
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (10): 1307-1315.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.10.013
收稿日期:2024-03-20
接受日期:2024-06-04
出版日期:2024-10-28
发布日期:2024-10-28
通讯作者:
刘 敏,电子信箱:lm4104@shtrhospital.com。作者简介:陈子旋(1999—),男,傣族,硕士生;电子信箱:czixuan2023@126.com。
基金资助:Received:2024-03-20
Accepted:2024-06-04
Online:2024-10-28
Published:2024-10-28
Contact:
LIU Min, E-mail: lm4104@shtrhospital.com.Supported by:摘要:
肾细胞癌(renal cell carcinoma,RCC)起源于肾小管上皮细胞,是最常见的肾癌类型,也是死亡率最高的泌尿系统肿瘤。近半个世纪以来,RCC的发病率和死亡率持续上升,给人类健康带来了极大的威胁。尽管手术治疗为大多数 RCC 患者提供了治愈的可能,但肿瘤的复发或转移导致传统治疗方案无法达到理想的效果。因此,受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂和免疫检查点抑制剂等靶向药物的出现,给RCC的治疗带来了新的希望。靶向治疗成为治疗晚期RCC的主要方式。舒尼替尼是一种受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂,其通过抑制表皮生长因子受体、血小板衍生生长因子受体、血管内皮生长因子受体等多种受体酪氨酸激酶的活性,抑制肿瘤的血管生成和细胞增殖,最终有效控制肿瘤进展,在RCC的治疗中发挥着关键作用。然而,相当多的RCC患者在使用舒尼替尼治疗后的15个月内对其产生耐药性,给RCC的治疗带来了新的挑战。该文总结了RCC舒尼替尼耐药性的发生机制,归纳了RCC舒尼替尼耐药性的治疗策略,以期为克服RCC对舒尼替尼的耐药,给晚期RCC患者制定更有效的治疗方案提供思路。
中图分类号:
陈子旋, 刘敏. 肾细胞癌舒尼替尼耐药性的机制及治疗研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(10): 1307-1315.
CHEN Zixuan, LIU Min. Progress in mechanisms and treatment of sunitinib resistance in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(10): 1307-1315.
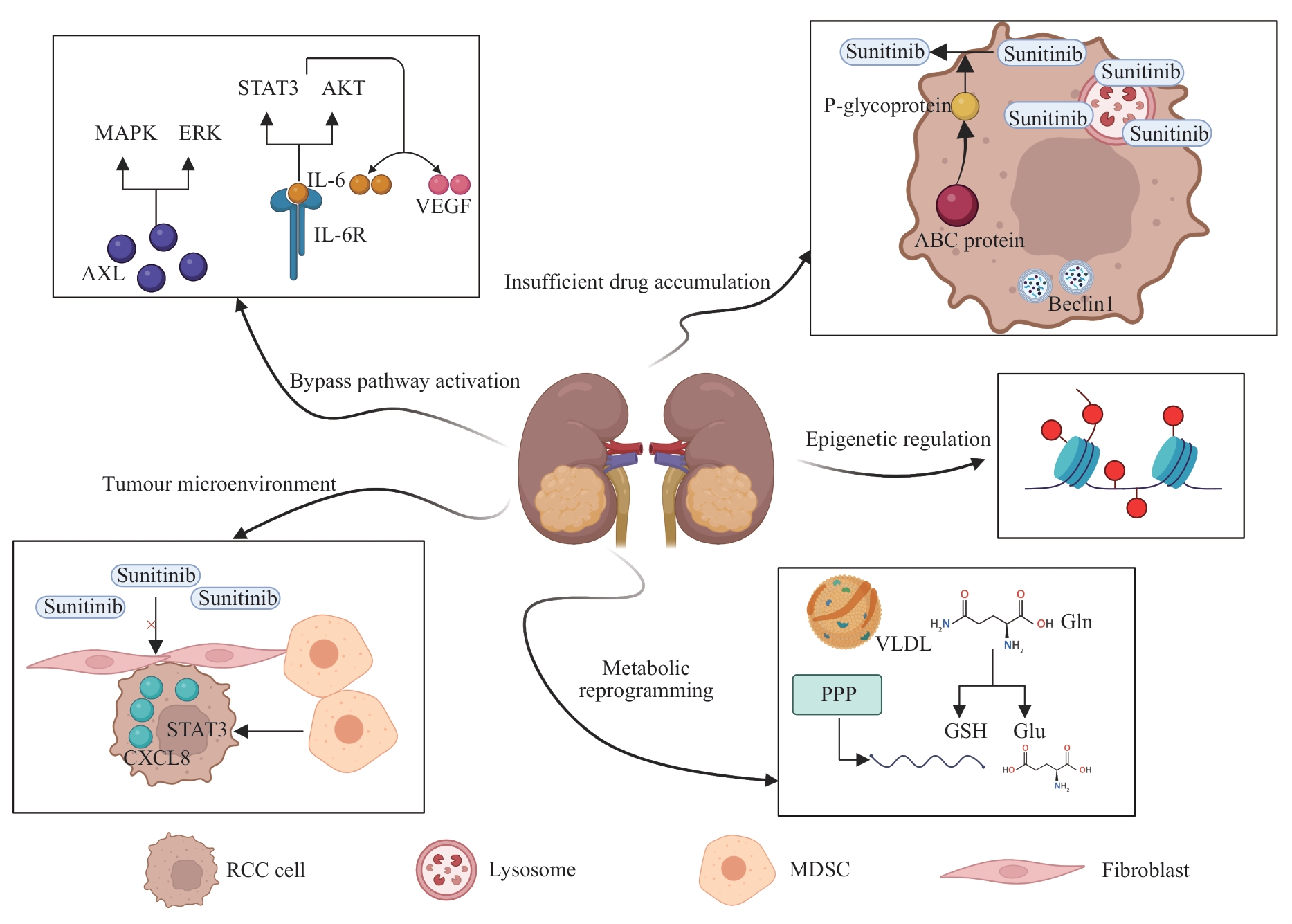
图1 肾细胞癌舒尼替尼耐药性的机制Note: MAPK—mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK—extracellular regulated protein kinase; IL-6—interleukin-6; STAT3—signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; AKT—protein kinase B; VEGF—vascular endothelial growth factor; AXL—AXR1-like; CXCL8—C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8; ABC—ATP-binding cassette; VLDL—very-low-density lipoprotein; PPP—pentose phosphate pathway; Gln—glutamine; GSH—glutathione; Glu—glutamate; MDSC—myeloid-derived suppressor cell.
Fig 1 Mechanisms of sunitinib resistance in renal cell carcinoma
| 1 | RAHIB L, WEHNER M R, MATRISIAN L M, et al. Estimated projection of US cancer incidence and death to 2040[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2021, 4(4): e214708. |
| 2 | SEMENESCU L E, KAMEL A, CIUBOTARU V, et al. An overview of systemic targeted therapy in renal cell carcinoma, with a focus on metastatic renal cell carcinoma and brain metastases[J]. Curr Issues Mol Biol, 2023, 45(9): 7680-7704. |
| 3 | JIN J, XIE Y H, ZHANG J S, et al. Sunitinib resistance in renal cell carcinoma: from molecular mechanisms to predictive biomarkers[J]. Drug Resist Updat, 2023, 67: 100929. |
| 4 | SHARMA R, KADIFE E, MYERS M, et al. Determinants of resistance to VEGF-TKI and immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 40(1): 186. |
| 5 | BI K, HE M X, BAKOUNY Z, et al. Tumor and immune reprogramming during immunotherapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Cell, 2021, 39(5): 649-661.e5. |
| 6 | MIKAMI S, MIZUNO R, KOSAKA T, et al. Significance of tumor microenvironment in acquiring resistance to vascular endothelial growth factor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor and recent advance of systemic treatment of clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Pathol Int, 2020, 70(10): 712-723. |
