
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 916-925.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.07.014
收稿日期:2024-12-10
接受日期:2025-04-03
出版日期:2025-07-28
发布日期:2025-07-15
通讯作者:
刘 敏,主任医师,博士;电子信箱:lm4104@shtrhospital.com。基金资助:Received:2024-12-10
Accepted:2025-04-03
Online:2025-07-28
Published:2025-07-15
Contact:
LIU Min, E-mail: lm4104@shtrhospital.com.Supported by:摘要:
肾细胞癌(renal cell carcinoma,RCC)是成人最常见的肾脏恶性肿瘤,占所有肾脏肿瘤的90%以上。RCC早期多无明显症状,常在体检或影像学检查中被偶然发现。尽管局限性RCC通过手术切除可获得良好结局,但对于晚期或转移性病例,传统治疗手段如化学治疗、放射治疗及靶向治疗的效果常常有限,预后仍不理想。RCC是一种具有高度免疫原性的肿瘤,能够通过多种机制逃避机体的免疫监视。因此,以细胞治疗为代表的免疫治疗作为一种新兴的治疗方式,近年来备受关注,展现出巨大的潜力。免疫细胞治疗利用患者自身的免疫系统或外源性免疫细胞来增强抗肿瘤免疫反应,恢复免疫系统的功能,从而有效清除肿瘤细胞,已成为治疗RCC的重要研究方向。然而免疫细胞治疗仍面临个体差异、免疫相关不良事件、肿瘤微环境免疫抑制及治疗后耐药等诸多挑战,严重制约其临床疗效提升。该文概括了RCC的免疫逃逸机制,归纳了RCC免疫细胞治疗的进展,分析了RCC免疫细胞治疗的前景,以期为更好地解决难治性RCC提供临床思路和方向。
中图分类号:
陈子旋, 刘敏. 肾细胞癌免疫细胞治疗的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(7): 916-925.
CHEN Zixuan, LIU Min. Research progress on immune cell therapy in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(7): 916-925.
