
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (11): 1359-1365.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2023.11.003
高雄( ), 张秋霞, 杨苗苗, 罗玮, 王月刚(
), 张秋霞, 杨苗苗, 罗玮, 王月刚( ), 修建成(
), 修建成( )
)
收稿日期:2023-09-19
接受日期:2023-11-03
出版日期:2023-11-28
发布日期:2023-11-28
通讯作者:
王月刚,电子信箱:wyg06@fimmu.com。作者简介:高 雄(1992—),男,主治医师,硕士;电子信箱:18779560759@163.com。
基金资助:
GAO Xiong( ), ZHANG Qiuxia, YANG Miaomiao, LUO Wei, WANG Yuegang(
), ZHANG Qiuxia, YANG Miaomiao, LUO Wei, WANG Yuegang( ), XIU Jiancheng(
), XIU Jiancheng( )
)
Received:2023-09-19
Accepted:2023-11-03
Online:2023-11-28
Published:2023-11-28
Contact:
WANG Yuegang, E-mail: wyg06@fimmu.com.Supported by:摘要:
目的·探讨心房颤动(房颤)与认知障碍之间的因果关系。方法·采用两样本孟德尔随机化(Mendelian randomization,MR)分析方法,利用房颤的大规模全基因组关联研究(genome-wide association study,GWAS)汇总数据集,提取与房颤强相关的单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphism,SNP)作为工具变量。基于公开的认知功能障碍的GWAS数据,分别提取SNPs与阿尔茨海默病性痴呆、帕金森病痴呆、血管性痴呆、路易体痴呆、额颞叶痴呆、未定义的痴呆、总体认知功能评估等的关联程度。采用逆方差加权法(inverse variance weighted,IVW)进行主要分析,Cochran′s Q检验、MR-Egger回归、留一法(leave-one-out)进行敏感性分析。为了验证结果的稳健性,使用不同GWAS数据进行重复分析及荟萃分析。结果·初次分析从一项涉及多达1 030 836名个体的全基因组关联研究荟萃分析中提取了101个SNPs作为工具变量,IVW结果未发现房颤与认知障碍的因果联系[痴呆:OR=1.032(95%CI 0.973~1.094),P=0.290;帕金森病痴呆:OR=1.004(95%CI 0.780~1.291),P=0.977;血管性痴呆:OR=1.123(95%CI 0.969~1.301),P=0.125;未定义的痴呆:OR=1.013(95%CI 0.910~1.129),P=0.807]。重复分析从FinnGen网站的房颤GWAS数据提取了27个SNPs作为工具变量,IVW结果与初次分析一致[认知功能:OR=0.999(95%CI 0.982~1.016),P=0.874;阿尔茨海默病性痴呆:OR=0.977(95%CI 0.943~1.012),P=0.193;路易体痴呆:OR=1.014(95%CI 0.898~1.145),P=0.826;额颞叶痴呆:OR=0.996(95%CI 0.745~1.333),P=0.980]。2次孟德尔随机化分析及荟萃分析均表明遗传预测的房颤与不同类型痴呆及总体认知功能评估均无相关证据。MR-Egger回归提示不存在水平多效性,留一法逐个剔除SNP后发现结果稳定。结论·未发现房颤与认知障碍之间的因果关系证据。在观察性研究中观察到的关联可部分归因于共同的生物学或共患病等混杂因素。
中图分类号:
高雄, 张秋霞, 杨苗苗, 罗玮, 王月刚, 修建成. 房颤与认知障碍的因果关系:一项孟德尔随机化研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(11): 1359-1365.
GAO Xiong, ZHANG Qiuxia, YANG Miaomiao, LUO Wei, WANG Yuegang, XIU Jiancheng. Causal relationship between atrial fibrillation and cognitive impairment: a Mendelian randomization study[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(11): 1359-1365.
