
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 684-692.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.06.003
孙磊1,2( ), 戴世锋1, 陈裕华1, 许新怡2, 姜克乐3, 李筱文2, 李承靖2, 吴婷婷1
), 戴世锋1, 陈裕华1, 许新怡2, 姜克乐3, 李筱文2, 李承靖2, 吴婷婷1
收稿日期:2025-01-13
接受日期:2025-04-03
出版日期:2025-06-28
发布日期:2025-06-28
通讯作者:
孙 磊(1984—),女,副教授,副主任医师,博士;电子信箱:sunlei@ahmu.edu.cn。基金资助:
SUN Lei1,2( ), DAI Shifeng1, CHEN Yuhua1, XU Xinyi2, JIANG Kele3, LI Xiaowen2, LI Chengjing2, WU Tingting1
), DAI Shifeng1, CHEN Yuhua1, XU Xinyi2, JIANG Kele3, LI Xiaowen2, LI Chengjing2, WU Tingting1
Received:2025-01-13
Accepted:2025-04-03
Online:2025-06-28
Published:2025-06-28
Contact:
SUN Lei, E-mail: sunlei@ahmu.edu.cn.Supported by:摘要:
目的·通过颞下颌关节磁共振(magnetic resonance imaging,MRI)检查,评价颞下颌关节紊乱病(temporomandibular disorders,TMD)患者盘髁距离(关节盘与髁突距离)与关节盘前移位、关节盘形态相关指标之间的关系。方法·选取2023年9月至2024年3月于安徽医科大学第二附属医院口腔科颞下颌关节门诊就诊且临床上出现TMD症状且MRI判断为颞下颌关节盘前移位或无明显移位的90位患者,将其180个颞下颌关节纳入研究。采集患者的临床资料,通过MRI图像测量关节盘移位角度、盘髁距离、关节盘长度及厚度,判断关节盘变形程度,分析患者临床症状与关节盘前移位之间的关系、关节盘前移位与关节盘形态及盘髁距离的关系,以及盘髁距离与关节盘形态的关系。结果·90例患者中男性16例、女性74例,平均年龄(28.1±14.5)岁。在180个颞下颌关节中,有临床症状的关节175个,无症状关节5个;未移位关节盘40个,可复性前移位关节盘78个,不可复性前移位关节盘62个。不可复性前移位关节盘中出现2个及以上症状的关节比例略高,为62.9%,但与关节盘未移位以及可复性前移位的关节之间差异无统计学意义。通过MRI评估发现,不可复性前移位的关节盘较未移位关节盘变形程度Ⅲ型及以上的占比显著升高,关节盘长度显著缩短,中间带厚度显著增大,闭口和最大开口位时的关节盘移位角度显著增大(均P<0.001)。未移位、可复性前移位和不可复性前移位关节盘的盘髁距离分别为3.10(2.70,3.70)、3.40(3.00,4.00)和6.60(4.78,7.90)mm,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.001);Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ/Ⅴ型关节盘的盘髁距离分别为3.10(2.80,3.60)、3.70(3.10,4.60)、5.10(4.00,7.30)、6.80(4.98,8.20)mm,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.001);盘髁距离与关节盘长度呈负相关(rs=-0.469,P<0.001),与关节盘中间带厚度呈正相关(rs=0.319,P<0.001),与闭口位时关节盘移位角度呈正相关(rs=0.626,P<0.001)。结论·随着颞下颌关节盘变形严重程度、中间带厚度、闭口位时前移位角度的增加,以及关节盘长度的缩短,盘髁距离增大;盘髁距离是MRI评估TMD病理改变的重要指标。
中图分类号:
孙磊, 戴世锋, 陈裕华, 许新怡, 姜克乐, 李筱文, 李承靖, 吴婷婷. 颞下颌关节紊乱病患者关节盘与髁突距离的定量分析研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(6): 684-692.
SUN Lei, DAI Shifeng, CHEN Yuhua, XU Xinyi, JIANG Kele, LI Xiaowen, LI Chengjing, WU Tingting. Quantitative analysis of the distance between articular disc and condyle in patients with temporomandibular disorders[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(6): 684-692.
