
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 951-958.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.08.003
收稿日期:2024-02-21
接受日期:2024-07-19
出版日期:2024-08-28
发布日期:2024-08-27
通讯作者:
江凌勇,电子信箱:jianglingyong@sjtu.edu.cn。作者简介:刘旌毅(1998—),男,博士生;电子信箱:liujy0406@sjtu.edu.cn。
基金资助:
LIU Jingyi( ), XU Hongyuan, DAI Qinggang, JIANG Lingyong(
), XU Hongyuan, DAI Qinggang, JIANG Lingyong( )
)
Received:2024-02-21
Accepted:2024-07-19
Online:2024-08-28
Published:2024-08-27
Contact:
JIANG Lingyong, E-mail: jianglingyong@sjtu.edu.cn.Supported by:摘要:
颞下颌关节是颅颌面骨骼系统中的唯一关节结构,负责执行日常生活中咀嚼、说话、表情等涉及张口、闭口的功能。下颌髁突作为颞下颌关节中的关键组成部分,起源于第一鳃弓所形成的下颌突,是下颌骨升支末端的关键生长中心。髁突由表面覆盖的软骨层和下方的软骨下骨组成,在生长发育的过程中具有独特的生物学过程。髁突的功能性运动依赖于其正常的生理解剖结构,对咬合的建立及面容的塑造起到关键作用。生长发育异常可导致髁突畸形的发生,通过影响患者的颌面部垂直向高度,最终引发不同程度的继发性骨性Ⅱ类或Ⅲ类颅颌面畸形。在生长发育的过程中,髁突受到复杂的信号调控作用。近年来,随着对颞下颌关节研究的深入,研究者开始从基因表达和分子水平的角度讨论髁突生长发育的调控机制,以解释颞下颌关节疾病以及髁突畸形的发生原因。该文就髁突的生发过程和结构、髁突畸形分类与病理表现、髁突生长发育中的信号调控及髁突畸形的致病机制作一综述,期望为临床上因下颌髁突发育异常导致的颞下颌关节疾病及颅颌面畸形的治疗提供研究思路。
中图分类号:
刘旌毅, 徐弘远, 代庆刚, 江凌勇. 下颌髁突发育及畸形的调控机制研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(8): 951-958.
LIU Jingyi, XU Hongyuan, DAI Qinggang, JIANG Lingyong. Progress in the regulatory mechanisms of mandibular condylar development and deformity[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(8): 951-958.