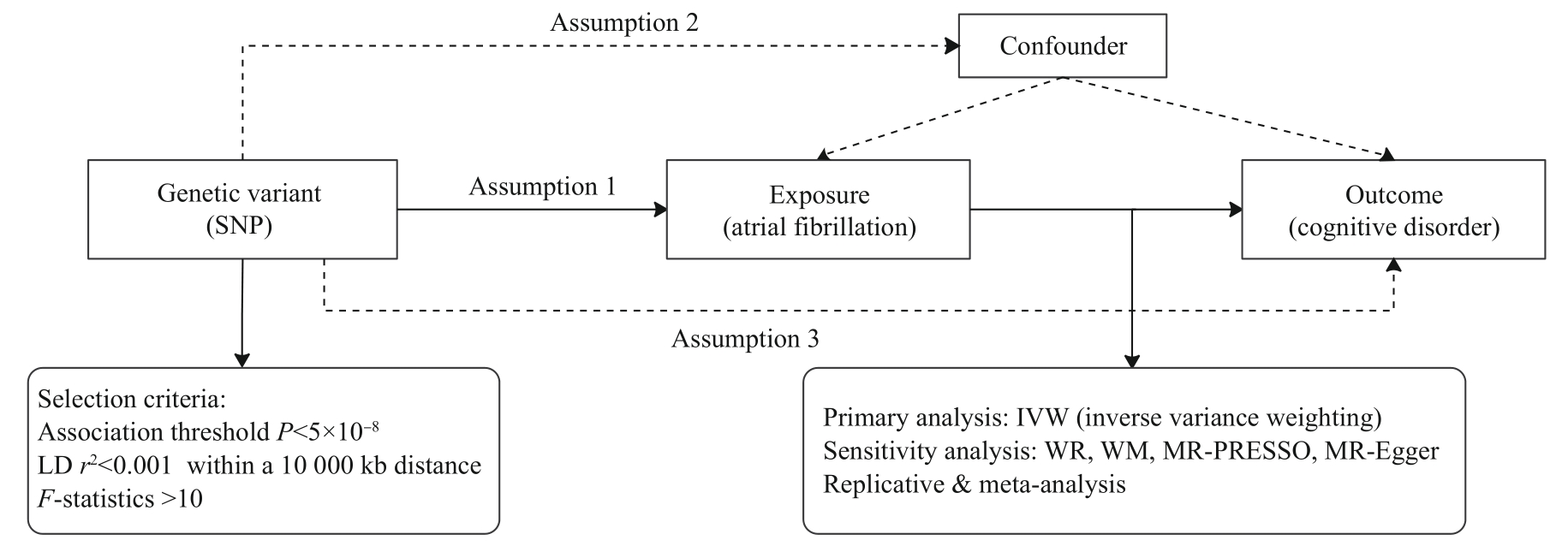
图1 孟德尔随机化研究设计Note: Assumption 1—Genetic variants were robustly associated with exposure. Assumption 2—Genetic variants were not associated with confounders. Assumption 3—Genetic variants affected the outcomes only through the exposure of interest. SNPs—single nucleotide polymorphisms. LD—linkage disequilibrium. WR—Wald ratio; WM—weighted median.