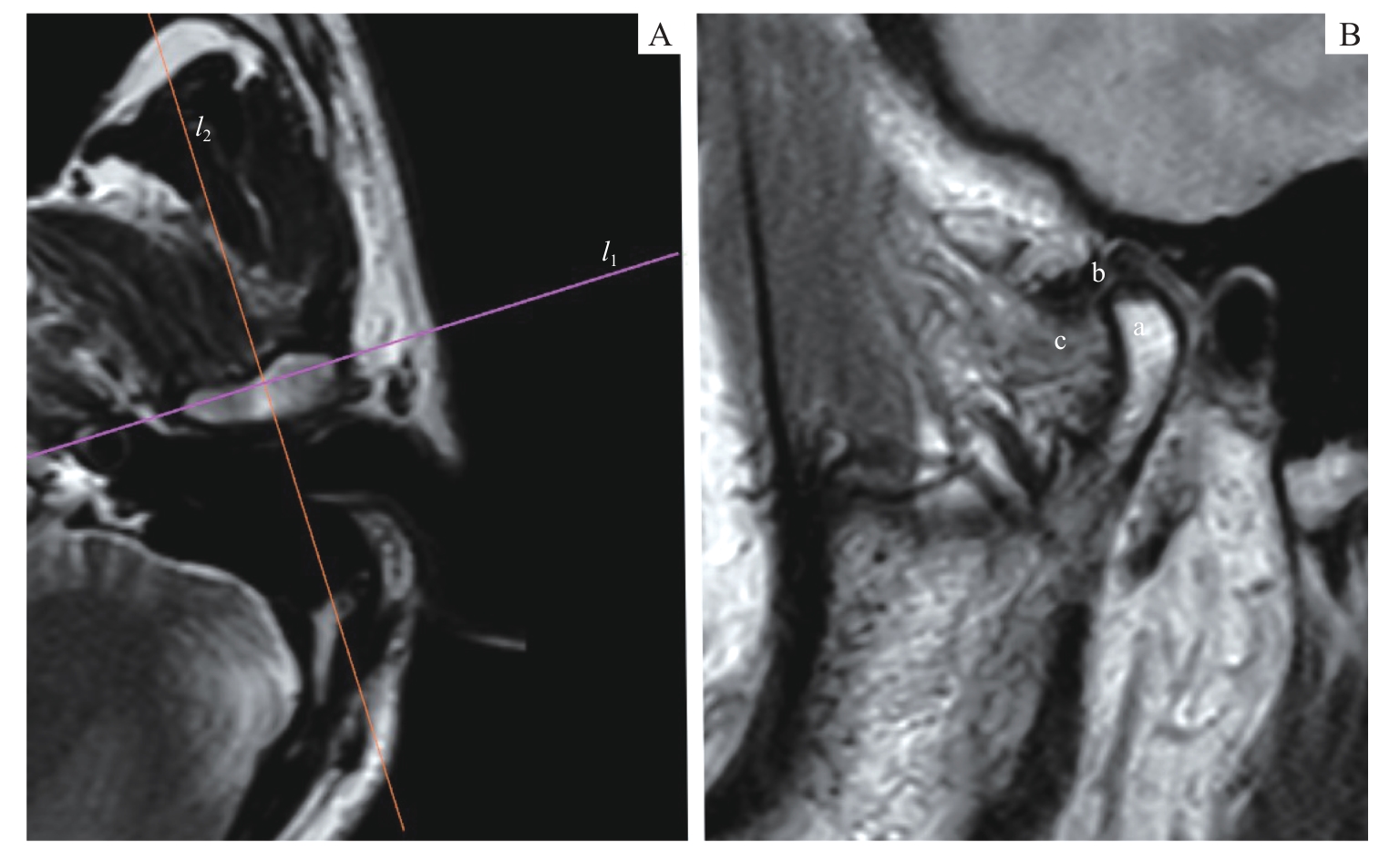
图1 MRI阅片时的定位平面Note: PDWI images. A. Axial plane. l1—the transverse axis of the condyle (the line connecting the internal and the external poles of the condyle); l2—the positioning plane perpendicular to the condylar transverse axis. B. Oblique sagittal plane. a—condyle; b—articular disc; c—lateral pterygoid muscle.
