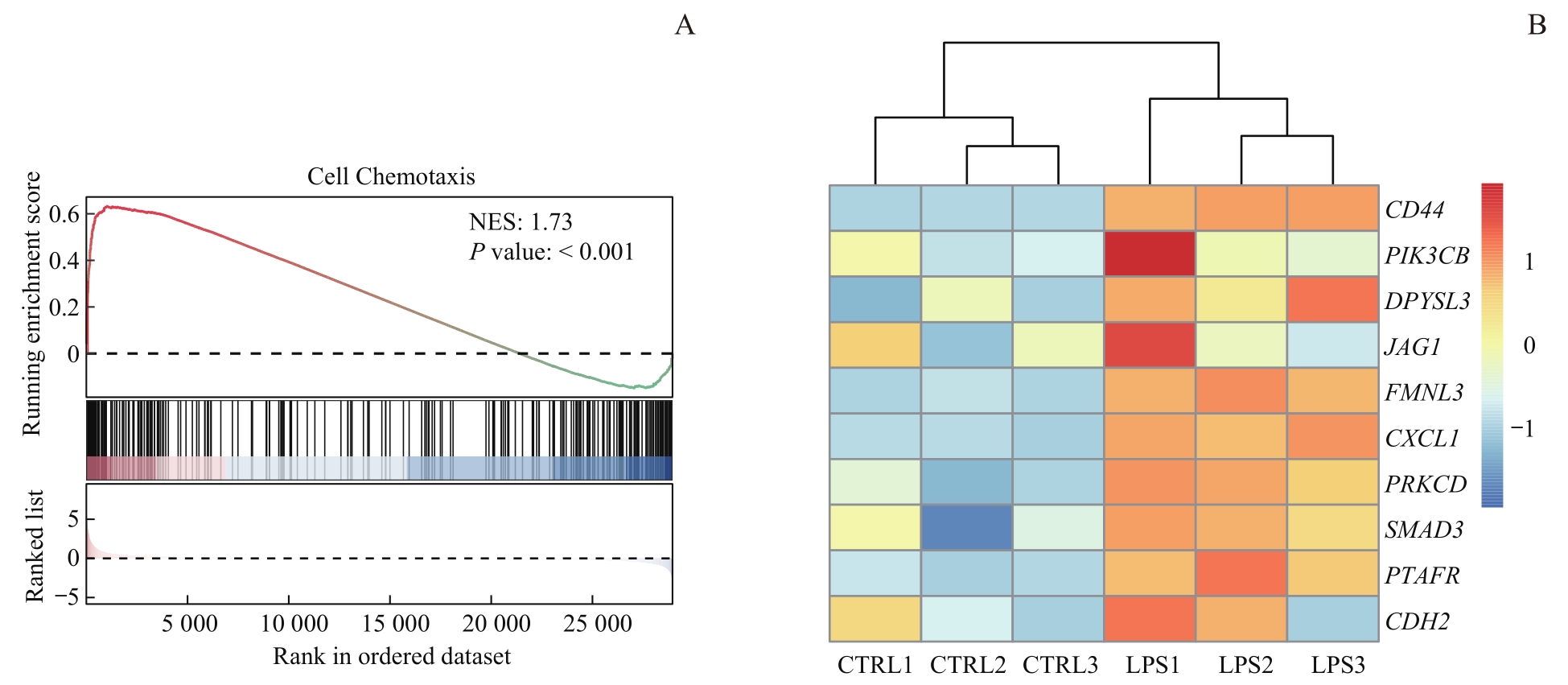
图6 RNA-seq及ChIP-seq交互分析Note: A. Gene set enrichment analysis of macrophages after LPS stimulation. NES—normalized enrichment score. B. Heatmap for macrophage chemotaxis- related genes bound to H4K8la. CTRL1, CTRL2, and CTRL3 were three replicate samples from the control group, while LPS1, LPS2, and LPS3 were three replicate samples from the LPS-treated infection group. PIK3CB—phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit beta; DPYSL3—dihydropyrimidinase like 3; JAG1—jagged canonical Notch ligand 1; FMNL3—formin like 3; CXCL1—C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1; PRKCD—protein kinase C delta; SMAD3—SMAD family member 3; PTAFR—platelet activating factor receptor; CDH2—cadherin 2.