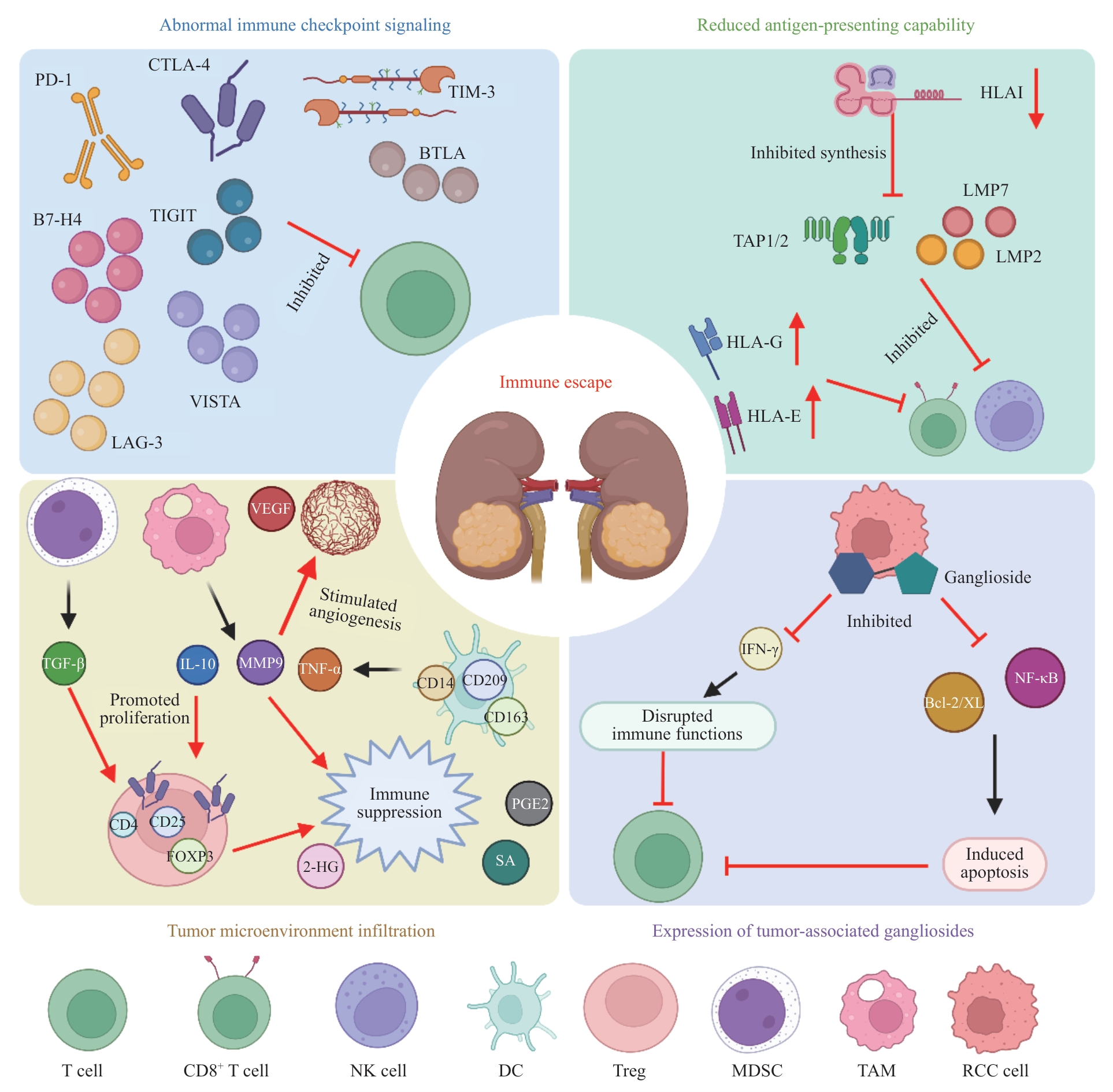
图1 RCC免疫逃逸机制Note: PD-1—programmed death-1; CTLA-4—cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; TIM-3—T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3; TIGTI—T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domain; BTLA—B and T lymphocyte attenuator; VISTA—V-domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation; LAG-3—lymphocyte activation gene 3; HLAⅠ—human leukocyte antigen Ⅰ; TAP1/2—transporter associated with antigen processing 1/2; LMP2—low molecular weight protein 2; VEGF—vascular endothelial growth factor; TGF-β—transforming growth factor β; IL-10—interleukin-10; MMP9—matrix metalloproteinase 9; TNF-α—tumor necrosis factor-α; FOXP3—forkhead box protein P3; 2-HG—2-hydroxyglutarate; PGE2—prostaglandin E2; SA—succinic acid; Bcl-2/XL—B-cell lymphoma-2/B-cell lmyphoma-extra large; IFN-γ—interferon-γ; NF-κB—nuclear factor-κB; NK cell—natural killer cell; DC—dendritic cell; Treg—regulatory T cell; MDSC—myeloid-derived suppressor cell; TAM—tumor-associated macrophage; RCC—renal cell carcinoma.