Fig 1 Positioning planes for MRI image reading
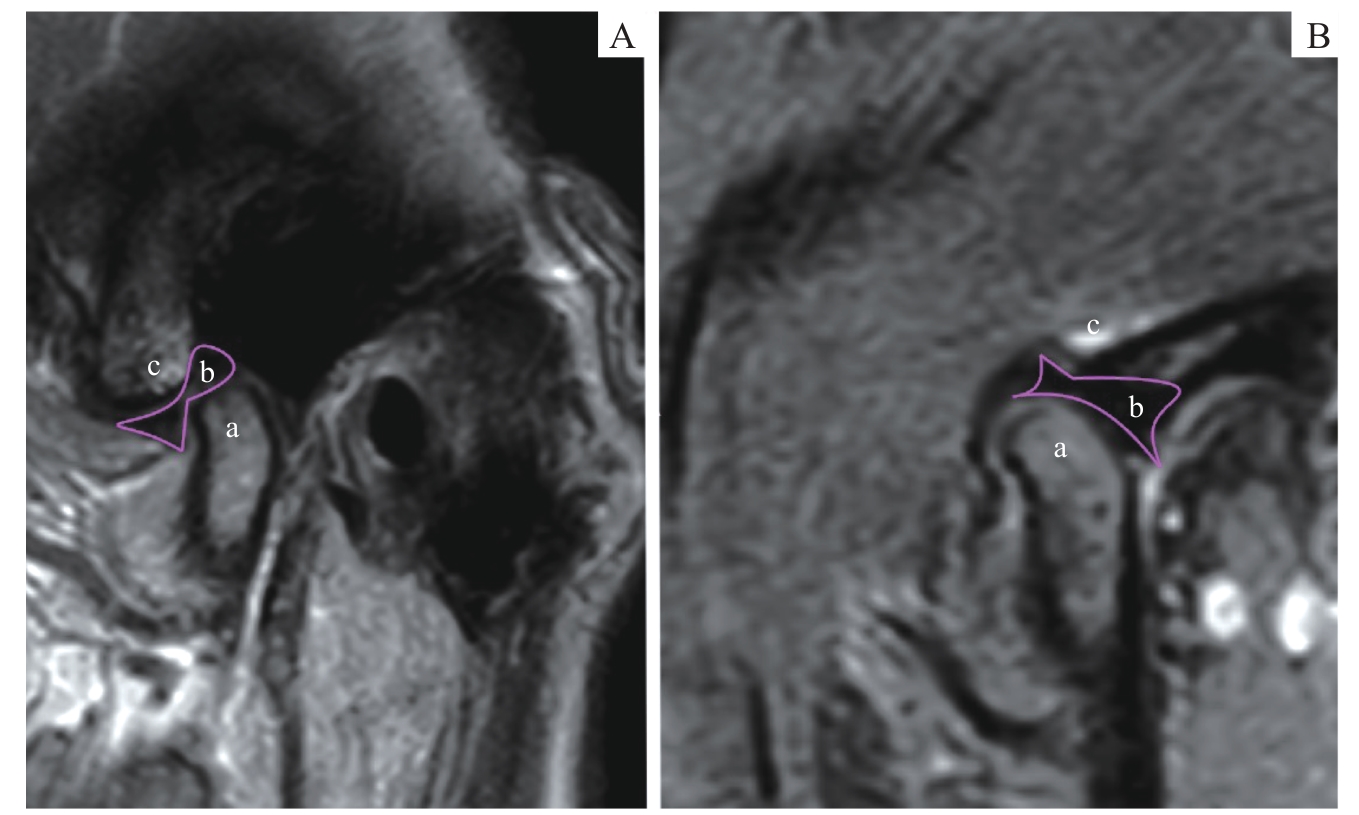
图2 MRI影像中正常的盘髁位置关系Note: Oblique sagittal PDWI images. A. Closed-mouth position. B. Open-mouth position. a—condyle; b—articular disc; c—articular eminence.
