
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 212-222.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.02.007
• 论著 · 临床研究 • 上一篇
吴丽蓉1( ), 陈瑞华2, 晁筱雯1, 郭雨槐1, 孙涛1, 李梦慈1, 陈天璐1(
), 陈瑞华2, 晁筱雯1, 郭雨槐1, 孙涛1, 李梦慈1, 陈天璐1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-03
接受日期:2023-11-30
出版日期:2024-02-28
发布日期:2024-03-25
通讯作者:
陈天璐
E-mail:wlr7089@163.com;chentianlu@sjtu.edu.cn
作者简介:吴丽蓉(1998—),女,硕士生;电子信箱:wlr7089@163.com。
基金资助:
WU Lirong1( ), CHEN Ruihua2, CHAO Xiaowen1, GUO Yuhuai1, SUN Tao1, LI Mengci1, CHEN Tianlu1(
), CHEN Ruihua2, CHAO Xiaowen1, GUO Yuhuai1, SUN Tao1, LI Mengci1, CHEN Tianlu1( )
)
Received:2023-08-03
Accepted:2023-11-30
Online:2024-02-28
Published:2024-03-25
Contact:
CHEN Tianlu
E-mail:wlr7089@163.com;chentianlu@sjtu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的·分析探讨空腹血糖(fasting blood glucose,FBG)升高人群中导致认知功能恶化的影响因素和导致认知功能恶化风险变化的代谢线索。方法·从阿尔茨海默病神经影像学计划数据库中下载阿尔茨海默病队列数据,并筛选出具有FBG数据和随访数据的样本,获得其临床资料[包括年龄、性别、身体质量指数、教育程度、载脂蛋白E4(apolipoprotein E4,APOE4)基因型、人种]和代谢指标数据(包括氨基酸、脂肪酸、蛋白质等)。根据受试者的FBG水平和认知障碍阶段诊断,将其分为正常FBG并无/有认知功能恶化组、FBG升高并无/有认知功能恶化组。采用单因素分析、Cox比例风险回归模型、正交偏最小二乘判别分析、Spearman相关性分析对数据进行分析。结果·共纳入1 317例具有FBG数据且具有较为完整的临床资料与代谢物数据的受试者,其中FBG正常(>3.9 mmol/L且<6.1 mmol/L)共1 153例,FBG升高(≥6.1 mmol/L)共164例。FBG正常的受试者中,275例有认知功能恶化;FBG升高的受试者中,53例有认知功能恶化。基线人口统计学特征分析结果显示,正常FBG组和高FBG组在性别、人种上差异有统计学意义,无认知功能恶化组和有认知功能恶化组在年龄、性别、APOE4基因携带率上差异有统计学意义(均P<0.05)。Cox回归分析表明,认知功能恶化的主要促进因素依次为APOE4基因阳性、FBG升高和年龄增长(HR=2.22,HR=1.38,HR=1.02;均P<0.05)。不同FBG水平下无认知功能恶化和有恶化组的基线代谢指标,以及认知功能恶化前与认知功能恶化后的代谢指标的差异分析结果显示:在认知功能恶化人群中,高密度脂蛋白(high-density lipoproteins,HDL)携带的磷脂在总脂质中的比值显著升高;低密度脂蛋白(low-density lipoprotein,LDL)颗粒浓度及其携带的脂质含量在认知功能恶化后显著升高。相关性分析结果显示,在认知功能恶化人群中,缬氨酸、亮氨酸不仅与FBG水平显著相关,还与血浆磷酸化tau蛋白(phosphorylated tau,pTau)水平显著相关;HDL携带的胆固醇含量、磷脂与总脂质的比值与脑脊液pTau水平显著相关。结论·相较于FBG正常的人群,FBG升高人群认知功能恶化风险显著增加;且不同FBG水平下,无认知功能恶化人群和有认知功能恶化的人群以及认知恶化前与认知恶化后显著差异的代谢指标有所不同。总体而言,LDL及其携带的脂质、HDL携带的磷脂在认知功能恶化过程中呈上升趋势,且支链氨基酸中的缬氨酸与亮氨酸与pTau水平有显著相关性,提示这几个代谢指标在认知功能恶化过程中或许起重要作用。
| Characteristic | Total (n=1 317) | Normal FBG (n=1 153) | High FBG (n=164) | χ2/U value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose/(mmol·L-1) | 5.36±0.90 | 5.11±0.47 | 7.10±1.23 | 0.00 | 0.000 |
| Age/year | 73.86±7.04 | 73.78±7.11 | 74.43±6.44 | 89 440.50 | 0.263 |
| BMI/(kg·m-2) | 26.80±4.61 | 26.80±4.53 | 26.78±5.12 | 73 600.50 | 0.475 |
| Gender/n(%) | 7.64 | 0.006 | |||
| Male | 727 (55.20) | 620 (53.77) | 107 (65.24) | ||
| Female | 590 (44.80) | 533 (46.23) | 57 (34.76) | ||
| Education/year | 15.94±2.79 | 15.94±2.81 | 15.95±2.66 | 93 899.50 | 0.886 |
| Race/n(%) | 23.57 | 0.001 | |||
| White | 1 224 (92.94) | 1 081 (93.76) | 143 (87.20) | ||
| Black | 52 (3.95) | 41 (3.56) | 11 (6.71) | ||
| Asian | 22 (1.67) | 18 (1.56) | 4 (2.44) | ||
| Other | 19 (1.44) | 13 (1.13) | 6 (3.66) | ||
| APOE4/n(%) | 0.05 | 0.828 | |||
| Negative | 693 (52.62) | 608 (52.73) | 85 (51.83) | ||
| Positive | 624 (47.38) | 545 (47.27) | 79 (48.17) |
表1 正常FBG组和高FBG组的基线特征比较
Tab 1 Comparison of baseline characteristics between the normal FBG group and high FBG group
| Characteristic | Total (n=1 317) | Normal FBG (n=1 153) | High FBG (n=164) | χ2/U value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose/(mmol·L-1) | 5.36±0.90 | 5.11±0.47 | 7.10±1.23 | 0.00 | 0.000 |