Fig 1 Mechanisms of immune evasion in RCC
| [1] | BRAY F, LAVERSANNE M, SUNG H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(3): 229-263. |
| [2] | EVANS S T, JANI Y, JANSEN C S, et al. Understanding and overcoming resistance to immunotherapy in genitourinary cancers[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2024, 25(1): 2342599. |
| [3] | HAN J, ZHANG B W, ZHENG S Y, et al. The progress and prospects of immune cell therapy for the treatment of cancer[J]. Cell Transplant, 2024, 33: 9636897241231892. |
| [4] | REN J, LI C C, XU D Z, et al. Synchronized autologous T-cell immunotherapy with hyperthermia to previously heavy treated advanced renal cell carcinoma[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2024, 41(1): 2431130. |
| [5] | HUANG T X, PENG Y L, LIU R Q, et al. Prognostic significance of immune evasion-related genes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma immunotherapy[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 142(Pt B): 113106. |
| [6] | WANG X Y, LOPEZ R, LUCHTEL R A, et al. Immune evasion in renal cell carcinoma: biology, clinical translation, future directions[J]. Kidney Int, 2021, 99(1): 75-85. |
| [7] | NAHAR S, HUANG Y, NAGY B A, et al. Regression and eradication of triple-negative breast carcinoma in 4T1 mouse model by combination immunotherapies[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2023, 15(8): 2366. |
| [8] | CUI J W, LI Y, YANG Y, et al. Tumor immunotherapy resistance: revealing the mechanism of PD-1/PD-L1-mediated tumor immune escape[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2024, 171: 116203. |
| [9] | KAHLMEYER A, STÖHR C G, HARTMANN A, et al. Expression of PD-1 and CTLA-4 are negative prognostic markers in renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Clin Med, 2019, 8(5): 743. |
| [10] | LI A Q, ZHANG N Y, ZHAO Z M, et al. Overexpression of B7-H4 promotes renal cell carcinoma progression by recruiting tumor-associated neutrophils via upregulation of CXCL8[J]. Oncol Lett, 2020, 20(2): 1535-1544. |
| [11] | ZELBA H, BEDKE J, HENNENLOTTER J, et al. PD-1 and LAG-3 dominate checkpoint receptor-mediated T-cell inhibition in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2019, 7(11): 1891-1899. |
| [12] | TAKAMATSU K, TANAKA N, HAKOZAKI K, et al. Profiling the inhibitory receptors LAG-3, TIM-3, and TIGIT in renal cell carcinoma reveals malignancy[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 5547. |
| [13] | BRAUN D A, BAKOUNY Z, HIRSCH L, et al. Beyond conventional immune-checkpoint inhibition: novel immunotherapies for renal cell carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2021, 18: 199-214. |
| [14] | KALLINGAL A, OLSZEWSKI M, MACIEJEWSKA N, et al. Cancer immune escape: the role of antigen presentation machinery[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2023, 149(10): 8131-8141. |
| [15] | JIAN Y L, YANG K K, SUN X X, et al. Current advance of immune evasion mechanisms and emerging immunotherapies in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 639636. |
| [16] | ROMERO J M, APTSIAURI N, VAZQUEZ F, et al. Analysis of the expression of HLA class Ⅰ, proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in primary tumors from patients with localized and metastatic renal cell carcinoma[J]. Tissue Antigens, 2006, 68(4): 303-310. |
| [17] | TRONIK-LE ROUX D, RENARD J, VÉRINE J, et al. Novel landscape of HLA-G isoforms expressed in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients[J]. Mol Oncol, 2017, 11(11): 1561-1578. |
| [18] | CHU G D, JIAO W, YANG X C, et al. C3, C3AR1, HLA-DRA, and HLA-E as potential prognostic biomarkers for renal clear cell carcinoma[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2020, 9(6): 2640-2656. |
| [19] | 张烨晟, 杨易静, 黄依雯, 等. 肿瘤微环境免疫细胞调节肿瘤细胞耐药性的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(7): 830-838. |