Fig 2 Normal disc-condyle relationship in MRI images
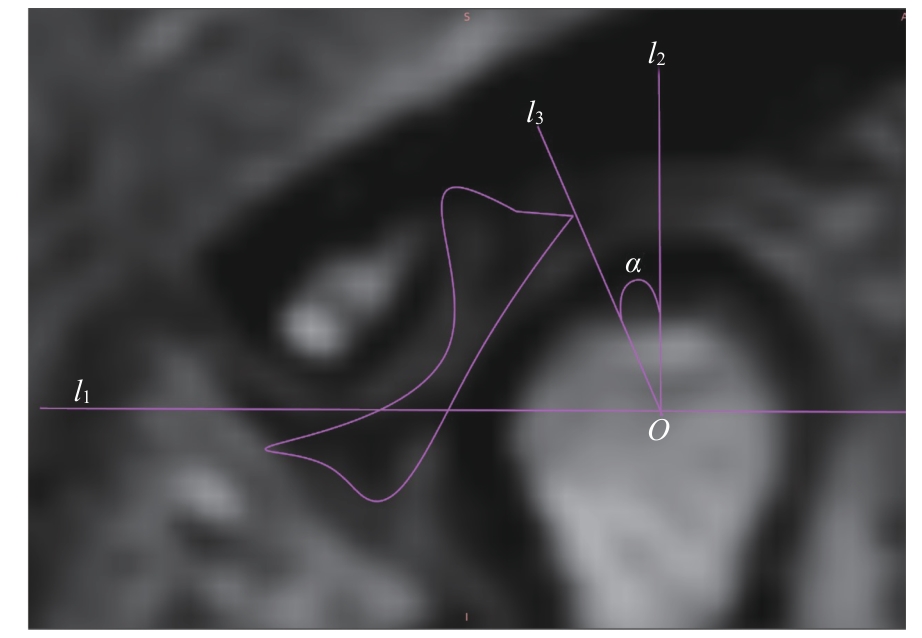
图3 关节盘移位角度的测量Note: An oblique sagittal PDWI image. l1—the line connecting the articular eminence and the vertex of the posterior tubercle; O—the midpoint of the intersection of line l1 with the condyle; l2—the perpendicular line to l1 through point O; l3—the line connecting the posterior edge of the articular disc with point O; α—the angle between l2 and l3, which is the angle of disc displacement.
Fig 3 Measurement of articular disc displacement angle
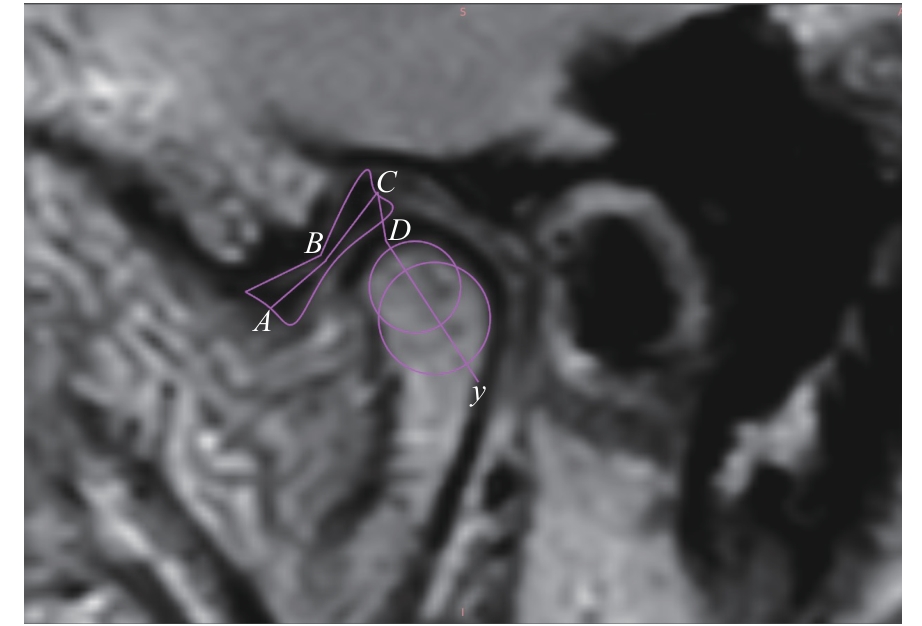
图4 盘髁距离及关节盘长度的测量Note: An oblique sagittal PDWI image. A—the midpoint of the anterior edge of the anterior band of the articular disc; B—the midpoint of the intermediate zone of the articular disc; C—the midpoint of the posterior edge of the posterior band of the articular disc; y—the long axis of the condylar head; D—the intersection of y-axis with the condyle; AB+BC—the length of the articular disc; CD—the disc-condyle distance.