| Age/year | 73.86±7.04 | 73.78±7.11 | 74.43±6.44 | 89 440.50 | 0.263 |
| BMI/(kg·m-2) | 26.80±4.61 | 26.80±4.53 | 26.78±5.12 | 73 600.50 | 0.475 |
| Gender/n(%) | 7.64 | 0.006 | |||
| Male | 727 (55.20) | 620 (53.77) | 107 (65.24) | ||
| Female | 590 (44.80) | 533 (46.23) | 57 (34.76) | ||
| Education/year | 15.94±2.79 | 15.94±2.81 | 15.95±2.66 | 93 899.50 | 0.886 |
| Race/n(%) | 23.57 | 0.001 | |||
| White | 1 224 (92.94) | 1 081 (93.76) | 143 (87.20) | ||
| Black | 52 (3.95) | 41 (3.56) | 11 (6.71) | ||
| Asian | 22 (1.67) | 18 (1.56) | 4 (2.44) | ||
| Other | 19 (1.44) | 13 (1.13) | 6 (3.66) | ||
| APOE4/n(%) | 0.05 | 0.828 | |||
| Negative | 693 (52.62) | 608 (52.73) | 85 (51.83) | ||
| Positive | 624 (47.38) | 545 (47.27) | 79 (48.17) |
| Characteristic | Without cognitive deterioration (n=989) | With cognitive deterioration (n=328) | χ2/U value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose/(mmol·L-1) | 5.34±0.86 | 5.41±1.02 | 158 106.00 | 0.493 |
| Age/year | 73.62±7.08 | 74.59±6.84 | 147 380.00 | 0.013 |
| BMI/(kg·m-2) | 26.79±4.65 | 26.82±4.47 | 126 838.50 | 0.700 |
| Gender/n(%) | 5.28 | 0.022 | ||
| Male | 528 (53.90) | 199 (60.67) | ||
| Female | 461 (46.61) | 129 (39.33) | ||
| Education/year | 15.93±2.83 | 15.98±2.65 | 161 357.50 | 0.887 |
| Race/n(%) | 4.66 | 0.588 | ||
| White | 913 (92.32) | 311 (94.82) | ||
| Black | 41 (4.15) | 11 (3.35) | ||
| Asian | 17 (1.72) | 5 (1.52) | ||
| Other | 18 (1.82) | 1 (0.30) | ||
| APOE4/n(%) | 29.54 | 0.000 | ||
| Negative | 563 (56.93) | 130 (39.63) | ||
| Positive | 426 (43.07) | 198 (60.37) |
表2 无认知功能恶化组和认知功能恶化组的基线特征比较(全人群)
Tab 2 Comparison of baseline characteristics between individuals without and with cognitive deterioration (all data)
| Characteristic | Without cognitive deterioration (n=989) | With cognitive deterioration (n=328) | χ2/U value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose/(mmol·L-1) | 5.34±0.86 | 5.41±1.02 | 158 106.00 | 0.493 |
| Age/year | 73.62±7.08 | 74.59±6.84 | 147 380.00 | 0.013 |
| BMI/(kg·m-2) | 26.79±4.65 | 26.82±4.47 | 126 838.50 | 0.700 |
| Gender/n(%) | 5.28 | 0.022 | ||
| Male | 528 (53.90) | 199 (60.67) | ||
| Female | 461 (46.61) | 129 (39.33) | ||
| Education/year | 15.93±2.83 | 15.98±2.65 | 161 357.50 | 0.887 |
| Race/n(%) | 4.66 | 0.588 | ||
| White | 913 (92.32) | 311 (94.82) | ||
| Black | 41 (4.15) | 11 (3.35) | ||
| Asian | 17 (1.72) | 5 (1.52) | ||
| Other | 18 (1.82) | 1 (0.30) | ||
| APOE4/n(%) | 29.54 | 0.000 | ||
| Negative | 563 (56.93) | 130 (39.63) | ||
| Positive | 426 (43.07) | 198 (60.37) |
| Characteristic | Without cognitive deterioration (n=878) | With cognitive deterioration (n=275) | χ2/U value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose/(mmol·L-1) | 5.11±0.47 | 5.09±0.46 | 117 183.00 | 0.462 |
| Age/year | 73.57±7.15 | 74.45±6.96 | 110 131.50 | 0.028 |
| BMI/(kg·m-2) | 26.80±4.60 | 26.80±4.32 | 93 583.00 | 0.627 |
| Gender/n(%) | 3.31 | 0.069 | ||
| Male | 459 (52.28) | 161 (58.55) | ||
| Female | 419 (47.72) | 114 (41.45) | ||
| Education/year | 15.96±2.84 | 15.90 ± 2.70 | 118 879.00 | 0.698 |
| Race/n(%) | 5.33 | 0.377 | ||
| White | 817 (93.05) | 264 (96.00) | ||
| Black | 34 (3.87) | 7 (2.55) | ||
| Asian | 14 (1.59) | 4 (1.45) | ||
