
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (12): 1493-1506.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2023.12.004
• 论著 · 基础研究 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-04-17
接受日期:2023-11-09
出版日期:2023-12-28
发布日期:2024-02-01
通讯作者:
虞志华
E-mail:ahmushaxudong@163.com;yuzhihua@shsmu.edu.cn
作者简介:沙旭栋(1998—),男,硕士生;电子信箱:ahmushaxudong@163.com。
基金资助:
SHA Xudong( ), WANG Chenfei, LU Jia, YU Zhihua(
), WANG Chenfei, LU Jia, YU Zhihua( )
)
Received:2023-04-17
Accepted:2023-11-09
Online:2023-12-28
Published:2024-02-01
Contact:
YU Zhihua
E-mail:ahmushaxudong@163.com;yuzhihua@shsmu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的·利用转录组以及脂质组分析技术研究瞬时受体电位香草素1型(transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1,TRPV1)通道的激活对高脂饮食诱导的小胶质细胞代谢的调控作用。方法·以8周龄C57BL/6J小鼠(WT)和Trpv1-/-(KO)小鼠为实验动物,高脂饲料(high-fat diet,HFD)分别喂养3d、7d、8周诱导造模(WT和KO组,n=3;WT-HFD和KO-HFD组,n=4)。通过免疫荧光试验测量WT-HFD和KO-HFD组小鼠大脑中TRPV1通道的表达以及细胞定位。通过RNA测序和液相色谱-质谱法确定WT-HFD和KO-HFD组小鼠的大脑表型。结果·与WT组小鼠相比,WT-HFD组小鼠体内小胶质细胞Trpv1 mRNA的表达水平显著增加。与WT-HFD组小鼠相比,KO-HFD组小鼠的脑脂质代谢、线粒体功能、葡萄糖转移以及糖酵解相关基因的表达水平下调。脂质组分析显示,虽然KO-HFD组小鼠的脑组织中脂质积累,但是Trpv1基因敲除减弱了HFD诱导的小胶质细胞活化,此外,TRPV1激动剂辣椒素在体外减弱棕榈酸诱导的线粒体膜电位去极化。结论·TRPV1通过线粒体驱动的燃料可用性机制调节小胶质细胞的脂质和葡萄糖代谢。
中图分类号:
沙旭栋, 王晨飞, 鲁佳, 虞志华. 瞬时受体电位香草素1型对高脂饮食诱导的小胶质细胞代谢的调控[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(12): 1493-1506.
SHA Xudong, WANG Chenfei, LU Jia, YU Zhihua. Regulation of high-fat diet-induced microglial metabolism by transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(12): 1493-1506.
| Oligonucleotide | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