Fig 4 Measurement of disc-condyle distance and articular disc length
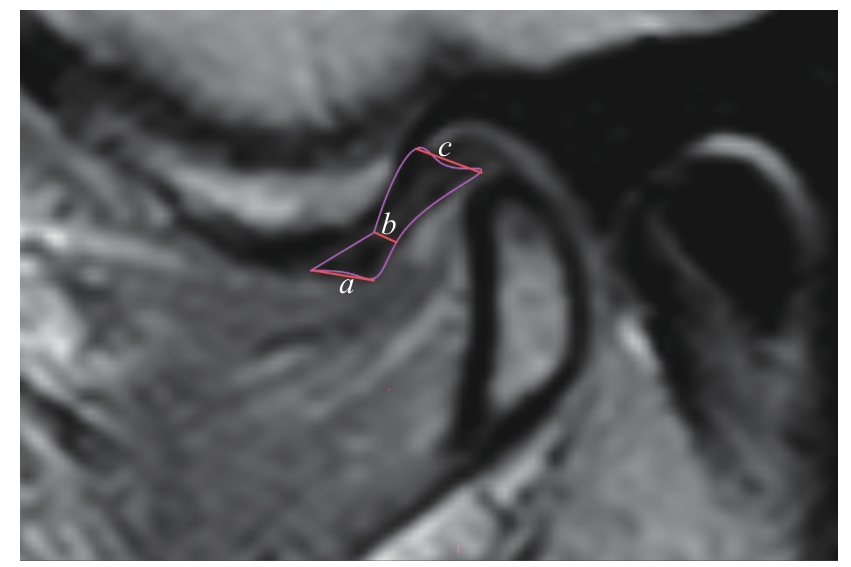
图5 颞下颌关节盘厚度测量Note: An oblique sagittal PDWI image. a—anterior band thickness; b—intermediate zone thickness; c—posterior band thickness.
Fig 5 Measurement of articular disc thickness
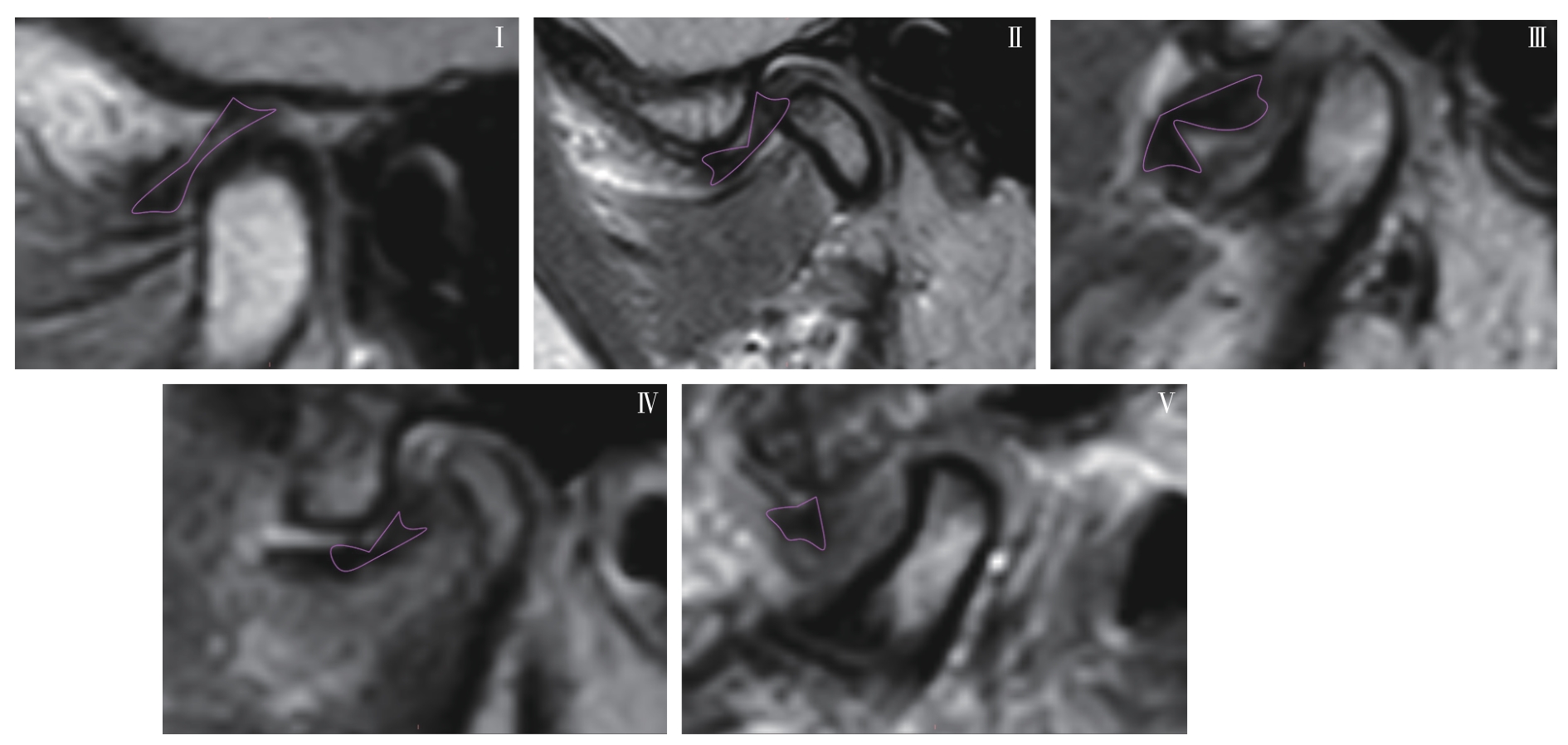
图6 关节盘变形程度分型Note: Oblique sagittal PDWI images. Typical articular disc morphology of type Ⅰ‒Ⅴ.