| ZHANG Y S, YANG Y J, HUANG Y W, et al. Research progress in immune cells regulating drug resistance of tumor cells in tumor microenvironment[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(7): 830-838. | |
| [20] | LIOTTA F, GACCI M, FROSALI F, et al. Frequency of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood and in tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes correlates with poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma[J]. BJU Int, 2011, 107(9): 1500-1506. |
| [21] | FIGEL A M, BRECH D, PRINZ P U, et al. Human renal cell carcinoma induces a dendritic cell subset that uses T-cell crosstalk for tumor-permissive milieu alterations[J]. Am J Pathol, 2011, 179(1): 436-451. |
| [22] | NAJJAR Y G, RAYMAN P, JIA X F, et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cell subset accumulation in renal cell carcinoma parenchyma is associated with intratumoral expression of IL1β, IL8, CXCL5, and Mip-1α[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2017, 23(9): 2346-2355. |
| [23] | LIU H, LV Z W, ZHANG G, et al. Molecular understanding and clinical aspects of tumor-associated macrophages in the immunotherapy of renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2024, 43(1): 242. |
| [24] | LAI Y C, TANG F C, HUANG Y P, et al. The tumour microenvironment and metabolism in renal cell carcinoma targeted or immune therapy[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(3): 1616-1627. |
| [25] | CHEN W J, PAN X W, CUI X G. RCC immune microenvironment subsequent to targeted therapy: a friend or a foe?[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 573690. |
| [26] | ITOH J, ITO A, SHIMADA S, et al. Clinicopathological significance of ganglioside DSGb5 expression in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Glycoconj J, 2017, 34(2): 267-273. |
| [27] | 曹鑫, 刘芹, 刘宝瑞. 靶向共有新抗原的肿瘤疫苗和细胞治疗新进展[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2024, 31(17): 1037-1042. |
| CAO X, LIU Q, LIU B R. Progress in tumor vaccines and cell therapies targeting shared neoantigens[J]. Chinese Journal of Cancer Prevention and Treatment, 2024, 31(17): 1037-1042. | |
| [28] | LI J N, ZHANG Y S, FU T, et al. Clinical advances and challenges associated with TCR-T cell therapy for cancer treatment[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1487782. |
| [29] | XU Y X, MORALES A J, CARGILL M J, et al. Preclinical development of T-cell receptor-engineered T-cell therapy targeting the 5T4 tumor antigen on renal cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2019, 68(12): 1979-1993. |
| [30] | NADAL R, BARISIC S, SCURTI G M, et al. Final results of a phase Ⅰ trial of HERV-E TCR transduced T cells for the treatment of HLA-A*11 patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (mccRCC)[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2024, 42(4_suppl): 435. |
| [31] | PAN K, FARRUKH H, CHITTEPU V C S R, et al. CAR race to cancer immunotherapy: from CAR T, CAR NK to CAR macrophage therapy[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 41(1): 119. |
| [32] | 张凯杰, 边诣聪, 王燕, 等. CAR-T细胞在血液恶性肿瘤治疗中的细胞动力学特征和研究进展[J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2025, 45(3): 337-342. |
| ZHANG K J, BIAN Y C, WANG Y, et al. Cellular dynamics and research progress of CAR-T cells in treating hematological malignancies[J]. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy, 2025, 45(3): 337-342. | |
| [33] | LAMERS C H J, SLEIJFER S, VULTO A G, et al. Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma with autologous T-lymphocytes genetically retargeted against carbonic anhydrase Ⅸ: first clinical experience[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2006, 24(13): e20-e22. |
| [34] | WANG Y F, SUAREZ E R, KASTRUNES G, et al. Evolution of cell therapy for renal cell carcinoma[J]. Mol Cancer, 2024, 23(1): 8. |