Fig 1 Overview of the current Mendelian randomization (MR) study
| Analysis | Exposure | ID | Sample size/n | Race | Year | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First analysis | Atrial fibrillation | ebi-a-GCST006414 | 1 030 836 | European | 2018 | 30061737 |
| Duplicate analysis | Atrial fibrillation | finn-b-I9 | 138 994 | European | 2021 | NA |
表1 孟德尔分析中暴露因素的GWAS信息
Tab 1 Exposure information of GWAS in the TSMR study
| Analysis | Exposure | ID | Sample size/n | Race | Year | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First analysis | Atrial fibrillation | ebi-a-GCST006414 | 1 030 836 | European | 2018 | 30061737 |
| Duplicate analysis | Atrial fibrillation | finn-b-I9 | 138 994 | European | 2021 | NA |
| Analysis | Outcome | ID | Sample size/n | Race | Year | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First analysis | Dementia | finn-b-F5_DEMENTIA | 216 771 | European | 2021 | NA |
| First analysis | Dementia due to Parkinson′s disease | finn-b-PD_DEMENTIA | 216 895 | European | 2021 | NA |
| First analysis | Vascular dementia | finn-b-F5_VASCDEM | 212 389 | European | 2021 | NA |
| First analysis | Undefined dementia | finn-b-F5_Dementia_U | 215 511 | European | 2021 | NA |
| Duplicate analysis | Cognitive performance | ebi-a-GCST006572 | 257 841 | European | 2018 | 30038396 |
| Duplicate analysis | Alzheimer′s disease | ebi-a-GCST90012877 | 472 868 | European | 2021 | 33589840 |
| Duplicate analysis | Dementia with Lewy body | ebi-a-GCST90001390 | 6 618 | European | 2021 | 33589841 |
| Duplicate analysis | Rontotemporal dementia | ieu-b-43 | 3 024 | European | 2010 | 20154673 |
表2 孟德尔分析中结局因素的GWAS信息
Tab 2 Outcome information of GWAS in the TSMR study
| Analysis | Outcome | ID | Sample size/n | Race | Year | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First analysis | Dementia | finn-b-F5_DEMENTIA | 216 771 | European | 2021 | NA |
| First analysis | Dementia due to Parkinson′s disease | finn-b-PD_DEMENTIA | 216 895 | European | 2021 | NA |
| First analysis | Vascular dementia | finn-b-F5_VASCDEM | 212 389 | European | 2021 | NA |
| First analysis | Undefined dementia | finn-b-F5_Dementia_U | 215 511 | European | 2021 | NA |
| Duplicate analysis | Cognitive performance | ebi-a-GCST006572 | 257 841 | European | 2018 | 30038396 |
| Duplicate analysis | Alzheimer′s disease | ebi-a-GCST90012877 | 472 868 | European | 2021 | 33589840 |
| Duplicate analysis | Dementia with Lewy body | ebi-a-GCST90001390 | 6 618 | European | 2021 | 33589841 |
| Duplicate analysis | Rontotemporal dementia | ieu-b-43 | 3 024 | European | 2010 | 20154673 |