| Characteristic | Condylar cartilage | Long bone articular cartilage |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Fibrocartilage | Hyaline cartilage |
| Classification | Secondary cartilage | Primary cartilage |
| Main collagen type | Collagen type Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, and Ⅹ | Collagen type Ⅱ, Ⅲ, and Ⅹ |
| Collagen arrangement direction | Front-to-back direction | Reticular crossing |
表1 髁突软骨与长骨关节软骨的区别
Tab 1 Comparison between condylar cartilage and long bone articular cartilage
| Characteristic | Condylar cartilage | Long bone articular cartilage |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Fibrocartilage | Hyaline cartilage |
| Classification | Secondary cartilage | Primary cartilage |
| Main collagen type | Collagen type Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, and Ⅹ | Collagen type Ⅱ, Ⅲ, and Ⅹ |
| Collagen arrangement direction | Front-to-back direction | Reticular crossing |
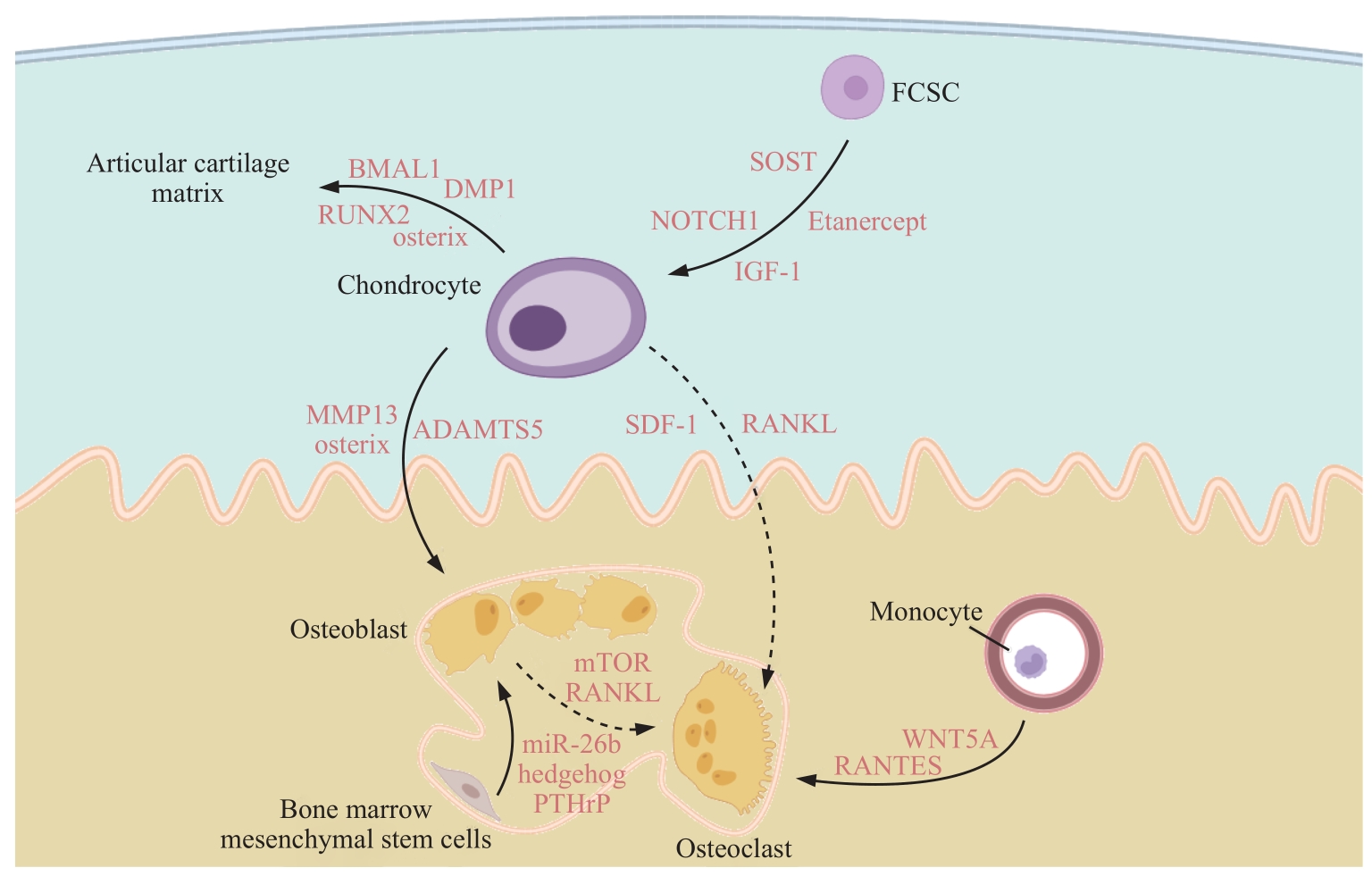
图2 髁突生长发育中的信号调控示意图Note: SOST—sclerostin; MMP13—matrix metalloproteinases-13. Solid lines represent cell differentiation and cartilage matrix generation; dashed lines represent the promoting effect on cell differentiation.