| 7 | 何凯桐, 周阳, 王明珠, 等. 受体酪氨酸激酶AXL在肿瘤生物学中的作用研究进展[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2024, 32(1): 167-171. |
| HE K T, ZHOU Y, WANG M Z, et al. Research progress on the role of receptor tyrosine kinase AXL in tumor biology [J]. Journal of Modern Oncology, 2024, 32(1): 167-171. | |
| 8 | CHEN S J, QIAN S B, ZHANG L, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages promote migration and invasion via modulating IL-6/STAT3 signaling in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2022, 111: 109139. |
| 9 | WANG Y, WANG Y Y, QIN Z Y, et al. The role of non-coding RNAs in ABC transporters regulation and their clinical implications of multidrug resistance in cancer[J]. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol, 2021, 17(3): 291-306. |
| 10 | LIU S Z, YAO S J, YANG H, et al. Autophagy: regulator of cell death[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(10): 648. |
| 11 | LI X H, HE S K, MA B Y. Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 12. |
| 12 | WONG J J W, BERSTAD M B, FREMSTEDAL A S V, et al. Photochemically-induced release of lysosomal sequestered sunitinib: obstacles for therapeutic efficacy[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(2): 417. |
| 13 | NAGASE K, AKUTAGAWA T, RIKITAKE-YAMAMOTO M, et al. Cellular and physical microenvironments regulate the aggressiveness and sunitinib chemosensitivity of clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Pathol, 2021, 254(1): 46-56. |
| 14 | AMBROSETTI D, COUTTS M, PAOLI C, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in renal cell carcinoma: implication in prognosis and resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy[J]. BJU Int, 2022, 129(1): 80-92. |
| 15 | XU C F, JOHNSON T, GARCIA-DONAS J, et al. IL8 polymorphisms and overall survival in pazopanib- or sunitinib-treated patients with renal cell carcinoma[J]. Br J Cancer, 2015, 112(7): 1190-1198. |
| 16 | 彭恬, 徐雷鸣. 表观遗传修饰与环状RNA在结直肠癌中相互作用的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(2): 237-243. |
| PENG T, XU L M. Crosstalk between epigenetic modification and circRNA in colorectal cancer: recent advances [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(2): 237-243. | |
| 17 | ZHAO T L, ZHOU Y L, WANG Q Y, et al. QPCT regulation by CTCF leads to sunitinib resistance in renal cell carcinoma by promoting angiogenesis[J]. Int J Oncol, 2021, 59(1): 48. |
| 18 | CHEN Y L, LU Z Y, QI C, et al. N6-methyladenosine-modified TRAF1 promotes sunitinib resistance by regulating apoptosis and angiogenesis in a METTL14-dependent manner in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 111. |
| 19 | WANG J F, WANG C, XU P, et al. PRMT1 is a novel molecular therapeutic target for clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(11): 5387-5403. |