mouse trpv1 FWD: TGGCTCATATTTGCCTTCAG mouse trpv1 REV: CAGCCCTAGGAGTTGATFGA | Sango Biotech | N/A |
mouse ucp2 FWD: GCTGGTGGTTCGGAGAT mouse ucp2 REV: TGAAGTGGCAAGGGAGG | Sango Biotech | N/A |
mouse tnf-α FWD: CAGGAGGGAGAACAGAAACTCCA mouse tnf-α REV: CCTGGTTGGCTGCTT | Sango Biotech | N/A |
mouse il-1β FWD: GGAGGTGGTGATAGCCGGTAT mouse il-1β REV: TGGGTAATCCATAGAGCCCAG | Sango Biotech | N/A |
mouse gapdh FWD: TGATGGCAACAATCTCCAC mouse gapdh REV: CGTCCCGTAGACAAAATGGT | Sango Biotech | N/A |
表1 用于qRT-PCR的引物序列 (5'→3')
Tab 1 Primer sequences used for qRT-PCR (5'→3')
| Oligonucleotide | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
mouse trpv1 FWD: TGGCTCATATTTGCCTTCAG mouse trpv1 REV: CAGCCCTAGGAGTTGATFGA | Sango Biotech | N/A |
mouse ucp2 FWD: GCTGGTGGTTCGGAGAT mouse ucp2 REV: TGAAGTGGCAAGGGAGG | Sango Biotech | N/A |
mouse tnf-α FWD: CAGGAGGGAGAACAGAAACTCCA mouse tnf-α REV: CCTGGTTGGCTGCTT | Sango Biotech | N/A |
mouse il-1β FWD: GGAGGTGGTGATAGCCGGTAT mouse il-1β REV: TGGGTAATCCATAGAGCCCAG | Sango Biotech | N/A |
mouse gapdh FWD: TGATGGCAACAATCTCCAC mouse gapdh REV: CGTCCCGTAGACAAAATGGT | Sango Biotech | N/A |
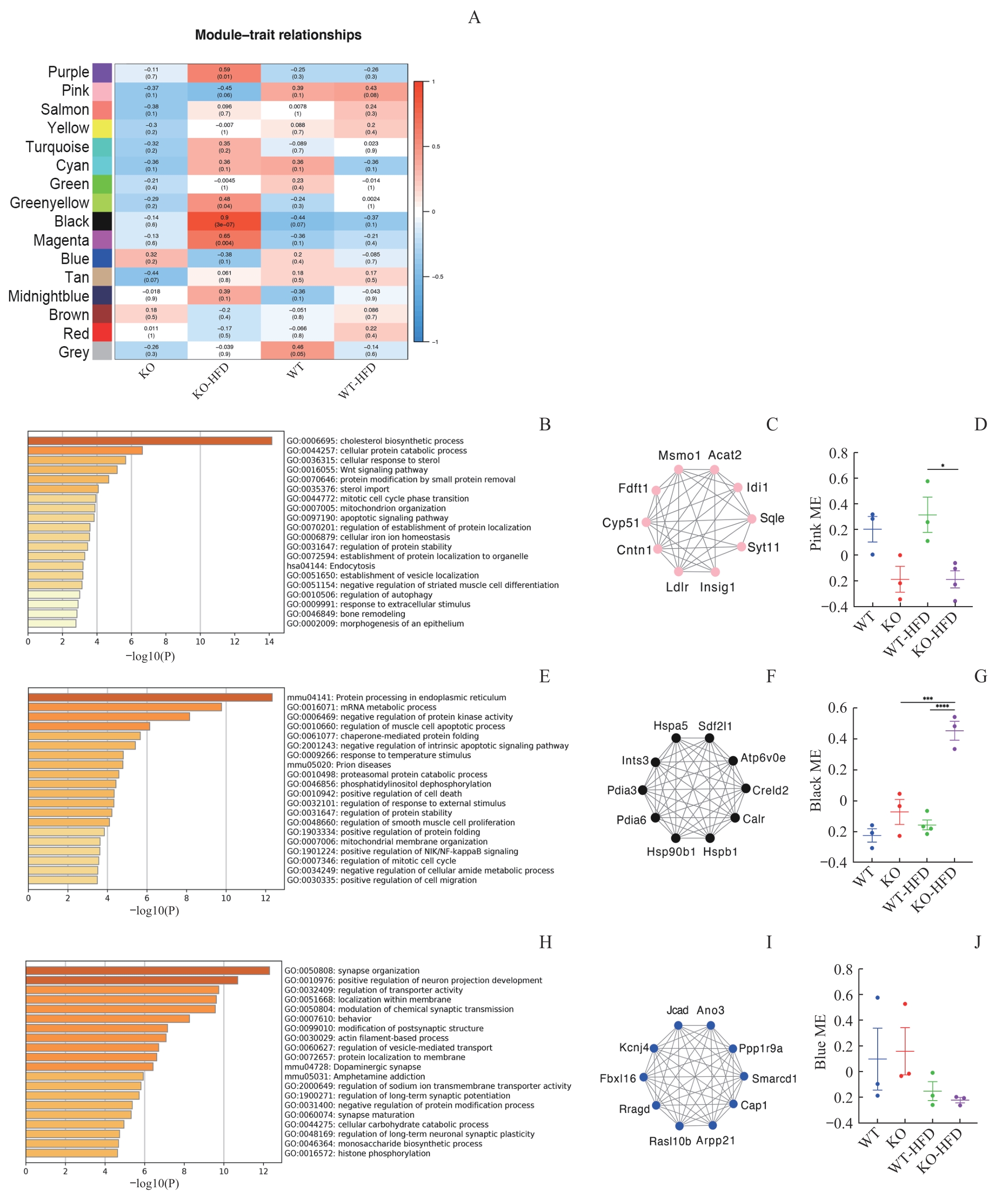
图1 高脂饮食喂养前后 WT 和 Trpv1 敲除的小鼠的WGCNANote: A. Modules of WT, KO, WT-HFD, and KO-HFD mice (n=3 mice in WT and KO group, n=4 mice in WT-HFD and KO-HFD group). B/E/H. Top 20 pathways of GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of the pink, black and blue module. C/F/I. Network plot of the top 10 genes in pink, black and blue module. D/G/J. Trajectory of the module eigengenes in pink, black and blue module. One-way ANOVA was applied. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P = 0.000.