| Analysis | Outcome | IVW method | WM method | MR-Egger method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | ||
| First analysis | Dementia | 1.032 (0.973‒1.094) | 0.290 | 1.020 (0.920‒1.131) | 0.703 | 1.077 (0.962‒1.206) | 0.203 |
| First analysis | Dementia due to Parkinson′s disease | 1.004 (0.780‒1.291) | 0.977 | 0.795 (0.508‒1.245) | 0.316 | 0.982 (0.603‒1.597) | 0.941 |
| First analysis | Vascular dementia | 1.123 (0.969‒1.301) | 0.125 | 1.180 (0.898‒1.550) | 0.234 | 1.260 (0.947‒1.676) | 0.116 |
| First analysis | Undefined dementia | 1.013 (0.910‒1.129) | 0.807 | 1.053 (0.862‒1.285) | 0.615 | 1.170 (0.951‒1.441) | 0.142 |
| Duplicate analysis | Cognitive performance | 0.999 (0.982‒1.016) | 0.874 | 0.989 (0.975‒1.004) | 0.168 | 0.983 (0.946‒1.022) | 0.405 |
| Duplicate analysis | Alzheimer′s disease | 0.977 (0.943‒1.012) | 0.193 | 0.976 (0.930‒1.024) | 0.324 | 0.994 (0.915‒1.079) | 0.885 |
| Duplicate analysis | Dementia with Lewy body | 1.014 (0.898‒1.145) | 0.826 | 1.106 (0.932‒1.311) | 0.248 | 1.253 (0.953‒1.647) | 0.120 |
| Duplicate analysis | Rontotemporal dementia | 0.996 (0.745‒1.333) | 0.980 | 0.966 (0.666‒1.399) | 0.853 | 0.874 (0.480‒1.590) | 0.672 |
表3 房颤与不同类型认知障碍之间关联的MR分析
Tab 3 MR analysis of the association between atrial fibrillation and different types of cognitive impairment
| Analysis | Outcome | IVW method | WM method | MR-Egger method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | ||
| First analysis | Dementia | 1.032 (0.973‒1.094) | 0.290 | 1.020 (0.920‒1.131) | 0.703 | 1.077 (0.962‒1.206) | 0.203 |
| First analysis | Dementia due to Parkinson′s disease | 1.004 (0.780‒1.291) | 0.977 | 0.795 (0.508‒1.245) | 0.316 | 0.982 (0.603‒1.597) | 0.941 |
| First analysis | Vascular dementia | 1.123 (0.969‒1.301) | 0.125 | 1.180 (0.898‒1.550) | 0.234 | 1.260 (0.947‒1.676) | 0.116 |
| First analysis | Undefined dementia | 1.013 (0.910‒1.129) | 0.807 | 1.053 (0.862‒1.285) | 0.615 | 1.170 (0.951‒1.441) | 0.142 |
| Duplicate analysis | Cognitive performance | 0.999 (0.982‒1.016) | 0.874 | 0.989 (0.975‒1.004) | 0.168 | 0.983 (0.946‒1.022) | 0.405 |
| Duplicate analysis | Alzheimer′s disease | 0.977 (0.943‒1.012) | 0.193 | 0.976 (0.930‒1.024) | 0.324 | 0.994 (0.915‒1.079) | 0.885 |
| Duplicate analysis | Dementia with Lewy body | 1.014 (0.898‒1.145) | 0.826 | 1.106 (0.932‒1.311) | 0.248 | 1.253 (0.953‒1.647) | 0.120 |
| Duplicate analysis | Rontotemporal dementia | 0.996 (0.745‒1.333) | 0.980 | 0.966 (0.666‒1.399) | 0.853 | 0.874 (0.480‒1.590) | 0.672 |
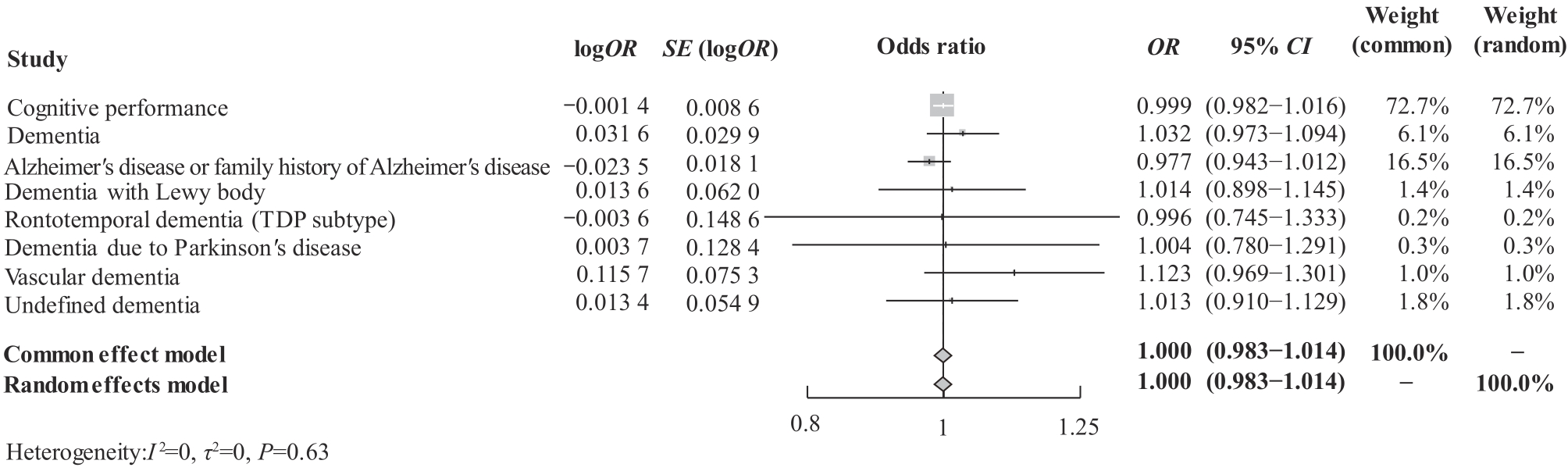
图2 遗传预测的房颤对不同认知障碍的荟萃分析Note: SE—standard error; OR—odds ratio; CI—confidence interval.