Fig 2 Schematic diagram of signal regulation during condylar growth and development
| 1 | STOCUM D L, ROBERTS W E. Part Ⅰ: development and physiology of the temporomandibular joint[J]. Curr Osteoporos Rep, 2018, 16(4): 360-368. |
| 2 | KAYIPMAZ S, AKÇAY S, SEZGIN Ö S, et al. Trabecular structural changes in the mandibular condyle caused by degenerative osteoarthritis: a comparative study by cone-beam computed tomography imaging[J]. Oral Radiol, 2019, 35(1): 51-58. |
| 3 | UMEDA M, TERAO F, MIYAZAKI K, et al. MicroRNA-200a regulates the development of mandibular condylar cartilage[J]. J Dent Res, 2015, 94(6): 795-802. |
| 4 | TSUTSUMI-ARAI C, ARAI Y, TRAN A, et al. A PTHrP gradient drives mandibular condylar chondrogenesis via Runx2[J]. J Dent Res, 2024, 103(1): 91-100. |
| 5 | TANG G H, RABIE A B. Runx2 regulates endochondral ossification in condyle during mandibular advancement[J]. J Dent Res, 2005, 84(2): 166-171. |
| 6 | HIROUCHI H, KITAMURA K, YAMAMOTO M, et al. Developmental characteristics of secondary cartilage in the mandibular condyle and sphenoid bone in mice[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2018, 89: 84-92. |
| 7 | XU X J, ZHANG Y J, ZHANG J, et al. Zonal interdependence in the temporomandibular joint cartilage[J]. FASEB J, 2023, 37(4): e22888. |
| 8 | GIBSON G. Active role of chondrocyte apoptosis in endochondral ossification[J]. Microsc Res Tech, 1998, 43(2): 191-204. |
| 9 | JING Y, ZHOU X, HAN X, et al. Chondrocytes directly transform into bone cells in mandibular condyle growth[J]. J Dent Res, 2015, 94(12): 1668-1675. |
| 10 | HINTON R J, JING Y, JING J, et al. Roles of chondrocytes in endochondral bone formation and fracture repair[J]. J Dent Res, 2017, 96(1): 23-30. |
| 11 | ZHU Q Q, TAN M Y, WANG C N, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis of the temporomandibular joint condyle in 3 and 4-month-old human embryos[J]. Cell Biosci, 2023, 13(1): 130. |
| 12 | 刘纯, 贾莹, 杨世榕, 等. 大鼠髁突软骨下骨骨微结构生长发育的特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(32): 5162-5166. |
| LIU C, JIA Y, YANG S S, et al. Characteristics of the growth, development and microarchitecture of condyle subchondral bone in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5162-5166. | |
| 13 | KANEYAMA K, SEGAMI N, HATTA T. Congenital deformities and developmental abnormalities of the mandibular condyle in the temporomandibular joint[J]. Congenit Anom, 2008, 48(3): 118-125. |
| 14 | GALEA C J, DASHOW J E, WOERNER J E. Congenital abnormalities of the temporomandibular joint[J]. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am, 2018, 30(1): 71-82. |
| 15 | CHOUINARD A F, KABAN L B, PEACOCK Z S. Acquired abnormalities of the temporomandibular joint[J]. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am, 2018, 30(1): 83-96. |
| 16 | YU J S, YANG T, DAI J W, et al. Histopathological features of condylar hyperplasia and condylar Osteochondroma: a comparison study[J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2019, 14(1): 293. |
| 17 | VÁSQUEZ B, OLATE S, CANTÍN M, et al. Histomorphometric analysis of unilateral condylar hyperplasia in the temporomandibular joint: the value of the condylar layer and cartilage island[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2017, 46(7): 861-866. |
| 18 | 陈宇翔, 黄群, 张武阳, 等. Sonic hedgehog参与人胰岛素样生长因子-1信号通路促使下颌骨髁突过度生长的实验研究[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2018, 34(8): 866-869. |
| CHEN Y X, HUANG Q, ZHANG W Y, et al. Animal experiment on cooperation between Shh and IGF-1 in promoting mandibular cartilage overgrowth[J]. Journal of Oral Science Research, 2018, 34 (8): 866-869. | |
| 19 | LI X H, LIANG W N, YE H Z, et al. Overexpression of Shox2 leads to congenital dysplasia of the temporomandibular joint in mice[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2014, 15(8): 13135-13150. |
| 20 | SUN L, ZHAO J, WANG H, et al. Mechanical stress promotes matrix synthesis of mandibular condylar cartilage via the RKIP-ERK pathway[J]. J Mol Histol, 2017, 48(5/6): 437-446. |