Fig 6 Classification of articular disc deformation degrees
| Disc displacement | Asymptomatic | With one symptom | With two or more symptoms | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (2.5) | 21 (52.5) | 18 (45.0) | 0.115 | |
| 3 (3.8) | 43 (55.1) | 32 (41.0) | ||
| 1 (1.6) | 22 (35.5) | 39 (62.9) |
表1 关节盘前移位与临床症状之间的关系
Tab 1 Relationship between clinical symptoms and anterior disc displacement
| Disc displacement | Asymptomatic | With one symptom | With two or more symptoms | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (2.5) | 21 (52.5) | 18 (45.0) | 0.115 | |
| 3 (3.8) | 43 (55.1) | 32 (41.0) | ||
| 1 (1.6) | 22 (35.5) | 39 (62.9) |
表2 不同关节盘前移位状态下关节盘形态及盘髁距离的差异
Tab 2 Differences in disc morphology and disc-condyle distance under different anterior disc displacement states
| [1] | DE LEEUW R, KLASSER G D. Orofacial pain: guidelines for assessment, diagnosis, and management[M]. 6th ed. Hanover Park: Quintessence Publishing, 2018. |
| [2] | AIELLO V, FERRILLO M, MAROTTA N, et al. Temporomandibular joint arthritis in rheumatic diseases patients: which are the effective rehabilitative approaches for pain relief? A systematic review[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2025, 26(1): 159. |
| [3] | BADRI O, DAVIS C M, WARBURTON G. Arthroscopic management and recent advancements in the treatment of temporomandibular joint disorders[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2024, 62(9): 820-825. |
| [4] | WARZOCHA J, GADOMSKA-KRASNY J, MROWIEC J. Etiologic factors of temporomandibular disorders: a systematic review of literature containing diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders (DC/TMD) and research diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders (RDC/TMD) from 2018 to 2022[J]. Healthcare (Basel), 2024, 12(5): 575. |
| [5] | BERNKOPF E, NARDONE M, CAPRIOTTI V. Follow-up clarifications concerning the authors' reply to the 'look at the elephant!' comment on 'prevalence of temporomandibular disorders in adult obstructive sleep apnoea patients: a cross-sectional controlled study'[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2024, 51(10): 2234-2236. |
| [6] | DWORKIN S F, LERESCHE L. Research diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders: review, criteria, examinations and specifications, critique[J]. J Craniomandib Disord, 1992, 6(4): 301-355. |
| [7] | SCHIFFMAN E, OHRBACH R, TRUELOVE E, et al. Diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders (DC/TMD) for clinical and research applications: recommendations of the International RDC/TMD Consortium Network and Orofacial Pain Special Interest Group[J]. J Oral Facial Pain Headache, 2014, 28(1): 6-27. |
| [8] | AZMA R, HAREENDRANATHAN A, LI M X, et al. Automated pediatric TMJ articular disk identification and displacement classification in MRI with machine learning[J]. J Dent, 2025, 155: 105622. |
| [9] | TAMIMI D, JALALI E, HATCHER D. Temporomandibular joint imaging[J]. Radiol Clin North Am, 2018, 56(1): 157-175. |
| [10] | AKAI H, YASAKA K, SUGAWARA H, et al. Faster acquisition of magnetic resonance imaging sequences of the knee via deep learning reconstruction: a volunteer study[J]. Clin Radiol, 2024, 79(6): 453-459. |
| [11] | LI C J, ZHANG Q B. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging findings in 880 temporomandibular disorder patients of different age groups: a retrospective study[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2022, 22(1): 651. |
| [12] | WOJCIECHOWSKA B, SZARMACH A, MICHCIK A, et al. Association between clinical manifestations in temporomandibular joint disorders and corresponding radiographic findings[J]. J Clin Med, 2024, 13(16): 4886. |