Fig 1 WGCNA in WT and genetic Trpv1 deletion mice before and after high fat feeding

图2 高脂饮食改变 Trpv1 敲除的小鼠脑内的脂质组成分Note: A. The composition of lipidome profiling of brain cells. B—C. Lipidome profiling of WT-HFD compared to WT and KO-HFD compared to KO mice brain. D. Distribution of PC, PE, and PG chain lengths of WT and KO mice induced by HFD treating. E—G. Distribution of PC, PE, and PG species of WT and KO mice induced by HFD treating. Data present the x±s (WT, WT-HFD, KO, n =3; KO-HFD, n =4). Statistical test: two-sided Student's t-test, two-way ANOVA followed by the Dunnett's post hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, **** P = 0.000.
Fig 2 HFD induced liposome switch of brain cells with Trpv1 deficiency

图3 Trpv1 敲除缓解高脂饮食对小鼠大脑转录组的多种影响Note: A. Top lipidome enriched KEGG pathways of WT-HFD compared to WT mice and KO-HFD compared to KO mice. B/C. Gene expression changes, top GO and KEGG pathways enriched pathways of KO compared to WT mice and KO-HFD compared to WT-HFD mice.D—I. Heat maps of KO compared to WT mice and KO-HFD compared to WT-HFD mice.
Fig 3 Genetic Trpv1 deletion reduced HFD-induced multiple effects on brain transcriptome

图4 Trpv1 敲除缓解高脂饮食对大脑代谢途径的多种影响Note: A. The expressions of genes involved in monocarboxylate transporters, gluconeogenesis, glucose transporter, lactate shuttle, glycolysis, TCA cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation of WT and KO mice treated on SCD or 7 d HFD (red, increase; blue, decrease). B—G. The bar graphs show the fold induction of those genes within the class in WT-HFD versus WT mice (blue), and KO-HFD versus KO mice (red). All replicates within a class were averaged to obtain fold induction. Color key on the bottom of the figure indicated the group of samples.
Fig 4 Genetic Trpv1 deletion reduced HFD-induced multiple effects on metabolic pathways of the brain

图5 Trpv1 敲除可改善高脂饮食诱导的小胶质细胞活化Note: A/B. Iba-1+ active microglia and GFAP+ reactive astrocytes of WT or TRPV1 KO mice fed on 3-day HFD. Data represent x±s. ?P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P = 0.000. Scale bar: 50 μm.