Fig 6 Interaction analysis of RNA-seq and ChIP-seq
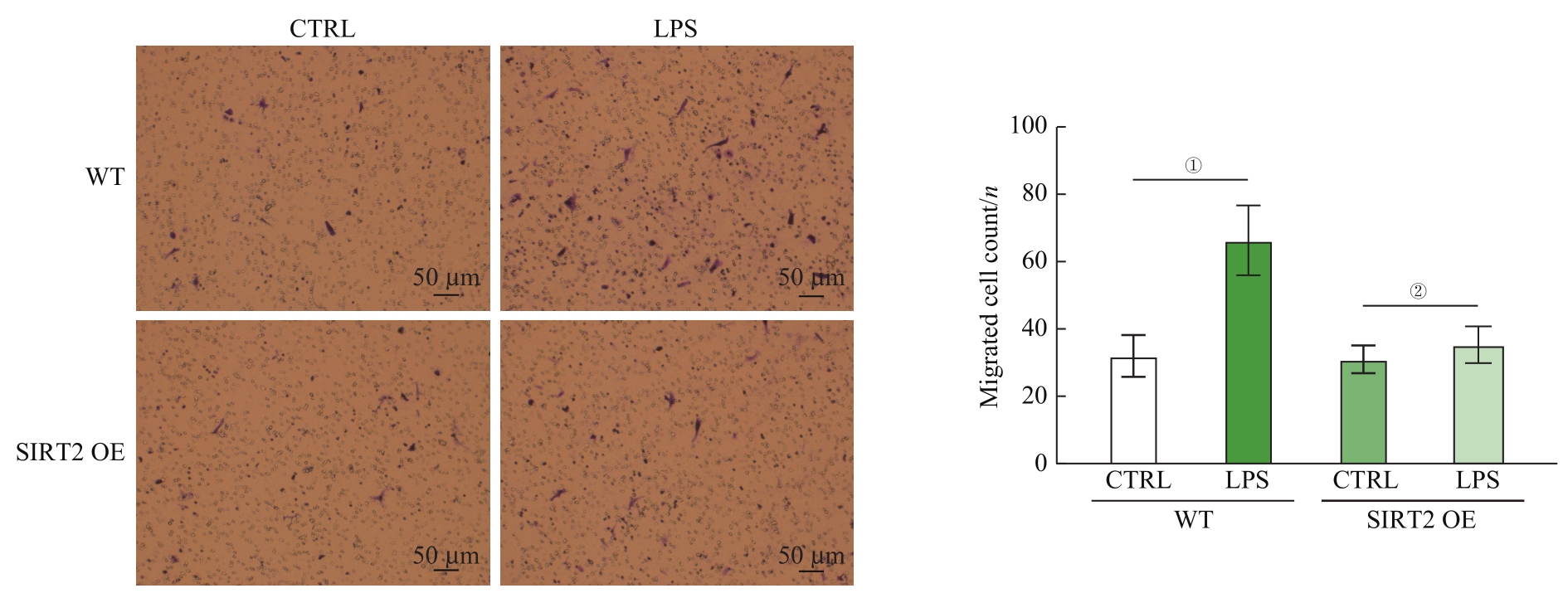
图7 SIRT2过表达抑制LPS诱导的巨噬细胞趋化作用(×10)Note: Detection of macrophage chemotaxis ability by Transwell.①P=0.008, ②P=0.766.