Fig 2 Meta-analysis of genetically predicted atrial fibrillation on different cognitive impairments
| Analysis | Outcome | Heterogeneity | Pleiotropy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVW method | MR-Egger method | P value | ||||
| Cochran′s Q | P value | Cochran′s Q | P value | |||
| First analysis | Dementia | 109.881 | 0.194 | 109.054 | 0.190 | 0.393 |
| First analysis | Dementia due to Parkinson′s disease | 83.717 | 0.848 | 83.706 | 0.830 | 0.917 |
| First analysis | Vascular dementia | 105.698 | 0.280 | 104.776 | 0.277 | 0.358 |
| First analysis | Undefined dementia | 94.739 | 0.574 | 92.231 | 0.618 | 0.117 |
| Duplicate analysis | Cognitive performance | 81.518 | 0.000 | 79.054 | 0.000 | 0.396 |
| Duplicate analysis | Alzheimer′s disease | 29.020 | 0.180 | 28.745 | 0.152 | 0.651 |
| Duplicate analysis | Dementia with Lewy body | 15.679 | 0.869 | 12.809 | 0.938 | 0.104 |
| Duplicate analysis | Rontotemporal dementia | 4.755 | 0.783 | 4.512 | 0.719 | 0.637 |
表4 房颤与不同类型认知障碍之间关联的敏感性分析
Tab 4 Sensitivity analysis of the association between atrial fibrillation and different types of cognitive impairment
| Analysis | Outcome | Heterogeneity | Pleiotropy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVW method | MR-Egger method | P value | ||||
| Cochran′s Q | P value | Cochran′s Q | P value | |||
| First analysis | Dementia | 109.881 | 0.194 | 109.054 | 0.190 | 0.393 |
| First analysis | Dementia due to Parkinson′s disease | 83.717 | 0.848 | 83.706 | 0.830 | 0.917 |
| First analysis | Vascular dementia | 105.698 | 0.280 | 104.776 | 0.277 | 0.358 |
| First analysis | Undefined dementia | 94.739 | 0.574 | 92.231 | 0.618 | 0.117 |
| Duplicate analysis | Cognitive performance | 81.518 | 0.000 | 79.054 | 0.000 | 0.396 |
| Duplicate analysis | Alzheimer′s disease | 29.020 | 0.180 | 28.745 | 0.152 | 0.651 |
| Duplicate analysis | Dementia with Lewy body | 15.679 | 0.869 | 12.809 | 0.938 | 0.104 |
| Duplicate analysis | Rontotemporal dementia | 4.755 | 0.783 | 4.512 | 0.719 | 0.637 |
| 1 | HINDRICKS G, POTPARA T, DAGRES N, et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): the Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC[J]. Eur Heart J, 2021, 42(5): 373-498. |
| 2 | SHI S B, TANG Y H, ZHAO Q Y, et al. Prevalence and risk of atrial fibrillation in China: a national cross-sectional epidemiological study[J]. Lancet Reg Health West Pac, 2022, 23: 100439. |
| 3 | BALL J, CARRINGTON M J, STEWART S, et al. Mild cognitive impairment in high-risk patients with chronic atrial fibrillation: a forgotten component of clinical management?[J]. Heart, 2013, 99(8): 542-547. |
| 4 | LIVINGSTON G, SOMMERLAD A, ORGETA V, et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care[J]. Lancet, 2017, 390(10113): 2673-2734. |
| 5 | de BRUIJN R F A G, HEERINGA J, WOLTERS F J, et al. Association between atrial fibrillation and dementia in the general population[J]. JAMA Neurol, 2015, 72(11): 1288-1294. |
| 6 | JARED T, BUNCH, MD, et al. Atrial fibrillation is independently associated with senile, vascular, and Alzheimer's dementia[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2010, 7(4): 433-437. |
| 7 | SINGH-MANOUX A, FAYOSSE A, SABIA S, et al. Atrial fibrillation as a risk factor for cognitive decline and dementia[J]. Eur Heart J, 2017, 38(34): 2612-2618. |