Fig 5 Genetic Trpv1 deletion ameliorates HFD-induced microglia activation
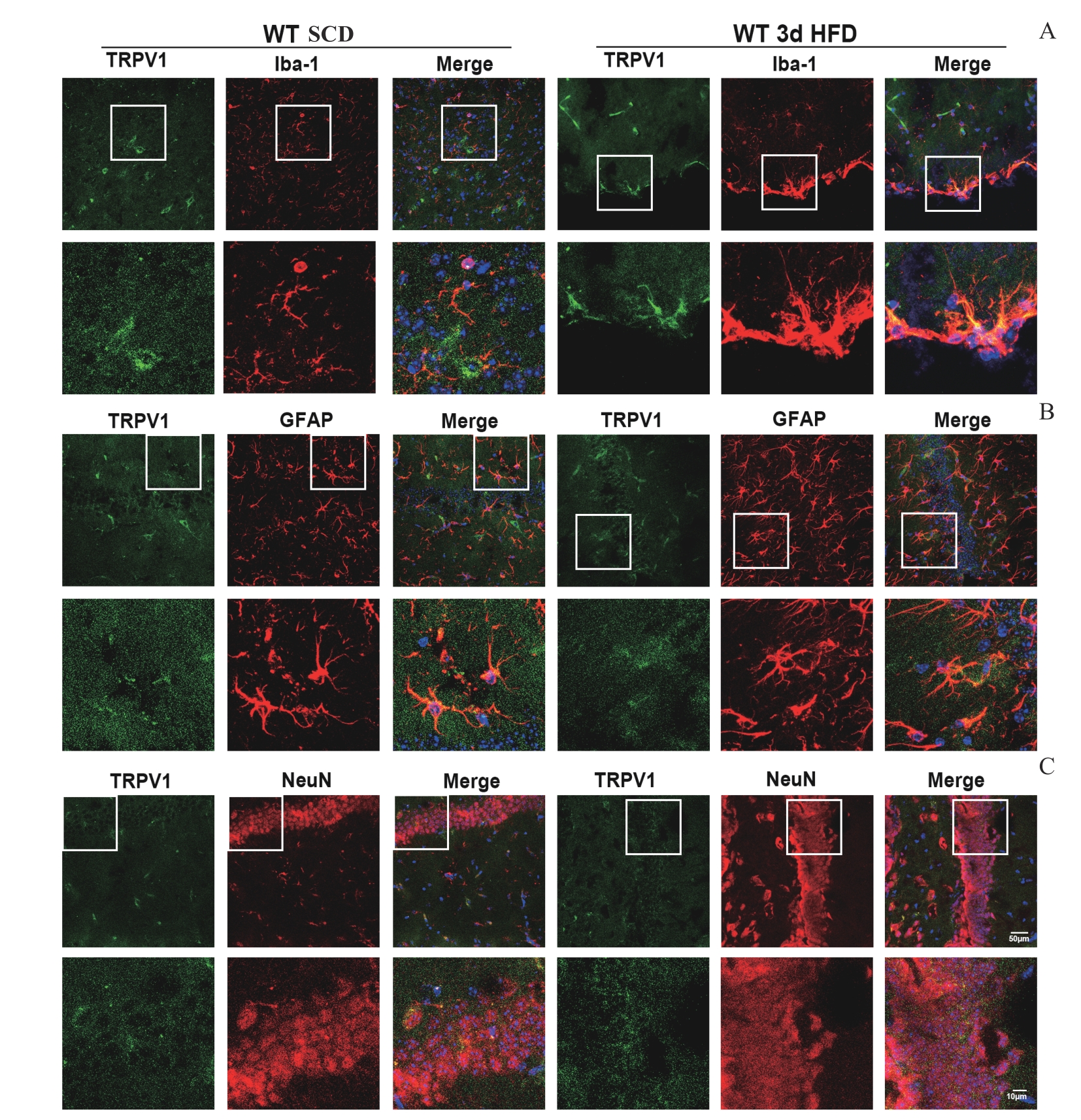
图6 高脂饮食的小鼠大脑内的小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞激活且上调表达TRPV1Note: A—C. Co-staining of TRPV1 and Iba1, TRPV1 and GFAP, TRPV1 and NeuN in SCD and 3-day HFD mice. Nuclei were stained in blue with DAPI. Scale bar: 50 μm; Scale bar: 10 μm.
Fig 6 Up-regulation of TRPV1 in active microglia and reactive astrocytes of HFD mice brains

图7 Trpv1 敲除可减轻高脂饮食诱导的神经炎症和线粒体激活Note: A—D. The mRNA levels of Trpv1, Ucp2, Tnf-α, and Il-1β in isolated cortical microglia (CD11b+ cells) from WT and KO mice mixed gender fed on SCD, 3 d HFD, 7 d HFD, or 8-week HFD (n=3). E/F. Mitochondrial membrane potential was detected by fluorescence microscopy (n=3). G. Indications of quantified lipid classes and acyl chains (circles) and genes (rectangles) of WT and KO mice by HFD. Data represent x±s. ?P < 0.05, ****P = 0.000. Scale bar: 50 μm.