| Other | 13 (1.48) | 0 (0) | ||
| APOE4/n(%) | 26.25 | 0.000 | ||
| Negative | 500 (56.95) | 108 (39.27) | ||
| Positive | 378 (43.05) | 167 (60.73) |
表3 无认知功能恶化组和认知功能恶化组的基线特征比较(正常FBG组)
Tab 3 Comparison of baseline characteristics between individuals without and with cognitive deterioration (normal FBG group)
| Characteristic | Without cognitive deterioration (n=878) | With cognitive deterioration (n=275) | χ2/U value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose/(mmol·L-1) | 5.11±0.47 | 5.09±0.46 | 117 183.00 | 0.462 |
| Age/year | 73.57±7.15 | 74.45±6.96 | 110 131.50 | 0.028 |
| BMI/(kg·m-2) | 26.80±4.60 | 26.80±4.32 | 93 583.00 | 0.627 |
| Gender/n(%) | 3.31 | 0.069 | ||
| Male | 459 (52.28) | 161 (58.55) | ||
| Female | 419 (47.72) | 114 (41.45) | ||
| Education/year | 15.96±2.84 | 15.90 ± 2.70 | 118 879.00 | 0.698 |
| Race/n(%) | 5.33 | 0.377 | ||
| White | 817 (93.05) | 264 (96.00) | ||
| Black | 34 (3.87) | 7 (2.55) | ||
| Asian | 14 (1.59) | 4 (1.45) | ||
| Other | 13 (1.48) | 0 (0) | ||
| APOE4/n(%) | 26.25 | 0.000 | ||
| Negative | 500 (56.95) | 108 (39.27) | ||
| Positive | 378 (43.05) | 167 (60.73) |
| Characteristic | Without cognitive impairment (n=111) | With cognitive impairment (n=53) | χ2/U value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose/(mmol·L-1) | 7.11±1.13 | 7.09±1.42 | 2 569.00 | 0.190 |
| Age/year | 74.00±6.54 | 75.33±6.19 | 2 635.50 | 0.282 |
| BMI/(kg·m-2) | 26.72±5.07 | 26.90±5.27 | 2 383.50 | 0.956 |
| Gender/n(%) | 1.44 | 0.230 | ||
| Male | 69 (62.16) | 38 (71.70) | ||
| Female | 42 (37.84) | 15 (28.30) | ||
| Education/year | 15.73±2.77 | 16.42±2.37 | 2 565.50 | 0.177 |
| Race/n(%) | 1.25 | 0.869 | ||
| White | 96 (86.49) | 47 (88.68) | ||
| Black | 7 (6.31) | 4 (7.55) | ||
| Asian | 3 (2.70) | 1 (1.89) | ||
| Other | 5 (4.50) | 1 (1.89) | ||
| APOE4/n(%) | 3.34 | 0.068 | ||
| Negative | 63 (56.76) | 22 (41.51) | ||
| Positive | 48 (43.24) | 31 (58.49) |
表4 无认知功能恶化组和认知功能恶化组的基线特征比较(高FBG组)
Tab 4 Comparison of baseline characteristics between individuals without and with cognitive deterioration (high FBG group)
| Characteristic | Without cognitive impairment (n=111) | With cognitive impairment (n=53) | χ2/U value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose/(mmol·L-1) | 7.11±1.13 | 7.09±1.42 | 2 569.00 | 0.190 |
| Age/year | 74.00±6.54 | 75.33±6.19 | 2 635.50 | 0.282 |
| BMI/(kg·m-2) | 26.72±5.07 | 26.90±5.27 | 2 383.50 | 0.956 |
| Gender/n(%) | 1.44 | 0.230 | ||
| Male | 69 (62.16) | 38 (71.70) | ||
| Female | 42 (37.84) | 15 (28.30) | ||
| Education/year | 15.73±2.77 | 16.42±2.37 | 2 565.50 | 0.177 |
| Race/n(%) | 1.25 | 0.869 | ||
| White | 96 (86.49) | 47 (88.68) | ||
| Black | 7 (6.31) | 4 (7.55) | ||
| Asian | 3 (2.70) | 1 (1.89) | ||
| Other | 5 (4.50) | 1 (1.89) | ||
| APOE4/n(%) | 3.34 | 0.068 | ||
| Negative | 63 (56.76) | 22 (41.51) | ||
| Positive | 48 (43.24) | 31 (58.49) |
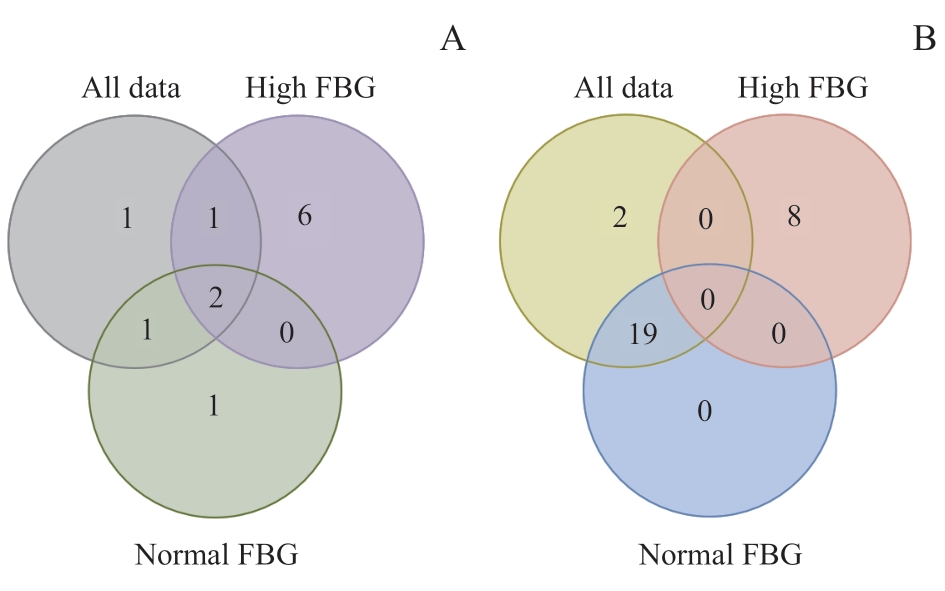
图2 差异代谢物维恩图Note: A. The Venn diagram of differential metabolites between the individuals with cognitive deterioration and without cognitive deterioration at baseline. B. The Venn diagram of differential metabolites between baseline and follow-up in the individuals with cognitive deterioration.