| 8 | KALANTARIAN S, STERN T A, MANSOUR M, et al. Cognitive impairment associated with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2013, 158(5 Pt 1): 338-346. |
| 9 | EMDIN C A, KHERA A V, KATHIRESAN S. Mendelian randomization[J]. JAMA, 2017, 318(19): 1925. |
| 10 | 王玉琢, 沈洪兵. 孟德尔随机化研究应用于因果推断的影响因素及其结果解读面临的挑战[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2020, 41(8): 1231-1236. |
| WANG Y Z, SHEN H B. Challenges and factors that influencing causal inference and interpretation, based on Mendelian randomization studies[J]. Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 2020, 41(8): 1231-1236. | |
| 11 | BOEF A G C, DEKKERS O M, LE CESSIE S. Mendelian randomization studies: a review of the approaches used and the quality of reporting[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2015, 44(2): 496-511. |
| 12 | NIELSEN J B, THOROLFSDOTTIR R B, FRITSCHE L G, et al. Biobank-driven genomic discovery yields new insight into atrial fibrillation biology[J]. Nat Genet, 2018, 50(9): 1234-1239. |
| 13 | LEE J J, WEDOW R, OKBAY A, et al. Gene discovery and polygenic prediction from a genome-wide association study of educational attainment in 1.1 million individuals[J]. Nat Genet, 2018, 50(8): 1112-1121. |
| 14 | SCHWARTZENTRUBER J, COOPER S, LIU J Z, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis, fine-mapping and integrative prioritization implicate new Alzheimer′s disease risk genes[J]. Nat Genet, 2021, 53(3): 392-402. |
| 15 | CHIA R, SABIR M S, BANDRES-CIGA S, et al. Genome sequencing analysis identifies new loci associated with Lewy body dementia and provides insights into its genetic architecture[J]. Nat Genet, 2021, 53(3): 294-303. |
| 16 | van DEERLIN V M, SLEIMAN P M A, MARTINEZ-LAGE M, et al. Common variants at 7p21 are associated with frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 inclusions[J]. Nat Genet, 2010, 42(3): 234-239. |
| 17 | BURGESS S, BUTTERWORTH A, THOMPSON S G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data[J]. Genet Epidemiol, 2013, 37(7): 658-665. |
| 18 | BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2015, 44(2): 512-525. |
| 19 | BURGESS S, DAVEY SMITH G, DAVIES N M, et al. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations: update for summer 2023[J]. Wellcome Open Res, 2023, 4: 186. |
| 20 | ALESSANDRA, MARENGONI,. Atrial fibrillation, stroke and dementia in the very old: a population-based study[J]. Neurobiol Aging, 2011, 32(7): 1336-1337. |
| 21 | HARING B, LENG X Y, ROBINSON J, et al. Cardiovascular disease and cognitive decline in postmenopausal women: results from the Women′s Health Initiative Memory Study[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2013, 2(6): e000369. |
| 22 | PETERS R, POULTER R, BECKETT N, et al. Cardiovascular and biochemical risk factors for incident dementia in the Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial[J]. J Hypertens, 2009, 27(10): 2055-2062. |
| 23 | ODUTAYO A, WONG C X, HSIAO A J, et al. Atrial fibrillation and risks of cardiovascular disease, renal disease, and death: systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMJ, 2016, 354: i4482. |
| 24 | NISHTALA A, PIERS R J, HIMALI J J, et al. Atrial fibrillation and cognitive decline in the Framingham Heart Study[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2018, 15(2): 166-172. |