Fig 7 SIRT2 overexpression inhibits LPS-induced macrophage chemotaxis ability (×10)
| 1 | GALLI G, SALEH M. Immunometabolism of macrophages in bacterial infections[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2021, 10: 607650. |
| 2 | VIOLA A, MUNARI F, SÁNCHEZ-RODRÍGUEZ R, et al. The metabolic signature of macrophage responses[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 1462. |
| 3 | PETER K, REHLI M, SINGER K, et al. Lactic acid delays the inflammatory response of human monocytes[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2015, 457(3): 412-418. |
| 4 | ERREA A, CAYET D, MARCHETTI P, et al. Lactate inhibits the pro-inflammatory response and metabolic reprogramming in murine macrophages in a GPR81-independent manner[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(11): e0163694. |
| 5 | NAREIKA A, HE L, GAME B A, et al. Sodium lactate increases LPS-stimulated MMP and cytokine expression in U937 histiocytes by enhancing AP-1 and NF-κB transcriptional activities[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2005, 289(4): E534-E542. |
| 6 | SAMUVEL D J, SUNDARARAJ K P, NAREIKA A, et al. Lactate boosts TLR4 signaling and NF-κB pathway-mediated gene transcription in macrophages via monocarboxylate transporters and MD-2 up-regulation[J]. J Immunol, 2009, 182(4): 2476-2484. |
| 7 | XU H W, WU M Y, MA X M, et al. Function and mechanism of novel histone posttranslational modifications in health and disease[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 6635225. |
| 8 | MOHAMMADI A, SHARIFI A, POURPAKNIA R, et al. Manipulating macrophage polarization and function using classical HDAC inhibitors: implications for autoimmunity and inflammation[J]. Crit Rev Oncol, 2018, 128: 1-18. |
| 9 | ZHANG D, TANG Z Y, HUANG H, et al. Metabolic regulation of gene expression by histone lactylation[J]. Nature, 2019, 574(7779): 575-580. |
| 10 | MURRAY P J, WYNN T A. Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2011, 11(11): 723-737. |
| 11 | NEWSHOLME P, GORDON S, NEWSHOLME E A. Rates of utilization and fates of glucose, glutamine, pyruvate, fatty acids and ketone bodies by mouse macrophages[J]. Biochem J, 1987, 242(3): 631-636. |
| 12 | PARK D, LIM G, YOON S J, et al. The role of immunomodulatory metabolites in shaping the inflammatory response of macrophages[J]. BMB Rep, 2022, 55(11): 519-527. |
| 13 | COLEGIO O R, CHU N Q, SZABO A L, et al. Functional polarization of tumour-associated macrophages by tumour-derived lactic acid[J]. Nature, 2014, 513(7519): 559-563. |
| 14 | DIETL K, RENNER K, DETTMER K, et al. Lactic acid and acidification inhibit TNF secretion and glycolysis of human monocytes[J]. J Immunol, 2010, 184(3): 1200-1209. |
| 15 | AWASTHI D, NAGARKOTI S, SADAF S, et al. Glycolysis dependent lactate formation in neutrophils: a metabolic link between NOX-dependent and independent NETosis[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2019, 1865(12): 165542. |
| 16 | ALARCÓN P, MANOSALVA C, CONEJEROS I, et al. D (-) lactic acid-induced adhesion of bovine neutrophils onto endothelial cells is dependent on neutrophils extracellular traps formation and CD11b expression[J]. Front Immunol, 2017, 8: 975. |
| 17 | WU D, SHI Y X, ZHANG H, et al. Epigenetic mechanisms of Immune remodeling in sepsis: targeting histone modification[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(2): 112. |
| 18 | CHEN L H, HUANG L X, GU Y, et al. Lactate-lactylation hands between metabolic reprogramming and immunosuppression[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(19): 11943. |
| 19 | IRIZARRY-CARO R A, MCDANIEL M M, OVERCAST G R, et al. TLR signaling adapter BCAP regulates inflammatory to reparatory macrophage transition by promoting histone lactylation[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020, 117(48): 30628-30638. |
| 20 | KOVACS L, CAO Y P, HAN W H, et al. PFKFB3 in smooth muscle promotes vascular remodeling in pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2019, 200(5): 617-627. |