Fig 2 Venn diagram of differential metabolites
| Indicator | P value | Trend | VIP value |
|---|---|---|---|
| All data | |||
| Sphingomyelins | 0.041 | ↓ | 1.66 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in medium HDL | 0.011 | ↑ | 1.93 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in medium HDL | 0.037 | ↓ | 1.31 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in IDL | 0.034 | ↑ | 2.71 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in very small VLDL | 0.009 | ↑ | 2.39 |
| Normal FBG group | |||
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in large HDL | 0.026 | ↓ | 1.13 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in medium HDL | 0.020 | ↑ | 2.23 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in medium HDL | 0.045 | ↓ | 1.78 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in very small VLDL | 0.049 | ↑ | 2.51 |
| High FBG group | |||
| Valine | 0.023 | ↑ | 1.02 |
| Histidine | 0.014 | ↑ | 1.38 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in medium HDL | 0.042 | ↑ | 1.08 |
| Free cholesterol to total lipids ratio in small HDL | 0.017 | ↓ | 1.21 |
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in IDL | 0.044 | ↓ | 1.53 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in IDL | 0.010 | ↑ | 2.16 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in very large VLDL | 0.049 | ↑ | 1.91 |
| Free cholesterol to total lipids ratio in very large VLDL | 0.016 | ↑ | 1.92 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in very small VLDL | 0.033 | ↑ | 1.75 |
表5 无认知功能恶化人群和有认知功能恶化人群的基线数据差异代谢指标(全人群)
Tab 5 Differential metabolic indicators between the individuals without and with cognitive deterioration at baseline (all data)
| Indicator | P value | Trend | VIP value |
|---|---|---|---|
| All data | |||
| Sphingomyelins | 0.041 | ↓ | 1.66 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in medium HDL | 0.011 | ↑ | 1.93 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in medium HDL | 0.037 | ↓ | 1.31 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in IDL | 0.034 | ↑ | 2.71 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in very small VLDL | 0.009 | ↑ | 2.39 |
| Normal FBG group | |||
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in large HDL | 0.026 | ↓ | 1.13 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in medium HDL | 0.020 | ↑ | 2.23 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in medium HDL | 0.045 | ↓ | 1.78 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in very small VLDL | 0.049 | ↑ | 2.51 |
| High FBG group | |||
| Valine | 0.023 | ↑ | 1.02 |
| Histidine | 0.014 | ↑ | 1.38 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in medium HDL | 0.042 | ↑ | 1.08 |
| Free cholesterol to total lipids ratio in small HDL | 0.017 | ↓ | 1.21 |
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in IDL | 0.044 | ↓ | 1.53 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in IDL | 0.010 | ↑ | 2.16 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in very large VLDL | 0.049 | ↑ | 1.91 |
| Free cholesterol to total lipids ratio in very large VLDL | 0.016 | ↑ | 1.92 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in very small VLDL | 0.033 | ↑ | 1.75 |
| Indicator | P value | Trend | VIP value |
|---|---|---|---|
| All data | |||
| Leucine | 0.001 | ↑ | 1.03 |
| Phenylalanine | <0.001 | ↑ | 1.63 |
| Albumin | 0.008 | ↑ | 1.24 |
| Total lipids in very large HDL | 0.046 | ↓ | 2.06 |