| [13] | ITURRIAGA V, BORNHARDT T, VELASQUEZ N. Temporomandibular joint: review of anatomy and clinical implications[J]. Dent Clin North Am, 2023, 67(2): 199-209. |
| [14] | ZHU J Y, GONG Y J, ZHENG F J, et al. Relationships between functional temporomandibular joint space and disc morphology, position, and condylar osseous condition in patients with temporomandibular disorder[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2024, 28(3): 193. |
| [15] | CHEN B Y, LI C J. The relationship between the articular disc in magnetic resonance imaging and the condyle in cone beam computed tomography: a retrospective study[J]. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2024, 125(5S1): 101940. |
| [16] | 张国来, 廖彦阳, 吴美娜, 等. 颞下颌关节盘前移位患者盘-髁复合体MRI特征及盘周附着半量化评级研究[J]. 核磁共振成像, 2024, 15(2): 7-13. |
| ZHANG G L, LIAO Y Y, WU M N, et al. Study on MRI features of disc-condylar complex and semiquantitative evaluation of peridisc attachment in cases of temporomandibular joint disc displacement[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2024, 15(2): 7-13. | |
| [17] | KOCA C G, GÜMRÜKÇÜ Z. Does clinical findings correlate with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings in patients with temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pain? A cross sectional study[J]. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2020, 25(4): e495-e501. |
| [18] | 张盈盈, 伊景如, 潘初. 颞下颌关节紊乱患者关节盘软骨形态学改变的MR定量研究[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2024, 43(11): 1865-1871. |
| ZHANG Y Y, YI J R, PAN C. Quantitative MR study of morphological changes in articular disc cartilage in patients with temporomandibular disorders[J]. Journal of Clinical Radiology, 2024, 43(11): 1865-1871. | |
| [19] | ARAYASANTIPARB R, TSUCHIMOCHI M. Quantification of disc displacement in internal derangement of the temporomandibular joint using magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Odontology, 2010, 98(1): 73-81. |
| [20] | YANG Z J, WANG M G, MA Y W, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) evaluation for anterior disc displacement of the temporomandibular joint[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2017, 23: 712-718. |
| [21] | XIE Q Y, YANG C, HE D M, et al. Will unilateral temporomandibular joint anterior disc displacement in teenagers lead to asymmetry of condyle and mandible? A longitudinal study[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2016, 44(5): 590-596. |
| [22] | ZHANG Q, YE Z, WU Y G, et al. Nonlinear relationship between temporomandibular joint disc displacement distance and disc length: a magnetic resonance imaging analysis[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(23): 7160. |
| [23] | LI Z Y, ZHOU J L, YU L X, et al. Disc-condyle relationship alterations following stabilization splint therapy or arthrocentesis plus hyaluronic acid injection in patients with anterior disc displacement: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Oral Radiol, 2023, 39(1): 198-206. |
| [24] | 傅开元, 胡敏, 余强, 等. 颞下颌关节常规MRI检查规范及关节盘移位诊断标准的专家共识[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2020, 55(9): 608-612. |
| FU K Y, HU M, YU Q, et al. Experts consensus on MRI examination specification and diagnostic criteria of temporomandibular joint disc displacement[J]. Chinese Journal of Stomatology, 2020, 55(9): 608-612. | |
| [25] | DRACE J E, ENZMANN D R. Defining the normal temporomandibular joint: closed-, partially open-, and open-mouth MR imaging of asymptomatic subjects[J]. Radiology, 1990, 177(1): 67-71. |
| [26] | PERSCHBACHER S. Chapter 27: temporomandibular joint abnormalities[M]//WHITE S C, PHAROAH M J. Oral radiology: principles and interpretation. 7th ed. St. Louis: Mosby, 2013: 492-523. |