| 25 | DIENER H C, HART R G, KOUDSTAAL P J, et al. Atrial fibrillation and cognitive function: JACC review topic of the week[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2019, 73(5): 612-619. |
| 26 | HU Y F, CHEN Y J, LIN Y J, et al. Inflammation and the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2015, 12(4): 230-243. |
| 27 | ENCIU A M, POPESCU B O. Is there a causal link between inflammation and dementia?[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2013, 2013: 316495. |
| 28 | BANERJEE G, CHAN E, AMBLER G, et al. Cognitive impairment before atrial fibrillation-related ischemic events: neuroimaging and prognostic associations[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2020, 9(1): e014537. |
| 29 | de TORRE J C. Cardiovascular risk factors promote brain hypoperfusion leading to cognitive decline and dementia[J]. Cardiovasc Psychiatry Neurol, 2012, 2012: 367516. |
| 30 | LARSSON S C. Mendelian randomization as a tool for causal inference in human nutrition and metabolism[J]. Curr Opin Lipidol, 2021, 32(1): 1-8. |
| 31 | van OORT S, BEULENS J W J, van BALLEGOOIJEN A J, et al. Association of cardiovascular risk factors and lifestyle behaviors with hypertension: a Mendelian randomization study[J]. Hypertension, 2020, 76(6): 1971-1979. |
| 32 | PAN Y S, WANG Y L, WANG Y J. Investigation of causal effect of atrial fibrillation on alzheimer disease: a Mendelian randomization study[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2020, 9(2): e014889. |
| [1] | 曹明明, 王辉, 尹雅芙. 帕金森病认知功能障碍影像标志物的研究现状[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(5): 646-652. |
| [2] | 张兰兰, 韩旭, 李牛, 王剑, 李淑元. 无创产前检测对17p12区域拷贝数变异的检测效能[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(3): 310-316. |
| [3] | 林祎嘉, 程丽珍, 胡廷军, 苗雅. 基于孟德尔随机化法的2型糖尿病与认知障碍因果关系研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 204-210. |
| [4] | 梁乐斌, 陈慧芳, 赖淑静, 顾靓, 苏冰. 基于空间ATAC-seq技术的Apcmin/+小鼠结肠肿瘤表观特征分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1261-1270. |
| [5] | 唐珺倩, 李本尚. 儿童高危细胞遗传学B系急性淋巴细胞白血病治疗新进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1390-1399. |
| [6] | 蔡单, 黄晶. 非经典型多梳抑制复合物1.6的电镜结构分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(9): 1136-1145. |
| [7] | 杜亚格, 卢言慧, 安宇, 宋颖, 郑婕. 肠道菌群在糖尿病认知功能障碍中的作用机制及靶向干预的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(4): 494-500. |
| [8] | 袁灏琳, 李念念, 胡珺晖, 沈锦虹, 高振飞, 关建, 刘峰, 殷善开. NOS1基因变异与失眠、睡眠时长以及阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停临床数量性状的相关性[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(12): 1490-1503. |
| [9] | 王青, 韩晓, 张晓波. 表观遗传修饰调控肺炎免疫应答的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 931-938. |
| [10] | 刘桃桃, 刘晓黎, 邬静莹, 倪瑞隆, 张梦圆, 季杜欣, 张梅, 曹立. 成人脑型肾上腺脑白质营养不良的临床及遗传学特征[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 592-599. |
| [11] | 王志明, 童冉, 杨晨, 焦慧媛, 王一好, 李林颖, 王烨欣, 张丰, 李令杰. 基于基因及调控区进化保守性评估细胞和组织发育潜能的定量分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(11): 1384-1395. |
| [12] | 郑诗凡, 马皎. 肿瘤干细胞代谢在肿瘤发展中作用的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(6): 825-832. |
| [13] | 朱啸巍, 詹飞霞, 张超, 刘时华, 钟平, 曹立, 栾兴华. PMP22基因相关性周围神经病的遗传学和临床特点分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(5): 609-616. |
| [14] | 段昱娟, 黄晶. 核小体重塑及组蛋白去乙酰化酶复合物的负染电镜结构分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(4): 455-463. |
| [15] | 赵志宏, 王赛华, 郝淑雯, 宋湘, 罗俊, 武英彪, 朱茜, 方明, 田蓓, 顾薇, 宁忠平. 心房颤动左心耳封堵前后左心房自发显影临床分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(3): 344-349. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||