| Free cholesterol in very large HDL | 0.027 | ↓ | 2.48 |
| Phospholipids in very large HDL | 0.030 | ↓ | 2.14 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in very large HDL | 0.029 | ↑ | 2.08 |
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in very large HDL | 0.006 | ↑ | 2.40 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in very large HDL | 0.017 | ↓ | 2.37 |
| Free cholesterol to total lipids ratio in large HDL | 0.014 | ↓ | 1.73 |
| Concentration of small HDL particles | 0.002 | ↑ | 2.78 |
| Total lipids in small HDL | 0.007 | ↑ | 2.38 |
| Total cholesterol in small HDL | 0.004 | ↑ | 2.83 |
| Free cholesterol in small HDL | 0.027 | ↑ | 1.91 |
| Cholesterol esters in small HDL | 0.002 | ↑ | 3.04 |
| Phospholipids in small HDL | 0.022 | ↑ | 2.05 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in small LDL | 0.002 | ↑ | 2.28 |
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in small LDL | 0.004 | ↑ | 1.16 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in small LDL | 0.001 | ↓ | 1.85 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in very large VLDL | 0.045 | ↑ | 1.22 |
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in very large VLDL | 0.038 | ↑ | 1.55 |
| Normal FBG group | |||
| Phenylalanine | <0.001 | ↑ | 1.64 |
| Leucine | 0.005 | ↑ | 1.01 |
| Albumin | 0.030 | ↑ | 1.35 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in very large HDL | 0.043 | ↑ | 2.22 |
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in very large HDL | 0.014 | ↑ | 2.57 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in very large HDL | 0.044 | ↓ | 2.14 |
| Free cholesterol in very large HDL | 0.048 | ↓ | 2.32 |
| Free cholesterol to total lipids ratio in large HDL | 0.022 | ↓ | 1.50 |
| Concentration of small HDL particles | 0.005 | ↑ | 2.95 |
| Total lipids in small HDL | 0.011 | ↑ | 2.60 |
| Free cholesterol in small HDL | 0.030 | ↑ | 2.19 |
| Total cholesterol in small HDL | 0.008 | ↑ | 2.97 |
| Cholesterol esters in small HDL | 0.006 | ↑ | 3.14 |
| Phospholipids in small HDL | 0.029 | ↑ | 2.29 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in small LDL | 0.003 | ↑ | 2.70 |
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in small LDL | 0.003 | ↑ | 1.71 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in small LDL | 0.002 | ↓ | 2.26 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in very large VLDL | 0.042 | ↑ | 1.40 |
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in very large VLDL | 0.043 | ↑ | 1.64 |
| High FBG group | |||
| Concentration of medium LDL particles | 0.031 | ↑ | 1.93 |
| Total lipids in medium LDL | 0.030 | ↑ | 2.15 |
| Cholesterol esters in medium LDL | 0.033 | ↑ | 2.15 |
| Phospholipids in medium LDL | 0.023 | ↑ | 2.18 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in IDL | 0.037 | ↓ | 1.94 |
| Total lipids in small LDL | 0.036 | ↑ | 1.96 |
| Cholesterol esters in small LDL | 0.049 | ↑ | 1.95 |
| Phospholipids in small LDL | 0.043 | ↑ | 1.82 |
表 6 认知功能恶化人群在认知恶化发生前后的显著差异代谢指标
Tab 6 Differential metabolic indicators between the individuals with cognitive deterioration before and after cognitive deterioration
| Indicator | P value | Trend | VIP value |
|---|---|---|---|
| All data | |||
| Leucine | 0.001 | ↑ | 1.03 |
| Phenylalanine | <0.001 | ↑ | 1.63 |
| Albumin | 0.008 | ↑ | 1.24 |
| Total lipids in very large HDL | 0.046 | ↓ | 2.06 |