| [27] | INCESU L, TAŞKAYA-YILMAZ N, OĞÜTCEN-TOLLER M, et al. Relationship of condylar position to disc position and morphology[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2004, 51(3): 269-273. |
| [28] | WANG M Q, CAO H T, GE Y L, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging on TMJ disc thickness in TMD patients: a pilot study[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2009, 102(2): 89-93. |
| [29] | HU Y K, YANG C, XIE Q Y. Changes in disc status in the reducing and nonreducing anterior disc displacement of temporomandibular joint: a longitudinal retrospective study[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 34253. |
| [30] | AKHTER R. Epidemiology of temporomandibular disorder in the general population: a systematic review[J]. Adv Dent Oral Health, 2019, 10(3): 555787. |
| [31] | MAIZLIN Z V, NUTIU N, DENT P B, et al. Displacement of the temporomandibular joint disk: correlation between clinical findings and MRI characteristics[J]. J Can Dent Assoc, 2010, 76: a3. |
| [32] | LIU Z J, YAMAGATA K, KUROE K, et al. Morphological and positional assessments of TMJ components and lateral pterygoid muscle in relation to symptoms and occlusion of patients with temporomandibular disorders[J]. J Oral Rehabil, 2000, 27(10): 860-874. |
| [33] | TOGNINI F, MANFREDINI D, MONTAGNANI G, et al. Is clinical assessment valid for the diagnosis of temporomandibular joint disk displacement?[J]. Minerva Stomatol, 2004, 53(7/8): 439-448. |
| [34] | 闫森, 乔永明, 段亮伟. 37例颞下颌关节盘不可复性前移位患者自然转归的临床及磁共振成像特征分析[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2024, 42(1): 82-88. |
| YAN S, QIAO Y M, DUAN L W. Analysis of clinical changes and magnetic resonance imaging features of 37 patients with temporomandibular joint disc condylar complex with anterior disc displacement without reduction[J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2024, 42(1): 82-88. |
| [1] | 王静怡, 邓佳丽, 朱仪, 丁心怡, 郭嘉婧, 王中领. 新型pH响应性锰基纳米探针用于乳腺癌铁死亡及磁共振成像实验研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(9): 1183-1193. |
| [2] | 王蕊, 袁瑛, 陶晓峰. 合成磁共振成像在口腔癌颈部淋巴结转移诊断中的应用价值[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(7): 900-909. |
| [3] | 李卓杭, 于新迪, 任婧雅, 沈佳, 董素贞, 王伟. 主动脉缩窄端侧吻合纠治术后的神经系统预后分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(6): 753-759. |
| [4] | 张钲佳, 李小敏, 周鑫, 马海荣, 艾松涛. 高阶磁共振功能成像评估骨与软组织肿瘤价值初探[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(5): 585-596. |
| [5] | 孙一丹, 杨鑫. 焦虑增强颞下颌关节疼痛的脑功能磁共振成像研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(3): 342-348. |
| [6] | 罗瑞, 杨功鑫, 石慧敏, 韩永顺, 何一宁, 田臻, 吴颖为. 头颈部木村病的影像学特征研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(9): 1182-1189. |
| [7] | 卢晓冰, 岳江, 何晟赟, 董莹, 路青, 麻静. 大腿骨骼肌肌内脂肪组织的含量对肥胖症男性患者糖代谢的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(9): 1169-1174. |
| [8] | 严叶青, 梁胜, 杨斌, 邹仁健, 马玉飞, 蔡利生, 王辉, 傅宏亮. 18F-MD-PSMA PET/CT显像在中高危前列腺癌初始分期中的应用价值[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 873-881. |
| [9] | 俞蕾蕾, 阮洪, 夏滴, 何美娟, 孙明媛, 郑吉驷. 自我效能理论主导的居家康复方案在颞下颌关节盘复位术后的应用效果[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 532-539. |
| [10] | 杨海霞, 徐丽丽, 王博成, 陈敏洁. 磁共振引导的咀嚼肌疼痛放松训练疗效评估[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 540-544. |
| [11] | 张晨, 郭其辉, 范青. 强迫症患者大脑形态学特征研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(4): 480-486. |
| [12] | 刘辰骏, 尹博浩, 孙辉, 张伟. 非侵入性影像学技术在骨质疏松症中的应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(3): 385-390. |
| [13] | 吴兵, 李小敏, 柳思宇, 赵露露, 武文, 郝永强, 艾松涛. 改良3D打印病理切片盒在骨肿瘤病理拼接中的应用初探[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(2): 180-187. |
| [14] | 柳思宇, 吴兵, 李小敏, 赵露露, 陈骏, 艾松涛. 弥散加权成像对隆突性皮肤纤维肉瘤术前规划的价值初探[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(8): 1095-1102. |
| [15] | 陈立奇, 薛卓维, 吴氢凯. 基于磁共振成像的女性盆底器官三维数字模型重建的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(3): 381-386. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||