| 20 | LIU Y Q, ZHANG H, FANG Y, et al. Non-coding RNAs in renal cell carcinoma: implications for drug resistance[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2023, 164: 115001. |
| 21 | ZHU H Y, WANG X, LU S H, et al. Metabolic reprogramming of clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2023, 14: 1195500. |
| 22 | SATO T, KAWASAKI Y, MAEKAWA M, et al. Metabolomic analysis to elucidate mechanisms of sunitinib resistance in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Metabolites, 2020, 11(1): 1. |
| 23 | LIBERTI M V, LOCASALE J W. The Warburg effect: how does it benefit cancer cells?[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2016, 41(3): 211-218. |
| 24 | CHEN W F, HILL H, CHRISTIE A, et al. Targeting renal cell carcinoma with a HIF-2 antagonist[J]. Nature, 2016, 539(7627): 112-117. |
| 25 | NAITO S, MAKHOV P, ASTSATUROV I, et al. LDL cholesterol counteracts the antitumour effect of tyrosine kinase inhibitors against renal cell carcinoma[J]. Br J Cancer, 2017, 116(9): 1203-1207. |
| 26 | GARCIA J, HURWITZ H I, SANDLER A B, et al. Bevacizumab (Avastin®) in cancer treatment: a review of 15years of clinical experience and future outlook[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2020, 86: 102017. |
| 27 | ZOU Z L, TAO T, LI H M, et al. mTOR signaling pathway and mTOR inhibitors in cancer: progress and challenges[J]. Cell Biosci, 2020, 10: 31. |
| 28 | MAKHOV P B, GOLOVINE K, KUTIKOV A, et al. Modulation of Akt/mTOR signaling overcomes sunitinib resistance in renal and prostate cancer cells[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2012, 11(7): 1510-1517. |
| 29 | SAHARINEN P, EKLUND L, ALITALO K. Therapeutic targeting of the angiopoietin-TIE pathway[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2017, 16(9): 635-661. |
| 30 | MOOI J, CHIONH F, SAVAS P, et al. Dual antiangiogenesis agents bevacizumab plus trebananib, without chemotherapy, in first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: results of a phase II study[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 27(8): 2159-2167. |
| 31 | ATKINS M B, GRAVIS G, DROSIK K, et al. Trebananib (AMG 386) in combination with sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer: an open-label, multicenter, phase II study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2015, 33(30): 3431-3438. |
| 32 | SAMMARCO E, MANFREDI F, NUZZO A, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor rechallenge in renal cell carcinoma: current evidence and future directions[J]. Cancers, 2023, 15(12): 3172. |
| 33 | MOTZER R J, POWLES T, BUROTTO M, et al. Nivolumab plus cabozantinib versus sunitinib in first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma (CheckMate 9ER): long-term follow-up results from an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2022, 23(7): 888-898. |
| 34 | BAJALIA E M, AZZOUZ F B, CHISM D A, et al. Phytochemicals for the prevention and treatment of renal cell carcinoma: preclinical and clinical evidence and molecular mechanisms[J]. Cancers, 2022, 14(13): 3278. |