| Free cholesterol in very large HDL | 0.027 | ↓ | 2.48 |
| Phospholipids in very large HDL | 0.030 | ↓ | 2.14 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in very large HDL | 0.029 | ↑ | 2.08 |
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in very large HDL | 0.006 | ↑ | 2.40 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in very large HDL | 0.017 | ↓ | 2.37 |
| Free cholesterol to total lipids ratio in large HDL | 0.014 | ↓ | 1.73 |
| Concentration of small HDL particles | 0.002 | ↑ | 2.78 |
| Total lipids in small HDL | 0.007 | ↑ | 2.38 |
| Total cholesterol in small HDL | 0.004 | ↑ | 2.83 |
| Free cholesterol in small HDL | 0.027 | ↑ | 1.91 |
| Cholesterol esters in small HDL | 0.002 | ↑ | 3.04 |
| Phospholipids in small HDL | 0.022 | ↑ | 2.05 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in small LDL | 0.002 | ↑ | 2.28 |
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in small LDL | 0.004 | ↑ | 1.16 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in small LDL | 0.001 | ↓ | 1.85 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in very large VLDL | 0.045 | ↑ | 1.22 |
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in very large VLDL | 0.038 | ↑ | 1.55 |
| Normal FBG group | |||
| Phenylalanine | <0.001 | ↑ | 1.64 |
| Leucine | 0.005 | ↑ | 1.01 |
| Albumin | 0.030 | ↑ | 1.35 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in very large HDL | 0.043 | ↑ | 2.22 |
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in very large HDL | 0.014 | ↑ | 2.57 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in very large HDL | 0.044 | ↓ | 2.14 |
| Free cholesterol in very large HDL | 0.048 | ↓ | 2.32 |
| Free cholesterol to total lipids ratio in large HDL | 0.022 | ↓ | 1.50 |
| Concentration of small HDL particles | 0.005 | ↑ | 2.95 |
| Total lipids in small HDL | 0.011 | ↑ | 2.60 |
| Free cholesterol in small HDL | 0.030 | ↑ | 2.19 |
| Total cholesterol in small HDL | 0.008 | ↑ | 2.97 |
| Cholesterol esters in small HDL | 0.006 | ↑ | 3.14 |
| Phospholipids in small HDL | 0.029 | ↑ | 2.29 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in small LDL | 0.003 | ↑ | 2.70 |
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in small LDL | 0.003 | ↑ | 1.71 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in small LDL | 0.002 | ↓ | 2.26 |
| Cholesterol to total lipids ratio in very large VLDL | 0.042 | ↑ | 1.40 |
| Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in very large VLDL | 0.043 | ↑ | 1.64 |
| High FBG group | |||
| Concentration of medium LDL particles | 0.031 | ↑ | 1.93 |
| Total lipids in medium LDL | 0.030 | ↑ | 2.15 |
| Cholesterol esters in medium LDL | 0.033 | ↑ | 2.15 |
| Phospholipids in medium LDL | 0.023 | ↑ | 2.18 |
| Phospholipids to total lipids ratio in IDL | 0.037 | ↓ | 1.94 |
| Total lipids in small LDL | 0.036 | ↑ | 1.96 |
| Cholesterol esters in small LDL | 0.049 | ↑ | 1.95 |
| Phospholipids in small LDL | 0.043 | ↑ | 1.82 |
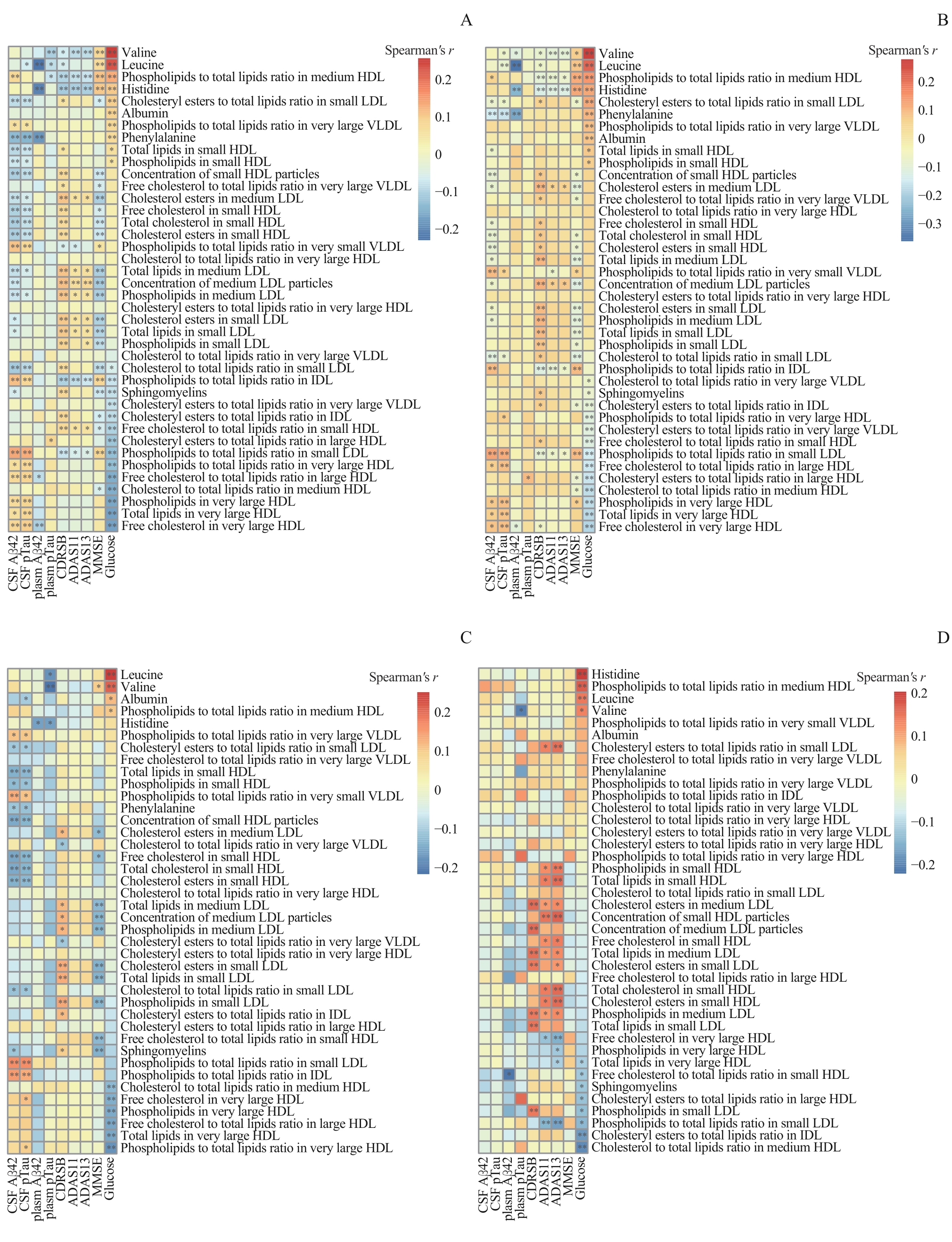
图3 代谢物与认知功能恶化指标的Spearman相关分析的热图Note:Spearman analysis results illustrating the correlation between disease biomarker levels and metabolite levels across various datasets: the entire baseline dataset (A), the baseline data of the individuals without cognitive deterioration (B), the baseline data of the individuals with cognitive deterioration (C), and the data at the onset of initial cognitive deterioration (D). * means P<0.05, ** means P<0.01.