| [35] | JI F, ZHANG F, ZHANG M, et al. Targeting the DNA damage response enhances CD70 CAR-T cell therapy for renal carcinoma by activating the cGAS-STING pathway[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2021, 14(1): 152. |
| [36] | LI H Z, WANG F, ZHAO H F, et al. Preclinical assessment of the efficacy of B7-H3 CAR-T in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Mol Immunol, 2024, 176: 1-10. |
| [37] | DENG W Y, WU L Y, CHEN L Y, et al. Development of B7-H3 targeted CAR-T cells for renal cell carcinoma therapy: in vitro and in vivo efficacy[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2024. |
| [38] | KOZLOWSKA A, ZHANG Y, FRITZ J, et al. 120 P-MUC1C-ALLO1: an allogeneic CAR-T for multiple solid tumor indications[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2020, 8(Suppl 3): A73. |
| [39] | MORI J I, ADACHI K, SAKODA Y, et al. Anti-tumor efficacy of human anti-c-met CAR-T cells against papillary renal cell carcinoma in an orthotopic model[J]. Cancer Sci, 2021, 112(4): 1417-1428. |
| [40] | MUKHERJEE A G, WANJARI U R, NAMACHIVAYAM A, et al. Role of immune cells and receptors in cancer treatment: an immunotherapeutic approach[J]. Vaccines (Basel), 2022, 10(9): 1493. |
| [41] | NIU Z Y, WANG M J, YAN Y C, et al. Challenges in the development of NK-92 cells as an effective universal off-the-shelf cellular therapeutic[J]. J Immunol, 2024, 213(9): 1318-1328. |
| [42] | ZHANG Q, XU J J, DING J G, et al. Bortezomib improves adoptive carbonic anhydrase Ⅸ-specific chimeric antigen receptor-modified NK92 cell therapy in mouse models of human renal cell carcinoma[J]. Oncol Rep, 2018, 40(6): 3714-3724. |
| [43] | ZHANG Q, TIAN K, XU J J, et al. Synergistic effects of cabozantinib and EGFR-specific CAR-NK-92 cells in renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Immunol Res, 2017, 2017: 6915912. |
| [44] | KREMER V, LIGTENBERG M A, ZENDEHDEL R, et al. Genetic engineering of human NK cells to express CXCR2 improves migration to renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2017, 5(1): 73. |
| [45] | BERNTSEN A, TREPIAKAS R, WENANDY L, et al. Therapeutic dendritic cell vaccination of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a clinical phase 1/2 trial[J]. J Immunother, 2008, 31(8): 771-780. |
| [46] | WEISS G R, MARGOLIN K A, ARONSON F R, et al. A randomized phase Ⅱ trial of continuous infusion interleukin-2 or bolus injection interleukin-2 plus lymphokine-activated killer cells for advanced renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Clin Oncol, 1992, 10(2): 275-281. |
| [47] | HAYAKAWA M. Lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) therapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma: clinical study on arterial LAK therapy and experimental study on LAK cell activity[J]. Hinyokika Kiyo, 1992, 38(11): 1311-1318. |
| [48] | GARCIA J, HURWITZ H I, SANDLER A B, et al. Bevacizumab (avastin®) in cancer treatment: a review of 15 years of clinical experience and future outlook[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2020, 86: 102017. |
| [49] | ZHENG K, TAN J M, WU W Z, et al. Adjuvant dendritic cells vaccine combined with cytokine-induced-killer cell therapy after renal cell carcinoma surgery[J]. J BUON, 2015, 20(2): 505-513. |
| [50] | MAI H X, MEI G H, ZHAO F L, et al. Retrospective analysis on the efficacy of sunitinib/sorafenib in combination with dendritic cells-cytokine-induced killer in metastasis renal cell carcinoma after radical nephrectomy[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2018, 14(Supplement): S427-S432. |
| [51] | FIGLIN R A, PIERCE W C, KABOO R, et al. Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma with nephrectomy, interleukin-2 and cytokine-primed or CD8+ selected tumor infiltrating lymphocytes from primary tumor[J]. J Urol, 1997, 158(3 Pt 1): 740-745. |