| 21 | MARTÍN A E, DEL R PANI M, HOLGADO N R, et al. Facial development disorders due to inhibition to endochondral ossification of mandibular condyle process caused by malnutrition[J]. Angle Orthod, 2014, 84(3): 473-478. |
| 22 | BI R Y, LI Q L, LI H H, et al. Divergent chondro/osteogenic transduction laws of fibrocartilage stem cell drive temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis in growing mice[J]. Int J Oral Sci, 2023, 15(1): 36. |
| 23 | NATHAN J, RUSCITTO A, PYLAWKA S, et al. Fibrocartilage stem cells engraft and self-organize into vascularized bone[J]. J Dent Res, 2018, 97(3): 329-337. |
| 24 | EMBREE M C, CHEN M, PYLAWKA S, et al. Exploiting endogenous fibrocartilage stem cells to regenerate cartilage and repair joint injury[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 13073. |
| 25 | RUSCITTO A, CHEN P, TOSA I, et al. Lgr5-expressing secretory cells form a Wnt inhibitory niche in cartilage critical for chondrocyte identity[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(9): 1179-1198.e7. |
| 26 | RUSCITTO A, SCARPA V, MOREL M, et al. Notch regulates fibrocartilage stem cell fate and is upregulated in inflammatory TMJ arthritis[J]. J Dent Res, 2020, 99(10): 1174-1181. |
| 27 | BI R, CHEN K, WANG Y, et al. Regulating fibrocartilage stem cells via TNF-α/NF-κB in TMJ osteoarthritis[J]. J Dent Res, 2022, 101(3): 312-322. |
| 28 | BI R Y, LUO X T, LI Q L, et al. Igf1 regulates fibrocartilage stem cells, cartilage growth, and homeostasis in the temporomandibular joint of mice[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2023, 38(4): 556-567. |
| 29 | JOSHI A S, HATCH N E, HAYAMI T, et al. IGF-1 TMJ injections enhance mandibular growth and bone quality in juvenile rats[J]. Orthod Craniofac Res, 2022, 25(2): 183-191. |
| 30 | WENG Y, LIU Y, DU H, et al. Glycosylation of DMP1 is essential for chondrogenesis of condylar cartilage[J]. J Dent Res, 2017, 96(13): 1535-1545. |
| 31 | KURIO N, SAUNDERS C, BECHTOLD T E, et al. Roles of Ihh signaling in chondroprogenitor function in postnatal condylar cartilage[J]. Matrix Biol, 2018, 67: 15-31. |
| 32 | YU S L, TANG Q M, XIE M R, et al. Circadian BMAL1 regulates mandibular condyle development by hedgehog pathway[J]. Cell Prolif, 2020, 53(1): e12727. |
| 33 | LIAO L F, ZHANG S X, ZHOU G Q, et al. Deletion of Runx2 in condylar chondrocytes disrupts TMJ tissue homeostasis[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(4): 3436-3444. |
| 34 | GE C, MOHAMED F, BINRAYES A, et al. Selective role of discoidin domain receptor 2 in murine temporomandibular joint development and aging[J]. J Dent Res, 2018, 97(3): 321-328. |
| 35 | KIM J M, LIN C J, STAVRE Z, et al. Osteoblast-osteoclast communication and bone homeostasis[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(9): 2073. |
| 36 | ZHANG J, PI C X, CUI C, et al. PTHrP promotes subchondral bone formation in TMJ-OA[J]. Int J Oral Sci, 2022, 14(1): 37. |
| 37 | LEI J, CHEN S, JING J, et al. Inhibiting Hh signaling in Gli1+ osteogenic progenitors alleviates TMJOA[J]. J Dent Res, 2022, 101(6): 664-674. |
| 38 | YANG J L, XU Y F, XUE X, et al. MicroRNA-26b regulates BMSC osteogenic differentiation of TMJ subchondral bone through β-catenin in osteoarthritis[J]. Bone, 2022, 162: 116448. |
| 39 | JING J, HINTON R J, JING Y, et al. Osterix couples chondrogenesis and osteogenesis in post-natal condylar growth[J]. J Dent Res, 2014, 93(10): 1014-1021. |
| 40 | ROGERS-DECOTES A W, PORTO S C, DUPUIS L E, et al. ADAMTS5 is required for normal trabeculated bone development in the mandibular condyle[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2021, 29(4): 547-557. |
| 41 | OYHANART S R, ESCUDERO N D, MANDALUNIS P M. Effect of alendronate on the mandible and long bones: an experimental study in vivo[J]. Pediatr Res, 2015, 78(6): 618-625. |
| 42 | YANG T, ZHANG J, CAO Y, et al. Wnt5a/Ror2 mediates temporomandibular joint subchondral bone remodeling[J]. J Dent Res, 2015, 94(6): 803-812. |