Fig 3 Spearman's correlation analysis heatmap between metabolites and indicators of cognitive impairment
| 1 | 《中国老年2型糖尿病防治临床指南》编写组. 中国老年2型糖尿病防治临床指南(2022年版)[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志, 2022, 30(1): 2-51. |
| Authoring Committee for the Clinical Guidelines on the Prevention and Treatment of Elderly Diabetes in China. Clinical guidelines for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the elderly in China (2022 edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Diabetes Mellitus, 2022, 30(1): 2-51. | |
| 2 | 中华医学会内分泌学分会. 糖尿病患者认知功能障碍专家共识[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2021, 13(7): 678-694. |
| Chinese Society of Endocrinology. Expert consensus on cognitive dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus[J]. Chinese Journal of Diabetes Mellitus, 2021, 13(7): 678-694. | |
| 3 | HOWARTH C, GLEESON P, ATTWELL D. Updated energy budgets for neural computation in the neocortex and cerebellum[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2012, 32(7): 1222-1232. |
| 4 | CAMANDOLA S, MATTSON M P. Brain metabolism in health, aging, and neurodegeneration[J]. EMBO J, 2017, 36(11): 1474-1492. |
| 5 | SZABLEWSKI L. Glucose transporters in brain: in health and in Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2017, 55(4): 1307-1320. |
| 6 | BAO H, LIU Y M, ZHANG M G, et al. Increased β-site APP cleaving enzyme 1-mediated insulin receptor cleavage in type 2 diabetes mellitus with cognitive impairment[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2021, 17(7): 1097-1108. |
| 7 | QU M L, ZUO L H, ZHANG M R, et al. High glucose induces tau hyperphosphorylation in hippocampal neurons via inhibition of ALKBH5-mediated Dgkh m6A demethylation: a potential mechanism for diabetic cognitive dysfunction[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(6): 385. |
| 8 | WANG J, LI L, ZHANG Z, et al. Extracellular vesicles mediate the communication of adipose tissue with brain and promote cognitive impairment associated with insulin resistance[J]. Cell Metab, 2022, 34(9): 1264-1279.e8. |
| 9 | NHO K, KUEIDER-PAISLEY A, MAHMOUDIANDEHKORDI S, et al. Altered bile acid profile in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: relationship to neuroimaging and CSF biomarkers[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2019, 15(2): 232-244. |
| 10 | SOININEN P, KANGAS A J, WÜRTZ P, et al. High-throughput serum NMR metabonomics for cost-effective holistic studies on systemic metabolism[J]. Analyst, 2009, 134(9): 1781-1785. |
| 11 | PETERSEN R C, AISEN P S, BECKETT L A, et al. Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI): clinical characterization[J]. Neurology, 2010, 74(3): 201-209. |
| 12 | MCKHANN G, DRACHMAN D, FOLSTEIN M, et al. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease[J]. Neurology, 1984, 34(7): 939-944. |
| 13 | JAGIELSKI A C, JIANG C Q, XU L, et al. Glycaemia is associated with cognitive impairment in older adults: the Guangzhou Biobank Cohort Study[J]. Age Ageing, 2015, 44(1): 65-71. |
| 14 | GONZÁLEZ H M, TARRAF W, GONZÁLEZ K A, et al. Diabetes, cognitive decline, and mild cognitive impairment among diverse Hispanics/Latinos: study of Latinos-investigation of neurocognitive aging results (HCHS/SOL)[J]. Diabetes Care, 2020, 43(5): 1111-1117. |
| 15 | WOODIE L, BLYTHE S. The differential effects of high-fat and high-fructose diets on physiology and behavior in male rats[J]. Nutr Neurosci, 2018, 21(5): 328-336. |
| 16 | TAN B L, NORHAIZAN M E. Effect of high-fat diets on oxidative stress, cellular inflammatory response and cognitive function[J]. Nutrients, 2019, 11(11): 2579. |
| 17 | REITZ C, TANG M X, LUCHSINGER J, et al. Relation of plasma lipids to Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia[J]. Arch Neurol, 2004, 61(5): 705-714. |
| 18 | BAUMGART M, SNYDER H M, CARRILLO M C, et al. Summary of the evidence on modifiable risk factors for cognitive decline and dementia: a population-based perspective[J]. Alzheimer's Dement, 2015, 11(6): 718-726. |
| 19 | STROM B L, SCHINNAR R, KARLAWISH J, et al. Statin therapy and risk of acute memory impairment[J]. JAMA Intern Med, 2015, 175(8): 1399-1405. |
| 20 | OLSSON A G, ANGELIN B, ASSMANN G, et al. Can LDL cholesterol be too low? Possible risks of extremely low levels[J]. J Intern Med, 2017, 281(6): 534-553. |
| 21 | ISO H, JACOBS D R Jr, WENTWORTH D, et al. Serum cholesterol levels and six-year mortality from stroke in 350 977 men screened for the multiple risk factor intervention trial[J]. N Engl J Med, 1989, 320(14): 904-910. |