| [52] | FIGLIN R A, THOMPSON J A, BUKOWSKI R M, et al. Multicenter, randomized, phase Ⅲ trial of CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in combination with recombinant interleukin-2 in metastatic renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Clin Oncol, 1999, 17(8): 2521-2529. |
| [53] | KOBAYASHI H, TANAKA Y, YAGI J, et al. Safety profile and anti-tumor effects of adoptive immunotherapy using gamma-delta T cells against advanced renal cell carcinoma: a pilot study[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2007, 56(4): 469-476. |
| [54] | CHAOUL N, LAURICELLA E, GIGLIO A, et al. The future of cellular therapy for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma[J]. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2024, 24(11): 1245-1259. |
| [55] | WANG Y Y, WANG W D, SUN Z J. Cancer stem cell-immune cell collusion in immunotherapy[J]. Int J Cancer, 2023, 153(4): 694-708. |
| [56] | MAI Y S, SU J Y, YANG C, et al. The strategies to cure cancer patients by eradicating cancer stem-like cells[J]. Mol Cancer, 2023, 22(1): 171. |
| [57] | ALCANTARA M B, TANG W S, WANG D F, et al. Targeting STAT3 in tumor-associated antigen-presenting cells as a strategy for kidney and bladder cancer immunotherapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 14: 1274781. |
| [58] | MORRISSEY M A, WILLIAMSON A P, STEINBACH A M, et al. Chimeric antigen receptors that trigger phagocytosis[J]. eLife, 2018, 7: e36688. |
| [59] | LAMARTHÉE B, MARCHAL A, CHARBONNIER S, et al. CD28 costimulatory domain protects against tonic signaling-induced functional impairment in CAR-Tregs[Z/OL]. (2020-11-19)[2024-12-10]. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.11.19.390450v1. |
| [60] | LULLA P D, BRENNER M. Emerging challenges to cellular therapy of cancer[J]. Cancer J, 2023, 29(1): 20-27. |
| [1] | 蒋婕, 张泓, 伦赫远, 潘芬, 于方圆, 何平. 儿童肺炎克雷伯菌感染分子流行病学特征[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(8): 1027-1034. |
| [2] | 孟靖, 谢玉婷, 左佳鑫, 熊屏. 纳米工程化T细胞体系的构建及其对口腔鳞状细胞癌的体外治疗研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(7): 866-873. |
| [3] | 王高明, 崔然, 黎彦璟, 刘颖斌. KRAS R68G继发突变引发KRASG12D靶向抑制剂MRTX1133耐药的机制研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(6): 705-716. |
| [4] | 梁效宁, 石亭旺, 陈云丰. 小菌落变异株的致病机制及治疗研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(6): 784-791. |
| [5] | 张涤凡, 王明慧, 赵洁, 万江波, 黄方, 郝思国. B7基因修饰的白血病细胞外泌体的抗白血病效应[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 129-137. |
| [6] | 邹沛辰, 刘鸿宇, 阿衣娜扎尔·艾合买提, 朱亮, 唐亚斌, 雷绘敏. 索托拉西布获得性耐药肺癌细胞的代谢轮廓分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 138-149. |
| [7] | 吴诗怡, 陈思, 刘泊含, 刘宇婷, 刘鷖雯, 何怡青, 杜艳, 张国良, 郭倩, 高锋, 杨翠霞. “HA糖外衣”调控ER+乳腺癌细胞干性在内分泌治疗耐药中的作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1298-1307. |
| [8] | 唐珺倩, 李本尚. 儿童高危细胞遗传学B系急性淋巴细胞白血病治疗新进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1390-1399. |
| [9] | 孙晨玮, 海汪溪, 屈骞, 席云. [18F]F-FMISO和[18F]F-FLT PET/CT双核素显像预测胰腺癌耐药性的体内研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(1): 60-68. |
| [10] | 何蕊, 颜克鹏, 王静. 靶向髓源性抑制细胞的叶酸循环增强肿瘤免疫治疗效果研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(8): 1011-1022. |
| [11] | 胡飞, 蔡晓涵, 程睿, 季诗雨, 苗嘉欣, 朱晏, 范广建. 骨肉瘤免疫微环境及其免疫治疗临床转化研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(7): 814-821. |
| [12] | 张烨晟, 杨易静, 黄依雯, 施珑玙, 王曼媛, 陈思思. 肿瘤微环境免疫细胞调节肿瘤细胞耐药性的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(7): 830-838. |
| [13] | 丁艳玲, 李杰, 袁军, 李燕. 慢性淋巴细胞白血病靶向治疗的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 264-270. |
| [14] | 陈子旋, 刘敏. 肾细胞癌舒尼替尼耐药性的机制及治疗研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(10): 1307-1315. |
| [15] | 周海霞, 张靖. m6A甲基化修饰调控肿瘤免疫的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(1): 137-144. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