| 43 | KUANG B, ZENG Z B, QIN Q. Biomechanically stimulated chondrocytes promote osteoclastic bone resorption in the mandibular condyle[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2019, 98: 248-257. |
| 44 | TIAN Y H, CHEN J B, YAN X, et al. Overloaded orthopedic force induces condylar subchondral bone absorption by stimulating rat mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into osteoclasts via mTOR-regulated RANKL/OPG secretion in osteoblasts[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2021, 30(1): 29-38. |
| 45 | FENG S Y, LEI J, LI Y X, et al. Increased joint loading induces subchondral bone loss of the temporomandibular joint via the RANTES-CCRs-Akt2 axis[J]. JCI Insight, 2022, 7(21): e158874. |
| 46 | HE L H, XIAO E, DUAN D H, et al. Osteoclast deficiency contributes to temporomandibular joint ankylosed bone mass formation[J]. J Dent Res, 2015, 94(10): 1392-1400. |
| 47 | TANG Y, HONG C, CAI Y, et al. HIF-1α mediates osteoclast-induced mandibular condyle growth via AMPK signaling[J]. J Dent Res, 2020, 99(12): 1377-1386. |
| 48 | CHEN Y, KE J, LONG X, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 boosts the developing process of condylar hyperplasia by stimulating chondrocytes proliferation[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2012, 20(4): 279-287. |
| 49 | CAO P, FENG Y, DENG M, et al. MiR-15b is a key regulator of proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes from patients with condylar hyperplasia by targeting IGF1, IGF1R and BCL2[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2019, 27(2): 336-346. |
| 50 | WEN X, WANG Y X, GU Y. Transferrin promotes chondrogenic differentiation in condylar growth through inducing autophagy via ULK1-ATG16L1 axis[J]. Clin Sci, 2023, 137(18): 1431-1449. |
| 51 | BIOSSE DUPLAN M, KOMLA-EBRI D, HEUZÉ Y, et al. Meckel's and condylar cartilages anomalies in achondroplasia result in defective development and growth of the mandible[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2016, 25(14): 2997-3010. |
| [1] | 章文益, 郑美里, 谢羽番, 江凌勇. 翼腭缝宏观解剖及其发育模式研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(8): 944-950. |
| [2] | 曹睿, 卫凯鑫, 张晓娜, 刘雨榕, 张丽. 视黄酸诱导的小鼠神经管畸形基因表达趋势分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(7): 859-870. |
| [3] | 江凌勇. 牙颌面骨畸形机制研究的现状与发展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(6): 663-675. |
| [4] | 孙思远, 刘媛琪, 崔怡雯, 黄紫晗, 梅李, 代庆刚, 江凌勇. 成骨细胞条件性视黄酸信号失活小鼠模型的构建与验证[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(6): 676-686. |
| [5] | 窦嘉琪, 高洁, 卞晓玲, 王凤, 代庆刚, 吴轶群. 伴有PAX9突变非综合征型先天缺牙患者的牙颌面表型研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(6): 687-693. |
| [6] | 王思婕, 斯佳萍, 周宇, 骆定雯, 高璐, 陈小燕. 不同矢状骨面型颞下颌关节形态的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 648-654. |
| [7] | 何冬梅, 杨驰. 下颌骨髁突骨折的诊治方案:基于上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院颞下颌关节中心的经验[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(6): 695-701. |
| [8] | 王学宏, 陈旭卓, 毛懿, 沈达, 张善勇. 青少年不同发育阶段颞下颌关节盘锚固术后复发率的差异[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(2): 173-177. |
| [9] | 万绍楠, 李佩伦, 谢千阳, 陈浚, 钱子悦, 杨驰. 颞下颌关节盘前移位青少年患者的下颌偏斜特征[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(11): 1557-1561. |
| [10] | 顾豪, 杨希, 张紫旻, 金云波, 胡丽, 陈辉, 林晓曦. 基于图像融合的手术导航系统在头颈部低流量脉管畸形硬化治疗中的应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(5): 695-700. |
| [11] | 夏志鹏1,袁 瑛2,杨 希2,顾 豪2,林晓曦2#,陶晓峰1#. 动态增强磁共振成像对静脉畸形硬化治疗中硬化剂选择的参考价值[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(7): 873-880. |
| [12] | 周知航 1*,毛懿 1*,陈旭卓 1*,张善勇 1,孙守福 2,甄锦泽 1. 新型锚固钉的抗力性分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2018, 38(8): 934-. |
| [13] | 赵欣荣,王彦林,范阳阳,杲丽. 胎儿颈项透明层增厚的临床咨询及预后分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2018, 38(5): 529-. |
| [14] | 徐丽娟,刘惠东,徐让,李奋,陈笋. 圆锥动脉干畸形患儿NOTCH1和JAG1基因3’非编码区变异分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2017, 37(2): 184-. |
| [15] | 刘春洁,李婷婷,李奋,徐让 . 内脏异位综合征的临床特征及死亡危险因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2016, 36(12): 1772-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||