| 21 | WANG N X, WANG W W, WANG X Q, et al. Histone lactylation boosts reparative gene activation post-myocardial infarction[J]. Circ Res, 2022, 131(11): 893-908. |
| 22 | MA W, AO S, ZHOU J, et al. Methylsulfonylmethane protects against lethal dose MRSA-induced sepsis through promoting M2 macrophage polarization[J]. Mol Immunol, 2022, 146: 69-77. |
| 23 | CHU X, DI C Y, CHANG P P, et al. Lactylated histone H3K18 as a potential biomarker for the diagnosis and predicting the severity of septic shock[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 12: 786666. |
| 24 | MORENO-YRUELA C, ZHANG D, WEI W, et al. Class Ⅰ histone deacetylases (HDAC1-3) are histone lysine delactylases[J]. Sci Adv, 2022, 8(3): eabi6696. |
| 25 | DAI H, SINCLAIR D A, ELLIS J L, et al. Sirtuin activators and inhibitors: promises, achievements, and challenges[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2018, 188: 140-154. |
| 26 | WANG Y, YANG J, HONG T, et al. SIRT2: controversy and multiple roles in disease and physiology[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2019, 55: 100961. |
| 27 | XU H, YU X, WANG B, et al. The clinical significance of the SIRT2 expression level in the early stage of sepsis patients[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2020, 9(4): 1413-1419. |
| 28 | SASSO G L, MENZIES K J, MOTTIS A, et al. SIRT2 deficiency modulates macrophage polarization and susceptibility to experimental colitis[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(7): e103573. |
| 29 | ZU H X, LI C, DAI C R, et al. SIRT2 functions as a histone delactylase and inhibits the proliferation and migration of neuroblastoma cells[J]. Cell Discov, 2022, 8(1): 54. |
| 30 | TU Q Q, YU X Y, XIE W, et al. Prokineticin 2 promotes macrophages-mediated antibacterial host defense against bacterial pneumonia[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2022, 125: 103-113. |
| [1] | 杜少倩, 陶梦玉, 曹源, 王红霞, 胡孝渠, 范广建, 臧丽娟. CXCL9在乳腺癌中的表达及其与肿瘤免疫浸润特征的相关性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 860-872. |
| [2] | 吴淇琦, 汪豪, 林砺, 晏博, 张舒林. miR-185-5p通过抑制巨噬细胞自噬促进胞内分枝杆菌生长[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(6): 699-708. |
| [3] | 魏兰懿, 薛晓川, 陈君君, 杨全军, 王梦月, 韩永龙. 骨肉瘤免疫微环境中肿瘤相关巨噬细胞及其靶向治疗的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 624-630. |
| [4] | 李旭冉, 陶诗聪, 郭尚春. 骨髓间充质干细胞来源小细胞外囊泡对骨质疏松症的改善作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(4): 406-416. |
| [5] | 朱忆文, 于庆, 吴欣睿, 路洁, 陈梓濠, GINHOUX Florent, 苏冰, 刘兆远. 单核细胞对食管和胃中巨噬细胞的更新[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(9): 1208-1215. |
| [6] | 栾家妍, 李朋, 韩邦旻. SUMO化修饰在精子发生过程中的作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(7): 925-930. |
| [7] | 戚炀炀, 熊鹰. Galectin-9阳性肿瘤相关巨噬细胞在肌层浸润性膀胱癌中的表型、功能及临床治疗意义[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(12): 1666-1676. |
| [8] | 赵艳娜, 邱荣, 沈南, 唐元家. 构建诱导型CRISPR/Cas9系统用于小鼠免疫细胞基因功能研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(3): 297-301. |
| [9] | 赵倩, 高霖, 王长谦, 张俊峰, 张绘莉, 卓杨. 冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病患者外周血单核细胞亚群CX3CR1表达的变化及意义[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(3): 328-333. |
| [10] | 夏卫东, 陈光夷, 戴文统, 赵胜, 李粟, 林才. 重组人粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子凝胶应用于糖尿病患者中厚皮移植术后供皮区的临床效果[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(11): 1498-1501. |
| [11] | 李艳花, 闫亚平, 刘晓琴, 席国萍, 宋国斌, 肖保国, 马存根. 法舒地尔联合过表达趋化因子受体5的间充质干细胞对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的治疗作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(1): 35-41. |
| [12] | 陆诗媛1,洪 洁1,陈萦晅1,陈锦先2,钟 鸣2,房静远1. 具核梭杆菌相关细菌生物膜促进巨噬细胞M2型极化和结肠癌化疗耐药的研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(8): 1018-1029. |
| [13] | 蒋毅弘,廖 宇,岳 江,黄 融,刘 伟. 基于蛋白芯片技术的多囊卵巢综合征患者卵泡液差异蛋白的研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(8): 1048-1054. |
| [14] | 杨施琪*,李梦瑶*,刘思明,刘智多. 基于CD169表达水平的小鼠脾红髓巨噬细胞分型研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(6): 752-760. |
| [15] | 林俊卿,郑宪友,鲍丙波,李星玮,高 涛,黄腾立. 巨噬细胞在脊髓损伤后自我修复中的作用及其治疗应用进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(1): 118-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||