Fig 7 Genetic Trpv1 deletion attenuate HFD-induced neuroinflammation and mitochondrial activation
| 1 | SANDOVAL D A, OBICI S, SEELEY R J. Targeting the CNS to treat type 2 diabetes[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2009, 8(5): 386-398. |
| 2 | HORVATH T L, SARMAN B, GARCÍA-CÁCERES C, et al. Synaptic input organization of the melanocortin system predicts diet-induced hypothalamic reactive gliosis and obesity[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2010, 107(33): 14875-14880. |
| 3 | VALDEARCOS M, DOUGLASS J D, ROBBLEE M M, et al. Microglial inflammatory signaling orchestrates the hypothalamic immune response to dietary excess and mediates obesity susceptibility[J]. Cell Metab, 2018, 27(6): 1356. |
| 4 | KIM J D, YOON N A, JIN S, et al. Microglial UCP2 mediates inflammation and obesity induced by high-fat feeding[J]. Cell Metab, 2019, 30(5): 952-962.e5. |
| 5 | CATERINA M J, SCHUMACHER M A, TOMINAGA M, et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway[J]. Nature, 1997, 389(6653): 816-824. |
| 6 | MARRONE M C, MORABITO A, GIUSTIZIERI M, et al. TRPV1 channels are critical brain inflammation detectors and neuropathic pain biomarkers in mice[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8: 15292. |
| 7 | GIBSON H E, EDWARDS J G, PAGE R S, et al. TRPV1 channels mediate long-term depression at synapses on hippocampal interneurons[J]. Neuron, 2008, 57(5): 746-759. |
| 8 | MARINELLI S, MARZO V, BERRETTA N, et al. Presynaptic facilitation of glutamatergic synapses to dopaminergic neurons of the rat substantia nigra by endogenous stimulation of vanilloid receptors[J]. J Neurosci, 2003, 23(8): 3136-3144. |
| 9 | DOYLE M W, BAILEY T W, JIN Y H, et al. Vanilloid receptors presynaptically modulate cranial visceral afferent synaptic transmission in nucleus tractus solitarius[J]. J Neurosci, 2002, 22(18): 8222-8229. |
| 10 | EDWARDS J G. TRPV1 in the central nervous system: synaptic plasticity, function, and pharmacological implications[J]. Prog Drug Res, 2014, 68: 77-104. |
| 11 | KIM S R, KIM S U, OH U, et al. Transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 mediates microglial cell death in vivo and in vitro via Ca2+-mediated mitochondrial damage and cytochrome c release[J]. J Immunol, 2006, 177(7): 4322-4329. |
| 12 | HASSAN S, ELDEEB K, MILLNS P J, et al. Cannabidiol enhances microglial phagocytosis via transient receptor potential (TRP) channel activation[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2014, 171(9): 2426-2439. |
| 13 | MIYAKE T, SHIRAKAWA H, NAKAGAWA T, et al. Activation of mitochondrial transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 channel contributes to microglial migration[J]. Glia, 2015, 63(10): 1870-1882. |
| 14 | SAPPINGTON R M, CALKINS D J. Contribution of TRPV1 to microglia-derived IL-6 and NFkappaB translocation with elevated hydrostatic pressure[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2008, 49(7): 3004-3017. |
| 15 | SCHILLING T, EDER C. Importance of the non-selective cation channel TRPV1 for microglial reactive oxygen species generation[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2009, 216(1/2): 118-121. |
| 16 | GAO W, SUN Y H, CAI M, et al. Copper sulfide nanoparticles as a photothermal switch for TRPV1 signaling to attenuate atherosclerosis[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 231. |
| 17 | BASKARAN P, KRISHNAN V, REN J, et al. Capsaicin induces browning of white adipose tissue and counters obesity by activating TRPV1 channel-dependent mechanisms[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2016, 173(15): 2369-2389. |
| 18 | WEI T J, WANG Y X, XU W R, et al. KCa3.1 deficiency attenuates neuroinflammation by regulating an astrocyte phenotype switch involving the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2019, 132: 104588. |