| 35 | ASHAQ A, MAQBOOL M F, MARYAM A, et al. Hispidulin: a novel natural compound with therapeutic potential against human cancers[J]. Phytother Res, 2021, 35(2): 771-789. |
| 36 | PORTA C, PROCOPIO G, CARTENÌ G, et al. Sequential use of sorafenib and sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma (RCC): an Italian multicentre retrospective analysis of 189 patient cases[J]. BJU Int, 2011, 108(8 Pt 2): E250-E257. |
| 37 | 张楠. 口服抗癌疫苗正在走向现实[N]. 中国科学报, 2022-05-16(3). |
| ZHANG N. Oral cancer vaccines are becoming a reality[N]. China Science Daily, 2022-05-16(3). | |
| 38 | DEBENEDETTE M, GAMBLE A, NORRIS M, et al. A review of the clinical experience with CMN-001, a tumor RNA loaded dendritic cell immunotherapy for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma[J]. Hum Vaccin Immunother, 2023, 19(2): 2220629. |
| 39 | CHEN R H, XIAO Z W, YAN X Q, et al. Tumor cell-secreted ISG15 promotes tumor cell migration and immune suppression by inducing the macrophage M2-like phenotype[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 594775. |
| 40 | NGUYEN H M, OLADEJO M, PAULISHAK W, et al. A Listeria-based vaccine targeting ISG15 exerts anti-tumor efficacy in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2023, 72(9): 2889-2903. |
| 41 | PUROHIT K, REDDY N, SUNNA A. Exploring the potential of bioactive peptides: from natural sources to therapeutics[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(3): 1391. |
| 42 | KUMAR V, BARWAL A, SHARMA N, et al. Therapeutic proteins: developments, progress, challenges, and future perspectives[J]. 3 Biotech, 2024, 14(4): 112. |
| 43 | ZHANG L, JIN G Z, LI D. Tat-hspb1 suppresses clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) growth via lysosomal membrane permeabilization[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2022, 14(22): 5710. |
| 44 | LI X, LIU M H, LIU H Y, et al. Tumor metabolic reprogramming in lung cancer progression[J]. Oncol Lett, 2022, 24(2): 287. |
| 45 | WANG R L, YAN Q, LIU X, et al. Unraveling lipid metabolism reprogramming for overcoming drug resistance in melanoma[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2024, 223: 116122. |
| 46 | JONASCH E, WALKER C L, RATHMELL W K. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma ontogeny and mechanisms of lethality[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2021, 17(4): 245-261. |
| 47 | CHOUEIRI T K, BAUER T M, PAPADOPOULOS K P, et al. Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-2α in renal cell carcinoma with belzutifan: a phase 1 trial and biomarker analysis[J]. Nat Med, 2021, 27(5): 802-805. |
| 48 | TAN S K, HOUGEN H Y, MERCHAN J R, et al. Fatty acid metabolism reprogramming in ccRCC: mechanisms and potential targets[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2023, 20(1): 48-60. |
| 49 | ZHOU L J, LUO Y B, LIU Y N, et al. Fatty acid oxidation mediated by malonyl-CoA decarboxylase represses renal cell carcinoma progression[J]. Cancer Res, 2023, 83(23): 3920-3939. |