| 22 | WHITE P J, MCGARRAH R W, HERMAN M A, et al. Insulin action, type 2 diabetes, and branched-chain amino acids: a two-way street[J]. Mol Metab, 2021, 52: 101261. |
| 23 | SHIDA Y, ENDO H, OWADA S, et al. Branched-chain amino acids govern the high learning ability phenotype in Tokai high avoider (THA) rats[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 23104. |
| 24 | COLE J T, MITALA C M, KUNDU S, et al. Dietary branched chain amino acids ameliorate injury-induced cognitive impairment[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010, 107(1): 366-371. |
| 25 | SIDDIK M A B, MULLINS C A, KRAMER A, et al. Branched-chain amino acids are linked with Alzheimer's disease-related pathology and cognitive deficits[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(21): 3523. |
| 26 | EUSER S M, SATTAR N, WITTEMAN J C M, et al. A prospective analysis of elevated fasting glucose levels and cognitive function in older people: results from PROSPER and the Rotterdam Study[J]. Diabetes, 2010, 59(7): 1601-1607. |
| 27 | GANGULI M, BEER J C, ZMUDA J M, et al. Aging, diabetes, obesity, and cognitive decline: a population-based study[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2020, 68(5): 991-998. |
| 28 | NAGAI N, ITO Y, SASAKI H. Hyperglycemia enhances the production of amyloid β1-42 in the lenses of Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats, a model of human type 2 diabetes[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2016, 57(3): 1408-1417. |
| 29 | YANG Y, WU Y L, ZHANG S T, et al. High glucose promotes Aβ production by inhibiting APP degradation[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(7): e69824. |
| 30 | EXALTO L G, van der FLIER W M, SCHELTENS P, et al. Glycemia and levels of cerebrospinal fluid amyloid and tau in patients attending a memory clinic[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2010, 58(7): 1318-1321. |
| 31 | LU Y H, JIANG X J, LIU S L, et al. Changes in cerebrospinal fluid tau and β-amyloid levels in diabetic and prediabetic patients: a meta-analysis[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2018, 10: 271. |
| 32 | ARNOLD S E, ARVANITAKIS Z, MACAULEY-RAMBACH S L, et al. Brain insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer disease: concepts and conundrums[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2018, 14(3): 168-181. |
| 33 | BUTTERFIELD D A, HALLIWELL B. Oxidative stress, dysfunctional glucose metabolism and Alzheimer disease[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2019, 20(3): 148-160. |
| 34 | NGUYEN T T, TA Q T H, NGUYEN T K O, et al. Type 3 diabetes and its role implications in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(9): 3165. |
| [1] | 吴倩, 李华婷. 代谢性疾病与嗅觉改变及其机制进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(1): 131-136. |
| [2] | 蒋昕婷, 黄高忠. 营养干预对阿尔茨海默病相关认知障碍影响的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(6): 788-794. |
| [3] | 刘桃桃, 刘晓黎, 邬静莹, 倪瑞隆, 张梦圆, 季杜欣, 张梅, 曹立. 成人脑型肾上腺脑白质营养不良的临床及遗传学特征[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 592-599. |
| [4] | 沈力, 黄亨烨, 于广军. 早中期早产儿校正18月龄神经发育状况和影响因素[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(4): 445-452. |
| [5] | 姜静, 卞勇, 郑吉建, 黄悦. 狭颅症儿童颅骨修补术中出血量的影响因素[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(4): 453-458. |
| [6] | 易小璇, 胡森林, 孙阳, 黄庆霞, 唐惠儒. 乙型肝炎病毒感染者血清脂蛋白亚类及其组分的定量特征[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(2): 143-151. |
| [7] | 薛淋淋, 李秉翰, 常丽仙, 李卫昆, 刘春云, 刘立. 丙型病毒性肝炎肝硬化失代偿期患者发生细菌感染的列线图预测模型构建及评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 52-60. |
| [8] | 黄治物, 吴皓. 年龄相关性听力损失研究进展与临床干预策略[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(9): 1182-1187. |
| [9] | 宗春燕, 何杰, 张哲, 贾仁兵, 沈键锋. APOBEC3B调控葡萄膜黑色素瘤复制应激的研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(8): 1034-1044. |
| [10] | 朱月悦, 张锦文, 马锐翔, 陈彩莲, 林羿, 刘晓瑞. 产后血栓性疾病的危险因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(4): 415-421. |
| [11] | 张梦吉, 黄琳, 李峥, 马卓然, 魏霖, 袁安彩, 胡刘华, 张薇, 钱昆, 卜军. 基于人群大队列探索心脑血管疾病相关血浆代谢组学特征[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(3): 259-266. |
| [12] | 张彤, 田雪, 左颖婷, 郑曼琪, 张怡君, 吴寿岭, 陈朔华, 马高亭, 佟旭, 王安心, 莫大鹏. 无传统危险因素人群中TyG指数与心脑血管疾病的关系[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(3): 267-274. |
| [13] | 李爱求, 张潇潇, 姜允丽, 肖艳赏, 丁国栋, 吴蓓蓉, 董晓艳. 学龄前儿童反复喘息的相关危险因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(10): 1435-1440. |
| [14] | 张佳思, 邹春波, 卢宇, 陈茜, 张伟亚, 何姣姣. 血脂蛋白磷脂酶A2和中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白在诊断早期糖尿病肾病中的价值[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(6): 770-775. |
| [15] | 丁远森, 王枫, 孙家悦, 邵正威, 邹德荣, 陆家瑜. 不同年龄2型糖尿病患者牙周健康流行病学调查[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(2): 217-222. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||