| 19 | ZHANG B, HORVATH S. A general framework for weighted gene co-expression network analysis[J]. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol, 2005, 4: Article17. |
| 20 | LANGFELDER P, HORVATH S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2008, 9: 559. |
| 21 | SHANNON P, MARKIEL A, OZIER O, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks[J]. Genome Res, 2003, 13(11): 2498-2504. |
| 22 | ZHOU Y Y, ZHOU B, PACHE L, et al. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 1523. |
| 23 | FALK T, YUE X, ZHANG S L, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-B is neuroprotective in an in vivo rat model of Parkinson's disease[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2011, 496(1): 43-47. |
| 24 | KORDOWER J H, EMBORG M E, BLOCH J, et al. Neurodegeneration prevented by lentiviral vector delivery of GDNF in primate models of Parkinson's disease[J]. Science, 2000, 290(5492): 767-773. |
| 25 | ARENA E T, RUEDEN C T, HINER M C, et al. Quantitating the cell: turning images into numbers with ImageJ[J]. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol, 2017, 6(2): 10.1002/wdev.260. |
| 26 | TRIEBL A, TRÖTZMÜLLER M, HARTLER J, et al. Lipidomics by ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry and its application to complex biological samples[J]. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci, 2017, 1053: 72-80. |
| 27 | DIRCKS L, SUL H S. Acyltransferases of de novo glycerophospholipid biosynthesis[J]. Prog Lipid Res, 1999, 38(5/6): 461-479. |
| 28 | TRACEY T J, STEYN F J, WOLVETANG E J, et al. Neuronal lipid metabolism: multiple pathways driving functional outcomes in health and disease[J]. Front Mol Neurosci, 2018, 11: 10. |
| 29 | LEPROPRE S, KAUTBALLY S, OCTAVE M, et al. AMPK-ACC signaling modulates platelet phospholipids and potentiates thrombus formation[J]. Blood, 2018, 132(11): 1180-1192. |
| 30 | VANCE J E. Phospholipid synthesis and transport in mammalian cells[J]. Traffic, 2015, 16(1): 1-18. |
| 31 | MONNI M, CORAZZI L, MIGLIORATI G, et al. Respiratory state and phosphatidylserine import in brain mitochondria in vitro[J]. J Membrane Biol, 2000, 173(2): 97-105. |
| 32 | THOMAS H E, ZHANG Y, STEFELY J A, et al. Mitochondrial complex I activity is required for maximal autophagy[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 24(9): 2404-2417.e8. |
| 33 | SHAHID R A, VIGNA S R, LAYNE A C, et al. Acinar cell production of leukotriene B4 contributes to development of neurogenic pancreatitis in mice[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 1(1): 75-86. |
| 34 | MA L Q, ZHONG J, ZHAO Z G, et al. Activation of TRPV1 reduces vascular lipid accumulation and attenuates atherosclerosis[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2011, 92(3): 504-513. |
| 35 | LI L, CHEN J, NI Y X, et al. TRPV1 activation prevents nonalcoholic fatty liver through UCP2 upregulation in mice[J]. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol, 2012, 463(5): 727-732. |
| 36 | ZHAO J F, CHING L C, KOU Y R, et al. Activation of TRPV1 prevents OxLDL-induced lipid accumulation and TNF-α-induced inflammation in macrophages: role of liver X receptor Α[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2013, 2013: 925171. |
| 37 | TANG W, FAN Y Y. SIRT6 as a potential target for treating insulin resistance[J]. Life Sci, 2019, 231: 116558. |
| 38 | LEE E, JUNG D Y, KIM J H, et al. Transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1 channel regulates diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance, and leptin resistance[J]. FASEB J, 2015, 29(8): 3182-3192. |
| 39 | RAZAVI R, CHAN Y, AFIFIYAN F N, et al. TRPV1+ sensory neurons control beta cell stress and islet inflammation in autoimmune diabetes[J]. Cell, 2006, 127(6): 1123-1135. |