| 50 | BENSAAD K, FAVARO E, LEWIS C A, et al. Fatty acid uptake and lipid storage induced by HIF-1α contribute to cell growth and survival after hypoxia-reoxygenation[J]. Cell Rep, 2014, 9(1): 349-365. |
| 51 | MURANAKA H, AKINSOLA R, BILLET S, et al. Glutamine supplementation as an anticancer strategy: a potential therapeutic alternative to the convention[J]. Cancers, 2024, 16(5): 1057. |
| 52 | MOROZUMI K, KAWASAKI Y, SATO T, et al. Elucidation and regulation of tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in renal cell carcinoma cells from the perspective of glutamine metabolism[J]. Metabolites, 2024, 14(3): 170. |
| 53 | SCHULTE M L, FU A, ZHAO P, et al. Pharmacological blockade of ASCT2-dependent glutamine transport leads to antitumor efficacy in preclinical models[J]. Nat Med, 2018, 24(2): 194-202. |
| 54 | LOI S, SETTLEMAN J, JOYCE J A, et al. The next big questions in cancer research[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(8): 1523-1527. |
| [1] | 朱子俊, 钱逸斐, 李倩玉, 李松玲, 覃雯莉, 刘艳丰. 后期促进复合体亚基10调控PI3K-AKT-mTOR通路促进肝细胞癌进展的研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(9): 1171-1182. |
| [2] | 杨全军, 柏丁源, 周雨萱, 白露, 郭澄. 异柠檬酸脱氢酶1突变介导D-2-羟基戊二酸代谢重编程在肿瘤免疫调控中的作用及相关药物研发进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(9): 1239-1248. |
| [3] | 蒋婕, 张泓, 伦赫远, 潘芬, 于方圆, 何平. 儿童肺炎克雷伯菌感染分子流行病学特征[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(8): 1027-1034. |
| [4] | 陈子旋, 刘敏. 肾细胞癌免疫细胞治疗的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(7): 916-925. |
| [5] | 王高明, 崔然, 黎彦璟, 刘颖斌. KRAS R68G继发突变引发KRASG12D靶向抑制剂MRTX1133耐药的机制研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(6): 705-716. |
| [6] | 梁效宁, 石亭旺, 陈云丰. 小菌落变异株的致病机制及治疗研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(6): 784-791. |
| [7] | 邹沛辰, 刘鸿宇, 阿衣娜扎尔·艾合买提, 朱亮, 唐亚斌, 雷绘敏. 索托拉西布获得性耐药肺癌细胞的代谢轮廓分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 138-149. |
| [8] | 吴诗怡, 陈思, 刘泊含, 刘宇婷, 刘鷖雯, 何怡青, 杜艳, 张国良, 郭倩, 高锋, 杨翠霞. “HA糖外衣”调控ER+乳腺癌细胞干性在内分泌治疗耐药中的作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1298-1307. |
| [9] | 孙晨玮, 海汪溪, 屈骞, 席云. [18F]F-FMISO和[18F]F-FLT PET/CT双核素显像预测胰腺癌耐药性的体内研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(1): 60-68. |
| [10] | 张烨晟, 杨易静, 黄依雯, 施珑玙, 王曼媛, 陈思思. 肿瘤微环境免疫细胞调节肿瘤细胞耐药性的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(7): 830-838. |
| [11] | 周婉桢, 滕银成. 非经典Wnt通路在卵巢癌中的作用与潜在治疗意义研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(8): 1056-1063. |
| [12] | 崔芷嫣, 陈尧, 陶悦, 沈树红, 李慧. PRPS1 I72位点突变对急性淋巴细胞白血病耐药性的影响及其机制研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(8): 977-987. |
| [13] | 赵富茂, 彭玫, 彭晓露, 舒韦韦, 彭丽. 鲍曼不动杆菌在环境美罗培南浓度变化时耐药性的改变及其机制[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(11): 1396-1407. |
| [14] | 张漪蓉, 魏玮庆, 马皎, 张雪. 靶向SOX9调控弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤代谢重编程的研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(10): 1236-1244. |
| [15] | 汤开然, 吴琼, 黄思佳, 邱旭东, 李文彦, 邓华云, 黄雷. 与MUC1共同调控肿瘤化疗耐药的MUCIN家族成员的筛选[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(9): 1288-1295. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