| 40 | GUILLEMOT-LEGRIS O, MUCCIOLI G G. Obesity-induced neuroinflammation: beyond the hypothalamus[J]. Trends Neurosci, 2017, 40(4): 237-253. |
| 41 | KETTENMANN H, HANISCH U K, NODA M, et al. Physiology of microglia[J]. Physiol Rev, 2011, 91(2): 461-553. |
| 42 | FERNANDES E S, BRITO C X L, TEIXEIRA S A, et al. TRPV1 antagonism by capsazepine modulates innate immune response in mice infected with Plasmodium berghei ANKA[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2014, 2014: 506450. |
| 43 | MANES T D, WANG V, POBER J S. Divergent TCR-initiated calcium signals govern recruitment versus activation of human alloreactive effector memory T cells by endothelial cells[J]. J Immunol, 2018, 201(11): 3167-3174. |
| 44 | HUANG W X, YU F, SANCHEZ R M, et al. TRPV1 promotes repetitive febrile seizures by pro-inflammatory cytokines in immature brain[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2015, 48: 68-77. |
| 45 | YOSHIDA A, FURUBE E, MANNARI T, et al. TRPV1 is crucial for proinflammatory STAT3 signaling and thermoregulation-associated pathways in the brain during inflammation[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 26088. |
| 46 | CHEN Y, WILLCOCKSON H H, VALTSCHANOFF J G. Influence of the vanilloid receptor TRPV1 on the activation of spinal cord glia in mouse models of pain[J]. Exp Neurol, 2009, 220(2): 383-390. |
| 47 | HO K W, WARD N J, CALKINS D J. TRPV1: a stress response protein in the central nervous system[J]. Am J Neurodegener Dis, 2012, 1(1): 1-14. |
| 48 | KONG W L, PENG Y Y, PENG B W. Modulation of neuroinflammation: role and therapeutic potential of TRPV1 in the neuro-immune axis[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2017, 64: 354-366. |
| 49 | LEONELLI M, MARTINS D O, BRITTO L R G. TRPV1 receptors are involved in protein nitration and Müller cell reaction in the acutely axotomized rat retina[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2010, 91(5): 755-768. |
| [1] | 卢晓冰, 岳江, 何晟赟, 董莹, 路青, 麻静. 大腿骨骼肌肌内脂肪组织的含量对肥胖症男性患者糖代谢的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(9): 1169-1174. |
| [2] | 高羽, 殷姗, 庞玥, 梁文懿, 刘玉敏. 大黄对大鼠体内肠道菌群-宿主共代谢作用的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(8): 997-1007. |
| [3] | 冯奕源, 徐忠匀, 尹雅芙, 王辉, 程维维. 二甲双胍改善由C9ORF72肌萎缩侧索硬化/额颞叶痴呆相关多聚甘氨酸-精氨酸诱导的线粒体损伤[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 839-847. |
| [4] | 朱晓晨, 谢欣宜, 赵旭日, 徐丽娜, 何智妍, 周薇. 小胶质细胞Stat3基因条件性敲除小鼠的构建及鉴定[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(6): 689-698. |
| [5] | 金芳全, 樊成虎, 唐晓栋, 陈彦同, 齐兵献. 线粒体功能障碍与骨质疏松症相关性研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(6): 761-767. |
| [6] | 王洁仪, 郑丹, 郑晓皎, 贾伟, 赵爱华. 茶褐素生物学活性及其作用机制的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(6): 768-774. |
| [7] | 刘芊若, 方子晨, 吴宇涵, 钟羡欣, 国沐禾, 贾洁. 肠道菌群及其代谢产物与妊娠期糖尿病相关性的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 641-647. |
| [8] | 马卓然, 袁安彩, 蒋惠如, 陈潇雨, 张薇, 卜军. 脂质蓄积指数与中国成年人高血压关系的meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(4): 466-473. |
| [9] | 洪晗馨, 王龙昊, 刘辉辉, 彭浒, 吴皓, 杨涛. 线粒体内膜转位酶8A基因敲除小鼠的构建及其内耳功能研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(3): 261-268. |
| [10] | 陈晨, 程卓安, 王存, 夏强. 铁死亡调控在肝脏疾病治疗中的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(3): 365-373. |
| [11] | 刘铁鑫, 林俊卿, 郑宪友. 靶向亚细胞结构治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(2): 230-236. |
| [12] | 张漪蓉, 魏玮庆, 马皎, 张雪. 靶向SOX9调控弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤代谢重编程的研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(10): 1236-1244. |
| [13] | 单颖仪, 于浩泳. 代谢手术术前内科管理进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(10): 1332-1338. |
| [14] | 谢小雷, 江佩欣, 张敬鸿, 莫骏健, 吴可凡, 曾康逸. 视网膜母细胞瘤结合锌指蛋白1调控肥胖和肿瘤信号通路研究综述[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 114-119. |
| [15] | 刘薇薇, 王龙. 女性绝经与非酒精性脂肪性肝病的关系及相关治疗的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 125-131. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||